Quote
Hi @all, it’s me again, btw this week is too boring, so i just sit back and continuous write a next session in
kubewekendseries. This session will discuss and give you some information aboutkindcluster, attach with that we will talk about detailing about architecture ofkubernetes,kindfor specific andkubernetesfor general. One more thing, this session will take you long to read, just feel free to read and enjoy, let’s digest now.

Before we start, first of all, I want to give the thankful for all of community, blogger to inspiring me on writing kubewekend, follow them if you want to understand more about Kubernetes
- Kubernetes Documentation - Super helpful and expose anything you want to learn
- the kube guy - Learn about Kubernetes with simple clarify
- Seifeddine Rajhi - The DevOps guy who will teach some very useful opensource with k8s
- Quan Huynh - Blogger from Vietnamese with huge respecting from mine, also you can know him via devopsvn.tech - Web Platform like mine where share about technically around DevOps and Software topics
List of topics in series
What is Kubernetes ?
Quote
Actually, I will not enough experience to tell you about detail inside
kubernetes, but I will try to brief that to easily to understand, guide you about the concept and give you reason why you need or not choosekubernetesfor your projectIf you familiar with docker and containerization, at least you will listen about
kubernetes, with me this one is solution can help you control and handle multiple container, and give that scenarios for them to working, to operating and to auditing with under much resonance and integration from open source
Introduction
![]()
But back to documentation to give the exactly definition about kubernetes, you can read at: Kubernetes Overview
Info
Kubernetes
A portable, extensible, open source platform for managing containerized workloads and services, that facilitates both declarative configuration and automation. It has a large, rapidly growing ecosystem. Kubernetes services, support, and tools are widely available.
This definition is really same as mine, but more specific to understand from kubernetes concept. So BTW, during the history, kubernetes is working hard in 10 years to give us huge platform, and powerful thing belong of some thing is big called container orchestration
Info
Container orchestration is the automation of much of the operational effort required to run containerized workloads and services. This includes a wide range of things software teams need to manage a container’s lifecycle, including provisioning, deployment, scaling (up and down), networking, load balancing and more.
Now, kubernetes becomes the popular concept, give potential to help your project, your company to cut off the effort to control and management multiple container in multiple environment, that will help you do a lot of things, like automation and give you more space to expand business for doing the great stuff with kubernetes and bring more valuable.
The evolution of deployment
Actually, It’s really evolving, from basic to advantage, honestly I want to relating about kubernetes. So we will go deeper with that architecture, IYKYK about virtualization environments, that tools to delivery the powerful solutions for technologies user and researcher as a revolution, you can list on 3 era
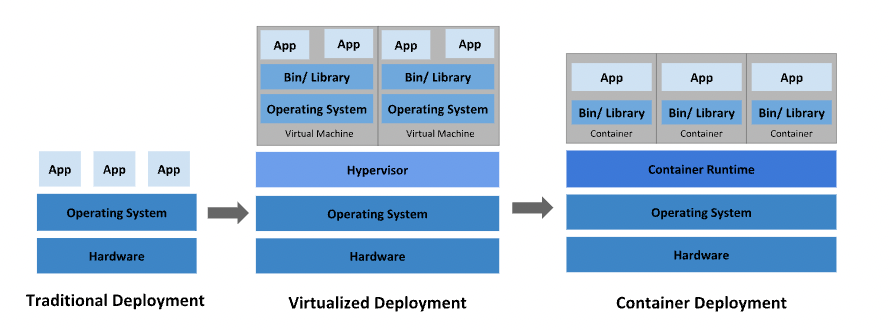
Traditional deployment era
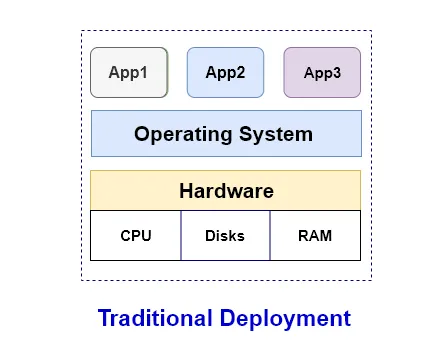
- Early on, organizations ran applications on physical servers.
- Use currently OS on the systems, and provide tools & dependencies
- Run application on it
Warning
And the issue occur when you want to managing and operate resources for server, you will not have way to do anything, that problems is tough.
Any trouble will come up, down time can be occur and no anyone want to. That reason why the deployment evolving to next era
Virtualized deployment era
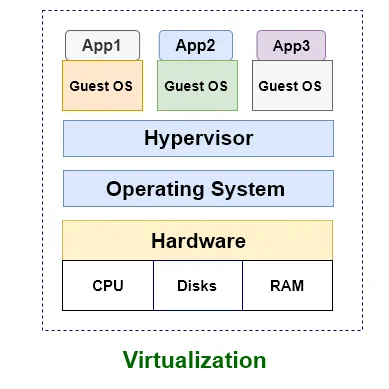
To resolve the problem of Traditional, virtualization was introduced.
- It allows you to run multiple Virtual Machines (VMs) on a single physical server’s CPU.
- Each VM is a full machine running all the components, including its own operating system, on top of the virtualized hardware.
- And the solution do great job to isolating applications for specific VM, give them best optional to secure, scalability, utilization of resources.
But it’s not perfect at all, some trouble you will directly meet when you operate virtual machine
- You will need more knowledge about system, about hardware, network and especially OS
- You will hard to delivery your applications with rapidly, and cost much time and resources to handle that problems. But It’s just in few cases, i mean nowadays we have multiple tools and extension can help us, like
ansibleandvagrantwhich reference in Kubewekend Session 1 and Kubewekend Session 2
That reason why Docker container was introduced in 2013 for solving the trouble
Container deployment era
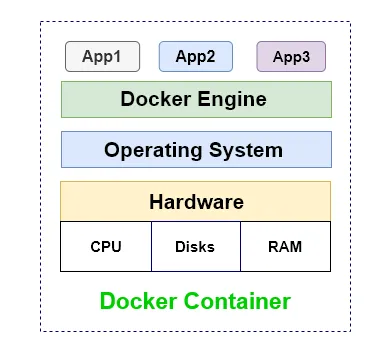
And afterward, we actually have powerful breakthrough with incredible evolution, how you think about Container
- Same as VM but but they have relaxed isolation properties to share the Operating System (OS) among the applications.
- Containers are considered lightweight
- Similar to a VM, a container has its own filesystem, share of CPU, memory, process space, and more. As they are decoupled from the underlying infrastructure, they are portable across clouds and OS distributions.
