Which reason do you concern AWS ?

Quote
The big reason why i choose AWS about unique idea of maintainer and developer from AWS company put inside their services. They give me other perspective to create, control and manage service, and that is creating the difference between
awsandazure. Especially, this cloud have some strange service and practice with it help me have more knowledge, and that why I concern to chooseAWSand one more thing huge community stand behind will help you resolve any problems, for sure.If I concern about
awsandazure, I will choose one of them depend on what I need to do. About trying to operate service like web dynamic - static, DB and container app, I will chooseazure, and in another task, if I want to practice with secrets management, simple storage as S3, Queue message, … I will chooseawsfor alternative
You can figure what you need to do for start with aws via some website and article
Architecture
- AWS Architecture Blog
- AWS Architecture Center
- AWS Decision Guides
- AWS Solutions Library
- AWS Prescriptive Guidance
- AWS Whitepapers & Guides
Community
General
- AWS Create Account Guide
- AWS Documentation
- AWS General Reference
- AWS CLI - Configure the AWS CLI
- AWS CLI - Installation Guide
Utilities
You can manage aws as organization via the tree and sub-organization inside root account
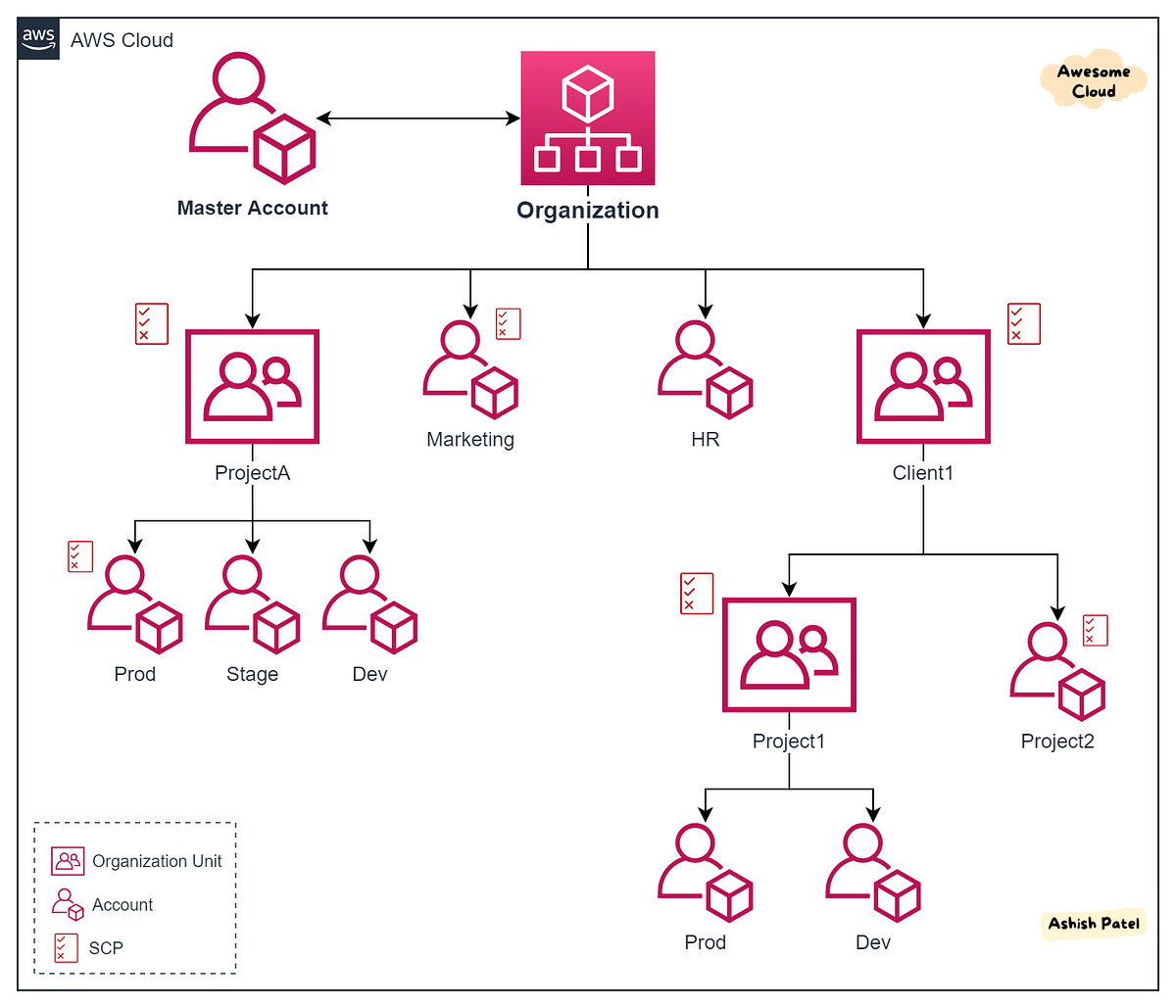
Therefore enjoying what you need, inside each article will share about how you CLI, cheatsheet, collection of useful article around aws
Externally, In AWS , I will share about some others topic, such as
- Services
- Certificates
- AWS Best Practice
Awesome AWS Repositories
Organization
- Github - Amazon Web Services - AWS Opensource Community
- Github - AWS Labs - AWS Labs
- Github - AWS Observability - AWS Observability Setup
- Github - AWS Samples - AWS Samples Community
Pages
- Compose-X Labs: Aims to show-case Compose-X projects to deploy on AWS ECS
Repository
- all_aws_managed_policies: A list of all AWS managed policies and they’re policy documents as well as a short script to generate the list
- awesome-aws - A curated list of awesome Amazon Web Services (AWS) libraries, open source repos, guides, blogs, and other resources.
- grafana-aws-cloudwatch-dashboards: 40+ Grafana dashboards for AWS CloudWatch metrics
- my-arsenal-of-aws-security-tools: List of open source tools for AWS security: defensive, offensive, auditing, DFIR, etc.
Tools
- Serverless Better Credentials: Plugin replaces the existing AWS credential resolution mechanism, support SSO (Single Sign On)
Blogs, Articles and Videos
Articles
- CloudZero - AWS NAT Gateway Pricing: Simple Strategies To Limit Costs
- PacketFabric - A Deep Dive into NAT Gateway Alternatives
- Medium - 18 AWS Lambda Microstacks