Containers become popular and help us to solving the hard problems, lastly we have more benefit from that, such as (base on: container deployment era - Kubernetes documentation)
- Create Agile application, to increase ease and efficiency of container image instead VM image
- Continuous development, integration, and deployment: provides for reliable and frequent container image build and deployment with quick and efficient rollbacks
- Dev and Ops separation of concerns: create application container images at build/release time rather than deployment time, thereby decoupling applications from infrastructure.
- Observability: not only surfaces OS-level information and metrics, but also application health and other signals.
- Environmental consistency across development, testing, and production: runs the same on a laptop as it does in the cloud.
- Cloud and OS distribution portability: runs on Ubuntu, RHEL, CoreOS, on-premises, on major public clouds, and anywhere else.
- Application-centric management: raises the level of abstraction from running an OS on virtual hardware to running an application on an OS using logical resources.
- Loosely coupled, distributed, elastic, liberated micro-services: applications are broken into smaller, independent pieces and can be deployed and managed dynamically – not a monolithic stack running on one big single-purpose machine.
- Resource isolation: predictable application performance.
- Resource utilization: high efficiency and density.
If you want to inspect more about the evolving, super recommend you to read some articles
- The Evolution of Software Deployment: From Physical Servers to Container Orchestration
- Kubernetes – Evolution of application deployment
- How Kubernetes Changed Deployment Process
- Traditional Deployment VS Virtualization VS Container
- Tại sao ta nên sử dụng kubernetes và nó giúp ta giải quyết vấn đề gì?
Why we need Kubernetes ?
Question
But we soon realized that container deployment also has its own problems, It comes up from we don’t have any plan to keep and self-healing if container downtime, and big problem you can not use simple controller like Docker to control over 1000 container simultaneous, impossible to monitoring or audit if one of them become stuck or whatever.
This reason why we have container orchestration, and kubernetes come up in the potential with huge efficiency for technology community. Kubernetes provides you with a framework to run distributed systems resiliently. It takes care of scaling and failover for your application, provides deployment patterns, and more.
Kubernetes provides you with
- Service discovery and load balancing
- Storage orchestration
- Automated rollouts and rollbacks
- Automatic bin packing
- Self-healing
- Secret and configuration management
- Batch execution
- Horizontal scaling
- IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack
- Designed for extensibility
- And moreover if you have more experience with this technology
But do you thinks about situation which kubernetes can’t handle. Yes, actually it does
Info
Kubernetes is not a traditional, all-inclusive PaaS (Platform as a Service) system. Since Kubernetes operates at the container level rather than at the hardware level, it provides some generally applicable features common to PaaS offerings, such as deployment, scaling, load balancing, and lets users integrate their logging, monitoring, and alerting solutions. However, Kubernetes is not monolithic, and these default solutions are optional and pluggable. Kubernetes provides the building blocks for building developer platforms, but preserves user choice and flexibility where it is important.
Read more about the disadvantage about Kubernetes: What Kubernetes is not
Do we have alternative of Kubernetes ?

The answer is yes, a lots of I think, you can google and more keyword can direct send to you, but like I said Kubernetes is potential when you thinks about container orchestration, and here are some another
- Docker Swarm : Swarm mode for natively managing a cluster of Docker Engines called a swarm, integrate inside
dockercommand - Openshift : The leading hybrid cloud application platform, bringing together a comprehensive set of tools and services that streamline the entire application lifecycle.
- Nomad : A highly available, distributed, data-center aware cluster and application scheduler designed to support the modern datacenter with support for long-running services, batch jobs, and much more.
- Apache Mesos : A container orchestration tool that provides easy resource allocation and sharing among multiple distributed frameworks. That is carried out through modern kernel features like Solaris’ Zones and CGroups in Linux.
- Serverless service with container like Azure Container App , AWS Elastic Container Service
And moreover, you can read and inspect them inside some articles
- WIZ - Kubernetes Alternatives for Container Orchestration
- Kubernetes Alternatives 2024: Top 8 Container Orchestration Tools
- Top 8 Kubernetes Alternatives & Competitors
Conclusion
With the evolving of container deployment is opportunity to bring up for community the huge platform, competition and in the end, we developer can earn useful from that
In time I write this article, Kubernetes reach to V1.30.2 and doing much things, and come up with more strategy, integration and actually I need to learn a lot of thing from them, that why we need to inspect and understand the fundamental components of Kubernetes if not you just a script kiddie guy 😅
Architecture of Kubernetes
Come up to pleasant part of Kubernetes, we will talk about architecture of one biggest thing which I have seen on my career, honestly for sure.
So If we inspect the difference between Kubernetes in Cloud managing and self-hosted, that will long story 😄. So I will talk about the general which you can find in any cluster out there, if it has any strange, this will secrets and mystery of Kubernetes
Cluster Architecture
Back to previous session 2, you know about kind to help you bring up local kubernetes cluster. As you can see, we you use get command with kubectl, you will see some fundamental components of kind cluster like
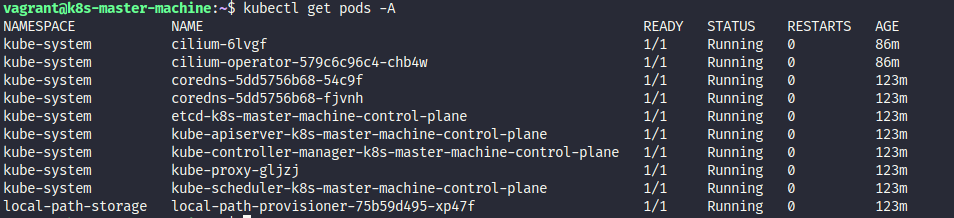
You will see lot of things huh, if you work with kubernetes on first time, It’s not suprising when you have pressure to hand on with them, normal btw 😄
Base on official documentation, you will see the image about cluster with including something inside cluster
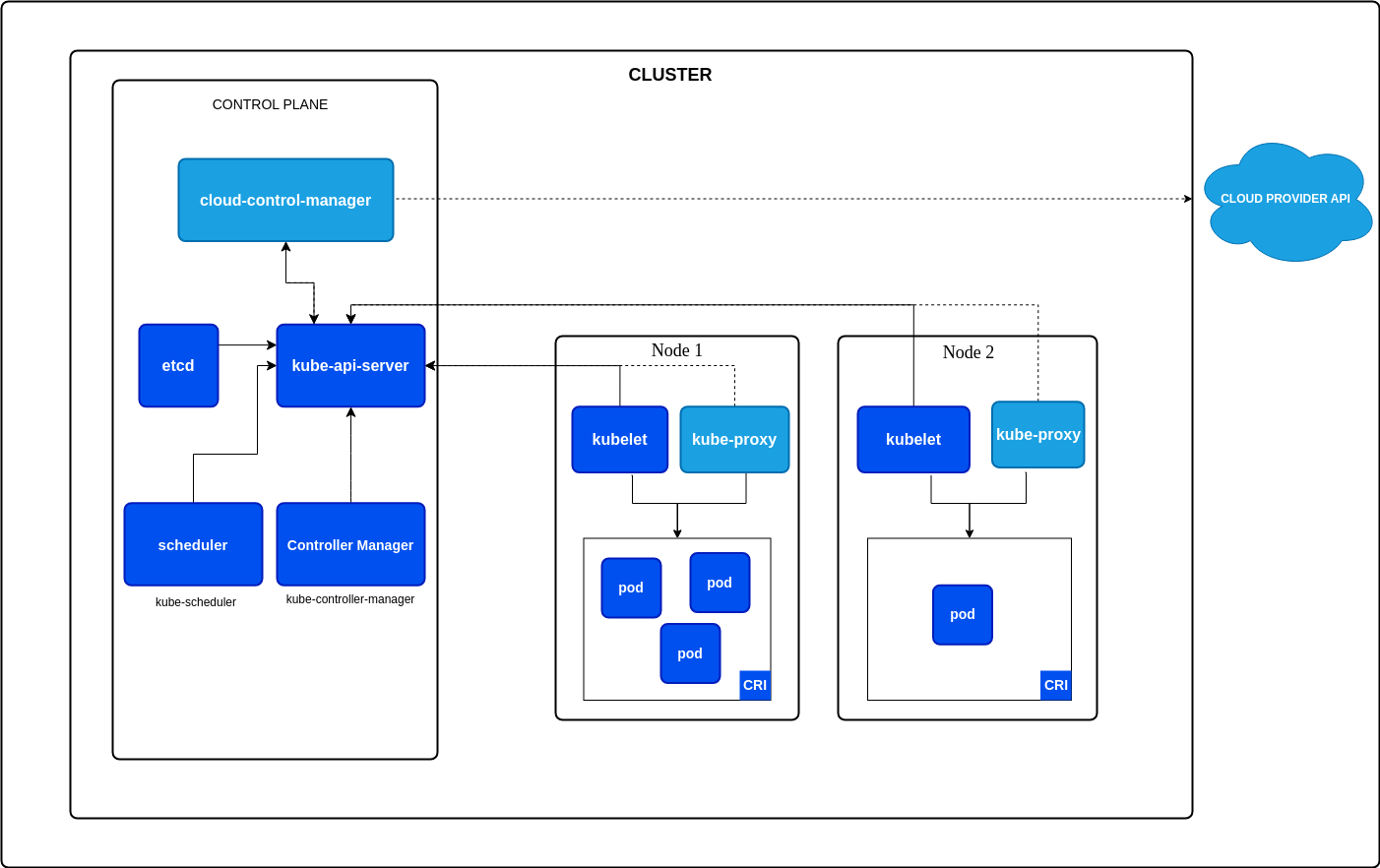
Note
When you deploy Kubernetes, you get a cluster.
A Kubernetes cluster consists of a set of worker machines, called nodes, that run containerized applications. Every cluster has at least one worker node.