- Medium - 14 AWS Security Microstacks
- Medium - 7 Effective Ways to Automate Cloud Infrastructure Auditing with AWS CloudTrail and AWS Config
- AWS Docs - Configuring IAM Identity Center authentication with the AWS CLI
- Medium - 10 Little-Known AWS Services That Could Supercharge Your Cloud Strategy in 2025
- Medium - AWS Console-to-Code Now Generally Available
- AWS Docs - Understanding Lambda function scaling
- AWS Blogs - 7 AWSome ways to use AWS Chatbot
- Medium - Full-stack Observability and Monitoring on AWS
- Linkedin - ISO 27001 Compliance in AWS
Blogs
- Medium - AWS in Plain English: New AWS, Cloud, and DevOps content every day.
- Medium - AWStip: Community of passionate AWS builders.
- Medium - Chris St. John
Development & Implementation
- Medium - ECS (Fargate) with ALB Deployment Using Terraform — Part 3
- Medium - Creating SSL Certificates using AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- AWS Blogs - AWS Multi-Account Security Reference Architecture
- AWS Docs - Configuring and managing a Multi-AZ deployment for Amazon RDS
- AWS Docs - Profiling Amazon DocumentDB operations
- AWS Blogs - Viewing Amazon CloudWatch metrics with Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus and Amazon Managed Grafana
- AWS Blogs - Monitoring metrics and setting up alarms on your Amazon DocumentDB (with MongoDB compatibility) clusters
Troubleshoot
- AWS re:Post - Getting an Access Denied error message when I upload files to my Amazon S3 bucket
- AWS - Troubleshoot access denied (403 Forbidden) errors in Amazon S3
Videos
AWS CLI
Question
You need to export some configuration before you can use
awscli, such as
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID (Obligatory)
- AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY (Obligatory)
- AWS_SESSION_TOKEN (If you have)
- AWS_DEFAULT_REGION (Obligatory)
S3
Warning
With
s3some situation i set it up--endpoint-urlit mean i uselocalstackfor virtualizationawscloud on my machine, so keep mind and skip the flag if you want to applied to yourawscloud
Create the bucket
aws --endpoint-url=http://localhost:4566 s3api create-bucket --bucket sample-bucketList the object in the bucket
aws --endpoint-url=http://localhost:4566 s3 ls s3://sample-bucket/Upload the object from directory to bucket, with single file or multiple files
# Upload only one file or dir
aws --endpoint-url=http://localhost:4566 s3 cp file|dir s3://sample-bucket
# Upload multiple
aws --endpoint-url=http://localhost:4566 s3 cp file|dir s3://sample-bucket --recursiveRead contents inside bucket
aws --endpoint-url=http://localhost:4566 s3 cp s3://sample-bucket/file -Delete a huge bucket with versioning enable
Discovery more about issue at StackOverFlow - How do I delete a versioned bucket in AWS S3 using the CLI?