The worker node(s) host the Pods that are the components of the application workload. The control plane manages the worker nodes and the Pods in the cluster
Simple you can understand, there is two type of part inside cluster as reference in Kubewekend Session 2
- Master Node (Control plane)
- Worker Node
When you work with Kubernetes this will contain some major features, and you need to understand. Read more at: Kubernetes Components for English Version and If you want to learn in Vietnamese, shout out to A. Quan Huynh - Kubernetes Series - Kubernetes internals architecture
Master Node (Control plane)
Info
The control plane’s components make global decisions about the cluster (for example, scheduling), as well as detecting and responding to cluster events
Note
Control plane components can be run on any machine in the cluster. However, for simplicity, setup scripts typically start all control plane components on the same machine, and do not run user containers on this machine. See Creating Highly Available clusters with kubeadm for an example control plane setup that runs across multiple machines.
So inside Control Plane, you will see
- etcd
- kube-apiserver
- kube-scheduler
- kube-controller-manager
- cloud-controller-manager (Optional, if you work in cloud)
Now we can spend some time to inspect some component of control plane to more understand about them
etcd
![]()
Actually, that part will hard to describe you about that, but you can understand about etcd kind database which become storage for all cluster data like resources inside kubernetes cluster and moreover. etcd work as key-value database, and kube-apiserver will read and write on etcd for events or resources
You can find more information about etcd in the documentation: https://etcd.io/docs/v3.5/, and figure out what etcd bring up to kubernetes at: https://www.armosec.io/glossary/etcd-kubernetes/
In our kind cluster, you can do something to inspect about etcd
- To view about detail
etcd, use can usegetcommand
kubectl get pods etcd-k8s-master-machine-control-plane -o jsonAnd currently on 1.28.9 kubernetes, etcd is already running on version registry.k8s.io/etcd:3.5.12-0
- You can access to
etcdshell, and can perform some practice with that useexeccommand
# Exec to stdin
kubectl exec --tty --stdin pods/etcd-k8s-master-machine-control-plane -- /bin/sh
# Use etcd to check version
etcd --version
# Practice etcd via etcdctl
etcdctl versionIf you want to understand about structure, you can follow some step inside blog of Quan Huynh - etcd to understand more inside etcd
kube-apiserver
You can take a look around full manual of kube-apiserver at kube-apiserver manual
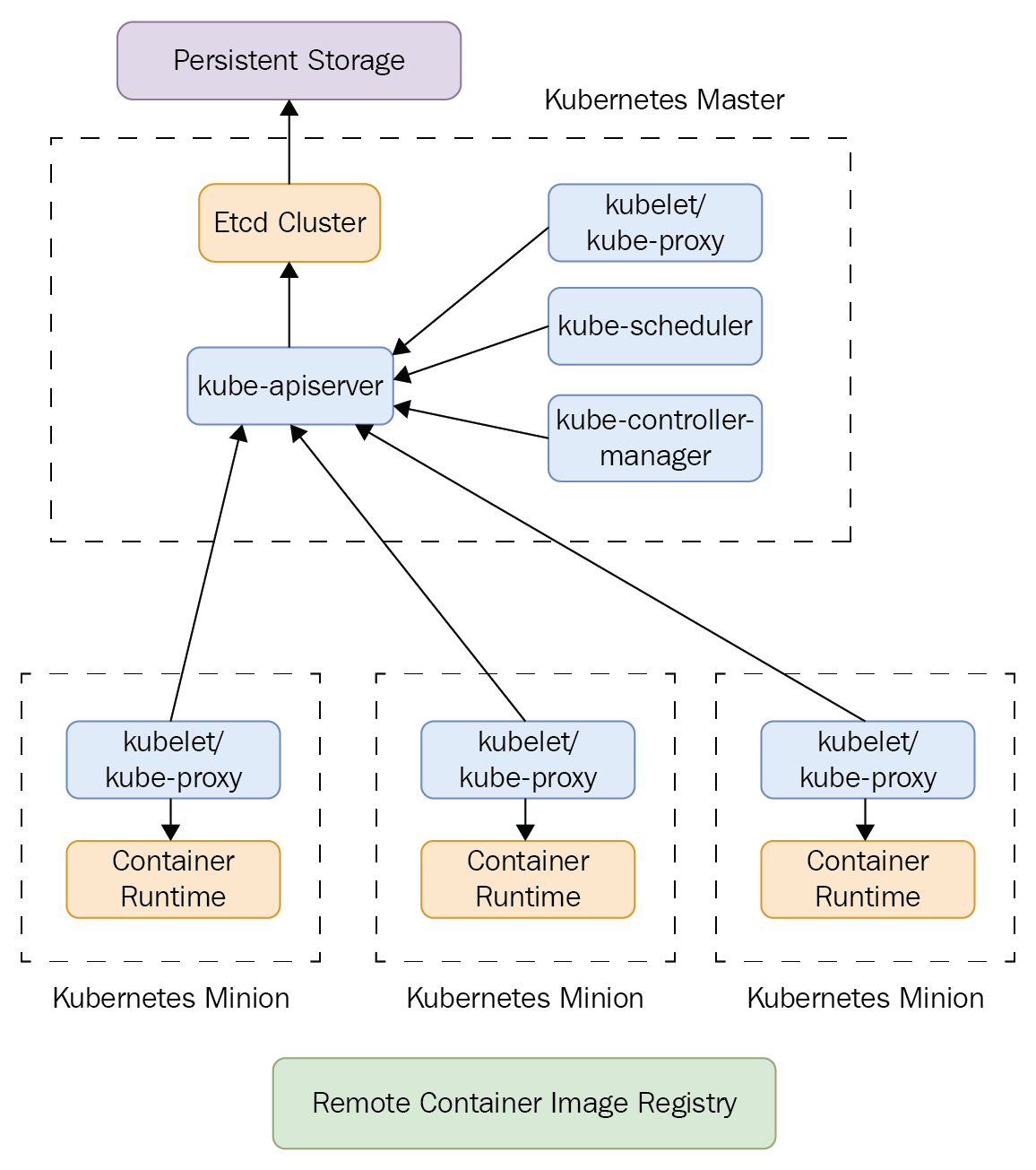
Info
The API server is a component of the Kubernetes control plane that exposes the Kubernetes API. The API server is the front end for the Kubernetes control plane.
This design like same as its name, about api , the connection between multiple node with control plane, It submits a role like brain of kubernetes cluster, how cool is it 🥶
Info
The main implementation of a Kubernetes API server is kube-apiserver. kube-apiserver is designed to scale horizontally—that is, it scales by deploying more instances. You can run several instances of kube-apiserver and balance traffic between those instances.
Back to kind cluster, if you want to inspect some information about kube-apiserver, you could do some thing like
# Inspect information about apiserver
kubectl describe pods/kube-apiserver-k8s-master-machine-control-planeIt usually uses same version of kubernetes, registry.k8s.io/kube-apiserver:v1.28.9, with configuration
kube-apiserver
--advertise-address=172.18.0.2
--allow-privileged=true
--authorization-mode=Node,RBAC
--client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
--enable-admission-plugins=NodeRestriction
--enable-bootstrap-token-auth=true
--etcd-cafile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
--etcd-certfile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.crt
--etcd-keyfile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.key
--etcd-servers=https://127.0.0.1:2379
--kubelet-client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.crt
--kubelet-client-key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.key
--kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
--proxy-client-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-client.crt
--proxy-client-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-client.key
--requestheader-allowed-names=front-proxy-client
--requestheader-client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-ca.crt
--requestheader-extra-headers-prefix=X-Remote-Extra-
--requestheader-group-headers=X-Remote-Group
--requestheader-username-headers=X-Remote-User
--runtime-config=
--secure-port=6443
--service-account-issuer=https://kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local
--service-account-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/sa.pub
--service-account-signing-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/sa.key
--service-cluster-ip-range=10.96.0.0/16
--tls-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.crt
--tls-private-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.keyMany more configuration to hand on, but you not need to understand much about that, we will practice and you can understand more little bit on my kubewekend, because actually I do not understand exactly about kube-apiserver to guiding you much about that
If you want to inspect more detail, we need a professional to give advice, come up Quan Huynh - API Server
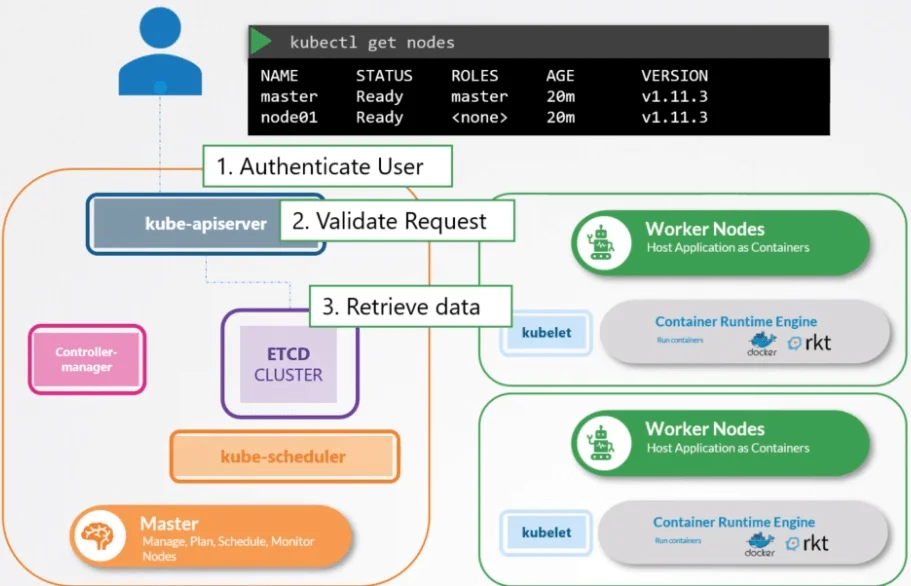
Note
Base on A. Quan Huynh article, he said about
kube-apiserverwill take a responsibility to do Authentication, Authorization client, validate config, convert configuration to style suitable to save inetcd
To make conversation with kube-apiserver, you will meet the popular can do that kubectl. When work kubectl will create post request and send that to kube-apiserver, this one will ensure about Authentication, Authorization and provide Admission to submit the result for part resource validation and save upgrade state of configuration to etcd
Warning
kube-apiserverdo not hand on in creatingworkloadinside cluster, but the actually component will do that job called kube-controller-manager
kube-controller-manager
Read more about kube-controller-manager at kube-controller-manager manual
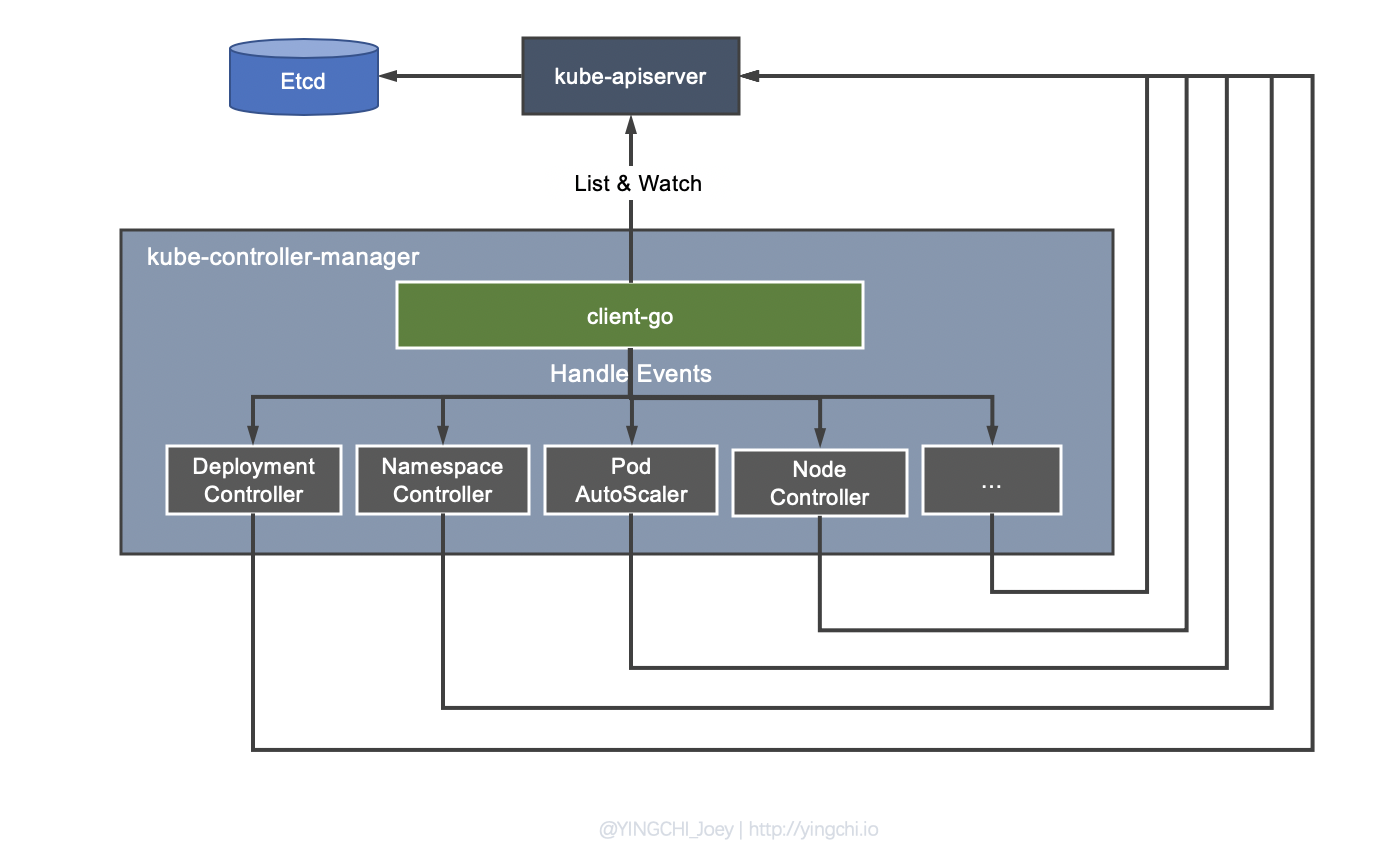
Info
Control plane component that runs controller processes.
Logically, each controller is a separate process, but to reduce complexity, they are all compiled into a single binary and run in a single process.