# Use command for deleting
aws s3api delete-objects \
--bucket name-bucket \
--delete "$(aws s3api list-object-versions \
--bucket "name-bucket" \
--output=json --max-items 500 --query='{Objects: Versions[].{Key:Key,VersionId:VersionId}}')"# Use loop for deleting
NB_OBJECTS=$(aws s3api list-object-versions --bucket ${buckettoempty} --query='length(Versions[*] || `[]` )' | awk '{ print $1 }')
echo " '${NB_OBJECTS}' objects to remove"
if [[ "$NB_OBJECTS" != "0" ]]; then
start=$SECONDS
while [[ $NB_OBJECTS -gt 0 ]]
do
aws s3api delete-objects --bucket ${buckettoempty} --delete "$(aws s3api list-object-versions --bucket ${buckettoempty} --max-items 500 --query='{Objects: Versions[0:500].{Key:Key,VersionId:VersionId}}')" --query 'length(Deleted[*] || `[]` )' > /dev/null
NB_OBJECTS=$((NB_OBJECTS > 500 ? NB_OBJECTS - 500 : 0))
echo " Removed batch of Objects... Remaining : $NB_OBJECTS ($(( SECONDS - start ))s)"
done
fi
NB_OBJECTS=$(aws s3api list-object-versions --bucket ${buckettoempty} --query='length(DeleteMarkers[*] || `[]` )' | awk '{ print $1 }')
echo " '${NB_OBJECTS}' markers to remove"
if [[ "$NB_OBJECTS" != "0" ]]; then
start=$SECONDS
while [[ $NB_OBJECTS -gt 0 ]]
do
aws s3api delete-objects --bucket ${buckettoempty} --delete "$(aws s3api list-object-versions --bucket ${buckettoempty} --max-items 500 --query='{Objects: DeleteMarkers[0:500].{Key:Key,VersionId:VersionId}}')" --query 'length(Deleted[*] || `[]` )' > /dev/null
NB_OBJECTS=$((NB_OBJECTS > 500 ? NB_OBJECTS - 500 : 0))
echo " Removed batch of Markers... Remaining : $NB_OBJECTS (took $(( SECONDS - start ))s)"
done
fiSTS
Get caller identity to detect whoami or role
aws sts get-caller-identityAssume role with web-identity
aws sts assume-role-with-web-identity \
--role-arn arn:aws:iam::xxxxx:role/rolename \
--role-session-name <what-ever-you-want> \
--web-identity-token $TOKEN # mostly token is JWT FormatAssume role with one-command
Documentation: StackOverFlow - AWS sts assume role in one command
export $(printf "AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=%s AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=%s AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=%s" \
$(aws sts assume-role \
--role-arn arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/MyAssumedRole \
--role-session-name MySessionName \
--query "Credentials.[AccessKeyId,SecretAccessKey,SessionToken]" \
--output text))ECS
List task inside ECS Cluster
aws ecs list-tasks --cluster <name-cluster>Execution command
Warning
In this part you need to confirm two thing to install inside cluster and your machine
In your machine, need to install session-manager-plugin. Use curl command to download
curl "https://s3.amazonaws.com/session-manager-downloads/plugin/latest/ubuntu_64bit/session-manager-plugin.deb" -o "session-manager-plugin.deb"In your task, you need enable feature execute-command if not
aws ecs update-service \
--cluster <cluster-name> --service <service-name> \
--enable-execute-command --force-new-deploymentAnd now if you confirm two thing about you can use execution to inject something inside container
# Exam: task-arn-specific = d274e386xxxxxxxxxxx2fd28b5ac
aws ecs execute-command --cluster <cluster-name> \
--container <name-container> --interactive --task <task-arn-specific> \
--command <your/command>ECR
Get login password of your ECR
aws ecr get-login-passwordLogin to your ECR
aws ecr get-login-password | crane auth login -u AWS --password-stdin <url-ecr>EKS
Get token of cluster
aws eks get-token --cluster-name <name>Create kubeconfig file automatically
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region region-code --name my-clusterSQS