This component is taking responsibility to create, deploy resources of cluster via kube-apiserver. It contains multiple controllers, and have unique work for each one, such as
- Replication controllers
- Deployment controllers
- Ingress controller
- …
You can take more example about controller not each resources belong of kubernetes, but expand more like database-controller, gitops-controller, and yup it has a lot. Don’t worry we will take some practice and hand on with that inside this series
Back to kind and see what kube-controller with cluster offer for us
kubectl describe pods/kube-controller-manager-k8s-master-machine-control-planeI know it just controller base on kubernetes version registry.k8s.io/kube-controller-manager:v1.28.9 with parameters
kube-controller-manager
--allocate-node-cidrs=true
--authentication-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/controller-manager.conf
--authorization-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/controller-manager.conf
--bind-address=127.0.0.1
--client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
--cluster-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
--cluster-name=k8s-master-machine
--cluster-signing-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
--cluster-signing-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.key
--controllers=*,bootstrapsigner,tokencleaner
--enable-hostpath-provisioner=true
--kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/controller-manager.conf
--leader-elect=true
--requestheader-client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-ca.crt
--root-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
--service-account-private-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/sa.key
--service-cluster-ip-range=10.96.0.0/16
--use-service-account-credentials=trueSo controller will wait call from kube-apiserver about event which one will change configuration about resource like creating, updating or deleting and kube-controller will do execution with each one, very simple 😄
kube-scheduler
You can have more information from manual of kube-scheduler at kube-scheduler manual
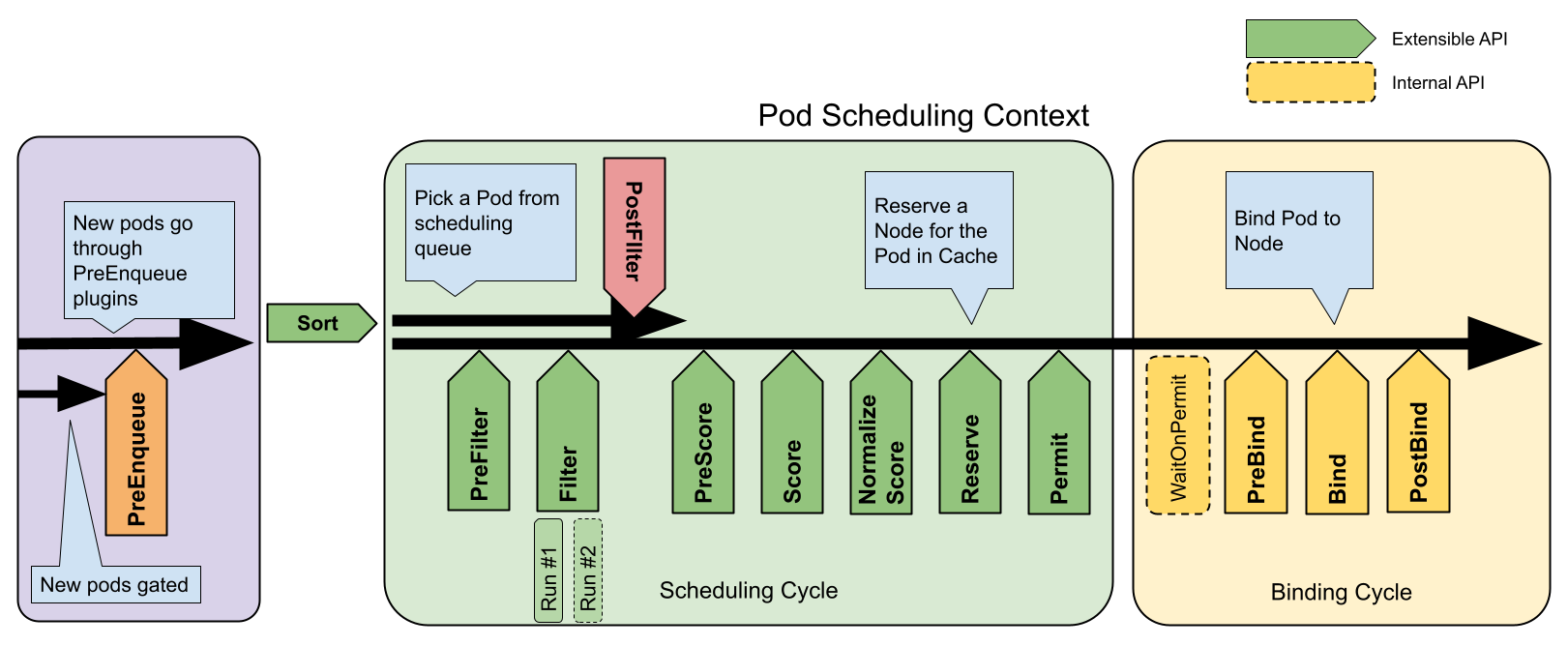 You can image
You can image kube-scheduler will wait announcement from kube-apiserver about which pod saved into etcd, if not have any node, kube-scheduler will mask your pod to node where can deploy into base on rating the quality of node
But it doesn’t easily than you think, I have terrify experience when try to manipulate deploy on Azure Kubernetes Cluster because this one has unique algorithm to deploy application, and it’s not separating with same number pods for node in cluster, and that cause problems about some node have pressure resources, and some one have not. Not kind to fun 😄, but kubernetes actually listen comunity, they give us multiple way to customize scheduler, and something make this become pleasant me, we will inspect about that on another session in this series
Basically, after inspect inside kind cluster you will have some quite fun configuration about kube-scheduler
# Inspect about kube-scheduler
kubectl describe pods/kube-scheduler-k8s-master-machine-control-planeAs you can see, It will run container in image registry.k8s.io/kube-scheduler:v1.28.9, and provide some configuration like
kube-scheduler
--authentication-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/scheduler.conf
--authorization-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/scheduler.conf
--bind-address=127.0.0.1
--kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/scheduler.conf
--leader-elect=trueYou can explore more about at: Scheduler Configuration
Follow the Linkedin - Demystifying the Kubernetes Scheduler: Assigning Pods to Nodes Behind the Scenes, and I can understand algorithm mostly use like
The default scheduler algorithm filters and prioritizes nodes to find optimal match.
- Filtering rules out nodes that don’t meet pod requirements like enough resources or match affinity rules.
- Prioritizing ranks remaining nodes to pick the best fit based on factors like resource utilization,spreading, etc.
So you need to learn to get used to difficulties with default kube-scheduler, it’s really tough but you can try manipulate that with quite great articles
- Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Pod Scheduling Readiness : Stable on v1.30
- Taints and Tolerations
- Scheduling Framework
- …
This is huge topic, if we talk, it will cost us a day to list 😄. So skip them, but I promise we will talk more about that in another session in series
Worker Node
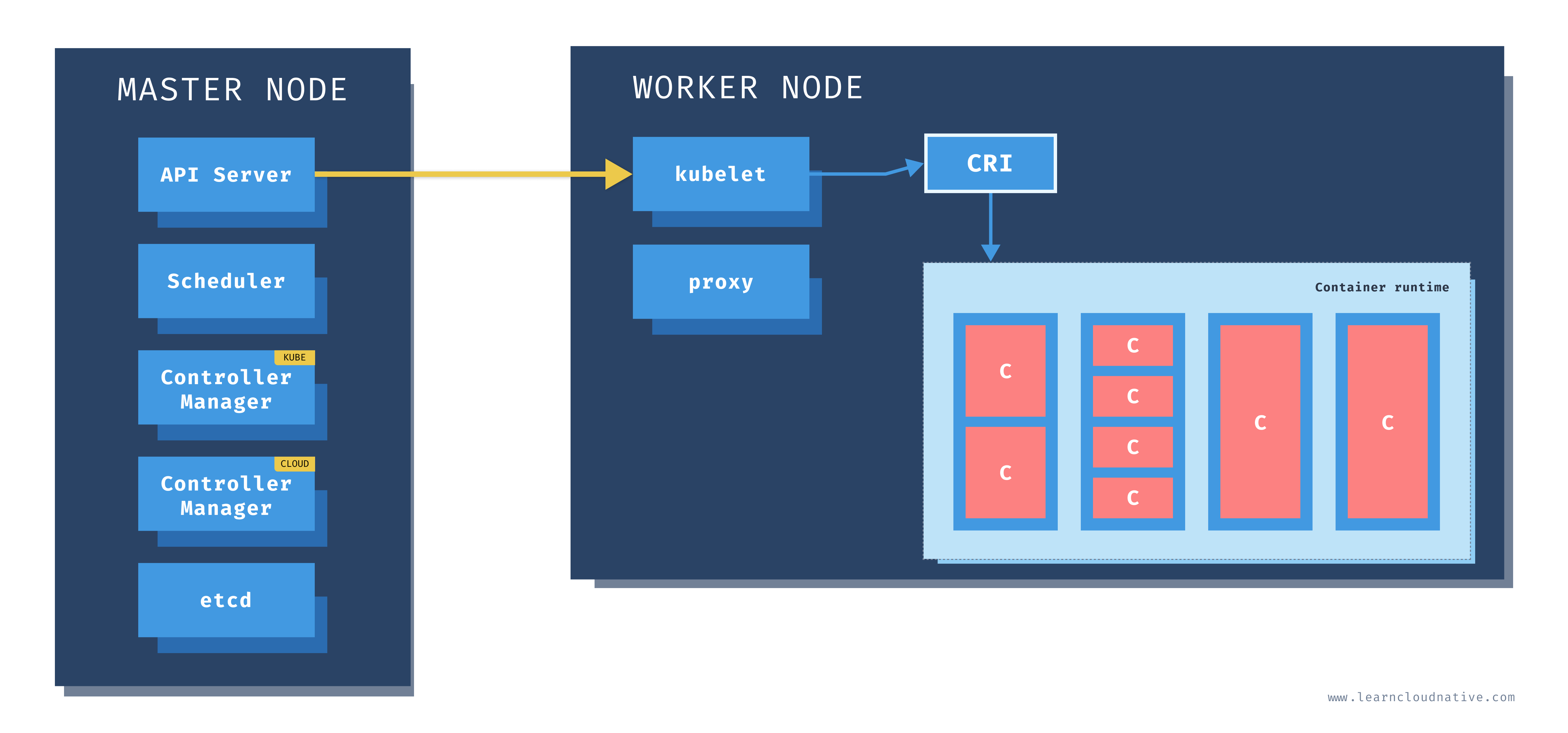
Info
Kubernetes runs your workload by placing containers into Pods to run on Nodes. A node may be a virtual or physical machine, depending on the cluster. Each node is managed by the control plane and contains the services necessary to run Pods.
Typically you have several nodes in a cluster; in a learning or resource-limited environment, you might have only one node.
Talk about little bit how we can management worker node. There are two main ways to have Nodes added to the API server:
- The kubelet on a node self-registers to the control plane
- You (or another human user) manually add a Node object
When you create a nodes, that will including some characteristic with you will interesting
- Node name uniqueness : The name identifies a Node. Two Nodes cannot have the same name at the same time.
- Self-registration of Nodes : When the kubelet flag
--register-nodeis true (the default), the kubelet will attempt to register itself with the API server. This is the preferred pattern, used by most distros. - Manual Node administration : You can create and modify Node objects using kubectl. When you want to create Node objects manually, set the kubelet flag
--register-node=false.
Nodes is big target on kubernetes, It has more concept and pattern, therefore, if you want to read more about, just follow the link: Nodes
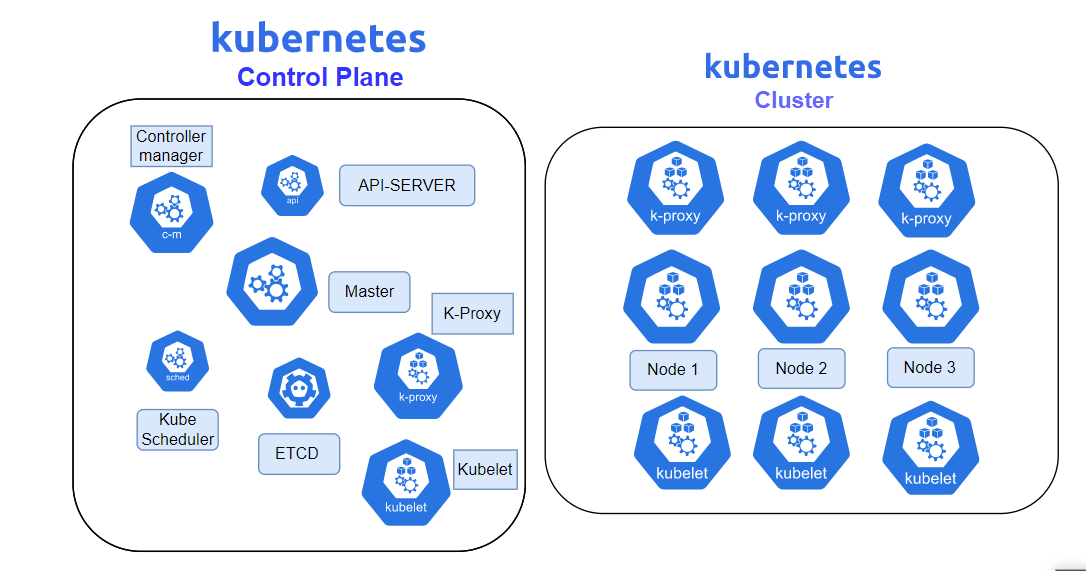
Info
Node components run on every node, maintaining running pods and providing the Kubernetes runtime environment.
The components on a node include
But another way, we will have some extend things you will see in the node, including
- DNS server
- Ingress controller
- Container Network Interface (CNI)
- Metrics controller
- …
Now we inspect some general of components inside one node
kubelet
Find more information about configuration of kubelet via kubelet manual
Info
An agent that runs on each node in the cluster. It makes sure that containers are running in a Pod.
The kubelet takes a set of PodSpecs that are provided through various mechanisms and ensures that the containers described in those PodSpecs are running and healthy. The kubelet doesn’t manage containers which were not created by Kubernetes.