Retrieve message from queue
aws sqs receive-message \
--queue-url <sqs-url> \
--attribute-names All --message-attribute-names All \
--max-number-of-messages 10SNS
Subscribe webhook with SNS
Use can use two platform to generate endpoint
- Beeceptor : API Mocking
- Webhook.site : Generates free, unique URLs and e-mail addresses and lets you see everything that’s sent there instantly. (Usage: Steal cookies, bypass authorized, …)
aws sns subscribe \
--topic-arn <topic-arn> \
--protocol https \
--notification-endpoint <endpoint>Cognito-identity
Get Identity
aws cognito-identity get-id --identity-pool-id <identity-pool-id>Get Credential
aws cognito-identity get-credentials-for-identity --identity-id <identity-from-get-identity>Get Open ID Token
Note
Use when you receive
open-idtoken to retrieve the credential to access AWS
aws cognito-identity get-open-id-token --identity-id <identity-from-get-identity>Configure
Set credential for profile
aws configure --profile <profile-name>And easily you can temporarily switch profiles with export to environment variable
# V1
export AWS_DEFAULT_PROFILE=<profile-name>
# V2
export AWS_PROFILE=<profile-name>Cheatsheet and Script
S3
Retrieve file data from S3
Abstract
This script will be helped you for retrieving the file from your S3 bucket
#!/bin/bash
bucket="$1"
amzFile="$2"
outputFile="$3"
resource="/${bucket}/${amzFile}"
contentType="application/x-compressed-tar"
dateValue=$(date -R)
stringToSign="GET\n\n${contentType}\n${dateValue}\n${resource}"
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="$4"
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="$5"
signature=$(echo -en "${stringToSign}" | openssl sha1 -hmac ${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} -binary | base64)
echo -n "$(curl -H "Host: ${bucket}.s3.amazonaws.com" \
-H "Date: ${dateValue}" \
-H "Content-Type: ${contentType}" \
-H "Authorization: AWS ${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}:${signature}" \
https://${bucket}.s3.amazonaws.com/${amzFile} -o "$outputFile")"Upload file to S3
Abstract
This script will help you upload a new file to S3 bucket
#!/bin/bash
file="FILEPATH"
bucket="BUCKET_NAME"
folder="FOLDER_IN_BUCKET"
resource="/${bucket}/${folder}/${file}"
contentType="text/plain"
dateValue=$(date -R)
s3Key="S3KEY"
s3Secret="S3SECRET"
# Check if the file exists on S3
httpResponseCode=$(curl -I -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" -X HEAD -H "Host: ${bucket}.s3.amazonaws.com" "https://${bucket}.s3.amazonaws.com/${folder}/${file}")
if [ $httpResponseCode -eq 200 ]; then
# If the file exists, delete it
deleteDateValue=$(date -R)
deleteResource="/${bucket}/${folder}/${file}"
deleteStringToSign="DELETE\n\n\n${deleteDateValue}\n${deleteResource}"
deleteSignature=$(echo -en "${deleteStringToSign}" | openssl sha1 -hmac "${s3Secret}" -binary | base64)
# Send the DELETE request
curl -X DELETE -H "Host: ${bucket}.s3.amazonaws.com" -H "Date: ${deleteDateValue}" -H "Authorization: AWS ${s3Key}:${deleteSignature}" "https://${bucket}.s3.amazonaws.com/${folder}/${file}"
echo ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> An existing file was deleted successfully!"
fi
# Now, upload the new file
stringToSign="PUT\n\n${contentType}\n${dateValue}\n${resource}"
signature=$(echo -en "${stringToSign}" | openssl sha1 -hmac "${s3Secret}" -binary | base64)
# Send the PUT request to upload the new file
curl -L -X PUT -T "${file}" -H "Host: ${bucket}.s3.amazonaws.com" -H "Date: ${dateValue}" -H "Content-Type: ${contentType}" -H "Authorization: AWS ${s3Key}:${signature}" "https://${bucket}.s3.amazonaws.com/${folder}/${file}"
echo ">>>>>>>>>>>>>> A new file was uploaded successfully!"