Connection between master node and worker node via this one, if you join worker node into master node, kubelet will handle and create post request with node-config and send that to kube-apiserver
But if you work more with kubelet, that kind will very complicated because characteristic of it with submit a role like systemd and cgroupfs, use that driver to control your node. For example, when your pod reach over limit resources like memory, kubelet will kill your application with exit 127
Nowaday, actually you can config kubelet inside kubelet-config-file to specific what configuration you want, read more about at Set Kubelet Parameters Via A Configuration File
Back to kind, you can view and read about kubelet by exec inside container because kubelet run as agent not workload inside kubernetes, therefore you need to that
# Exec to docker control-plane
docker exec -it k8s-master-machine-control-plane /bin/bash
# View kubelet configuration
kubectl get --raw "/api/v1/nodes/k8s-master-machine-control-plane/proxy/configz" | jqand yeah you can view kubelet configuration right now
kube-proxy
With kube-proxy, this component use to control traffic and network inside worker node, with worker, it means you can set configuration to give your reqeust to pod after service, and kube-proxy offer you 3 mode
- userspace
- iptables
- ipvs
With our kind cluster, I choose iptables for control networking. iptables is firewall inside linux os, you can use that to set the rule and route for traffic inside host
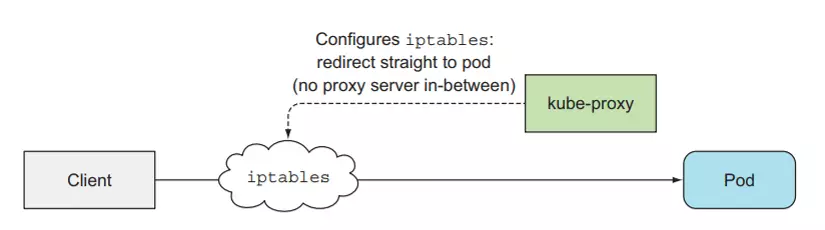
BTW, you can choose ipvs for improving the performance but actually you will need to have knowledge of them. And one more thing, in kubewekend we will learn how to set up for own proxy use cilium and do more thing around with this tool.
And, if you want to check out kube-proxy, access this kube-proxy manual
Container runtime
So with container runtime, that is component will actually help you run the container inside. At the moment, you can use several common runtime with kubernetes
With kind, we actually use docker runtime because to operating kubernetes with kind you need docker to bring up, and this is reason why kind use this one for runtime
Another components
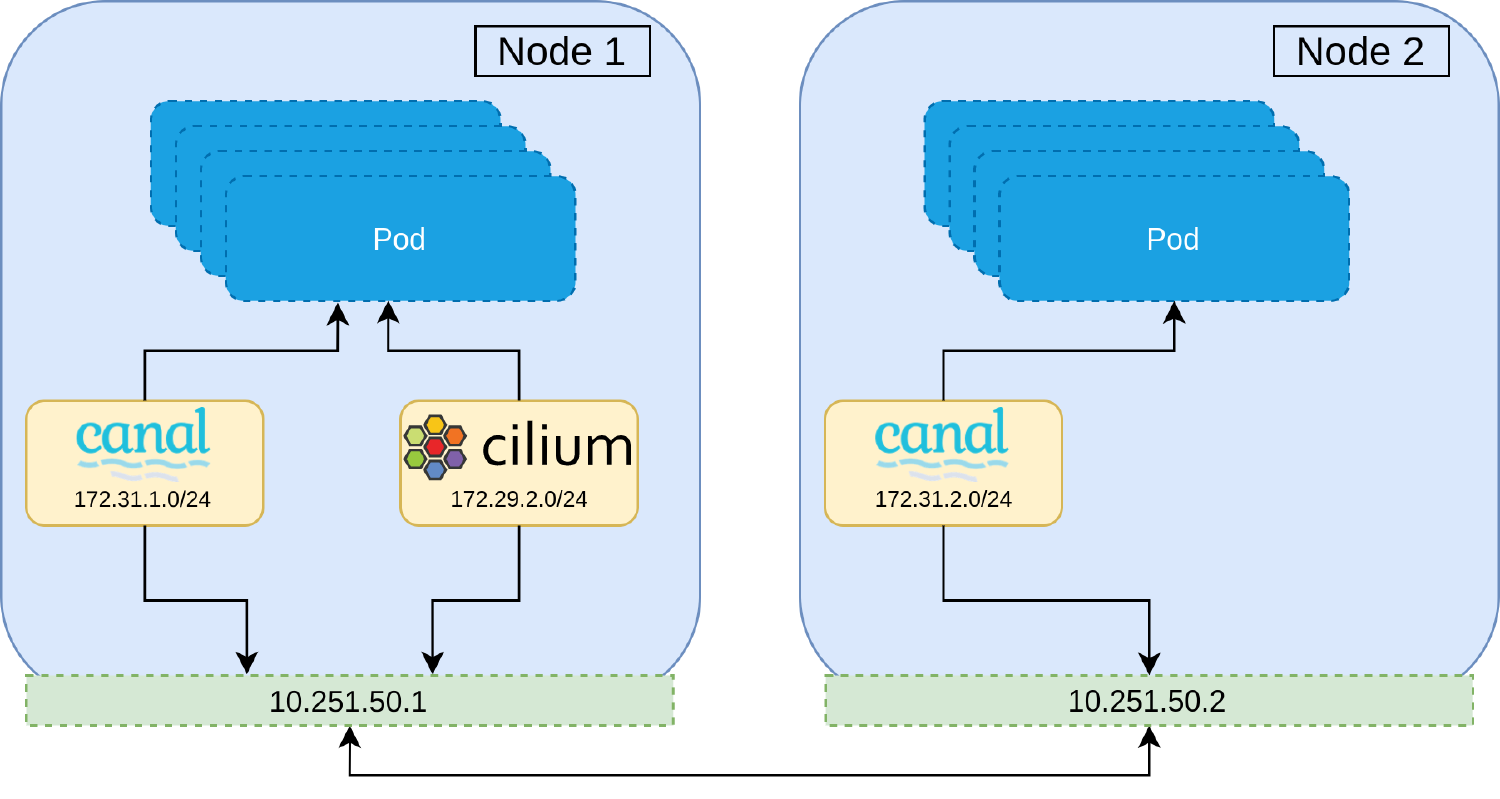
So with kind configuration of mine, we don’t setup any container network interface, so on next session we will talk around this one, spoil to you about cilium will be the target cni of mine on this series
Not only cni, kind cluster actually provide us about kube-dns is coredns, that is dns service which offer from kubernetes, mostly use for dns and service discovery purpose
kubectl describe deployments coredns As you can see, coredns will use configuration from configmap to operate and start with image registry.k8s.io/coredns/coredns:v1.10.1, that will help your service understand, give dns inside cluster to give route for service can commnuncate with each others
![]()
The config is quite new for me, but that kind of clearly to understanding what that want to definition
Corefile: |
.:53 { Corefile: |
.:53 {
errors
health {
lameduck 5s
}
ready
kubernetes cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa {
pods insecure
fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa
ttl 30
}
prometheus :9153
forward . /etc/resolv.conf {
max_concurrent 1000
}
cache 30
loop
reload
loadbalance
}
errors
health {
lameduck 5s
}
ready
kubernetes cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa {
pods insecure
fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa
ttl 30
}
prometheus :9153
forward . /etc/resolv.conf {
max_concurrent 1000
}
cache 30
loop
reload
loadbalance
}So with that configuration, you can image about the operation of coredns like
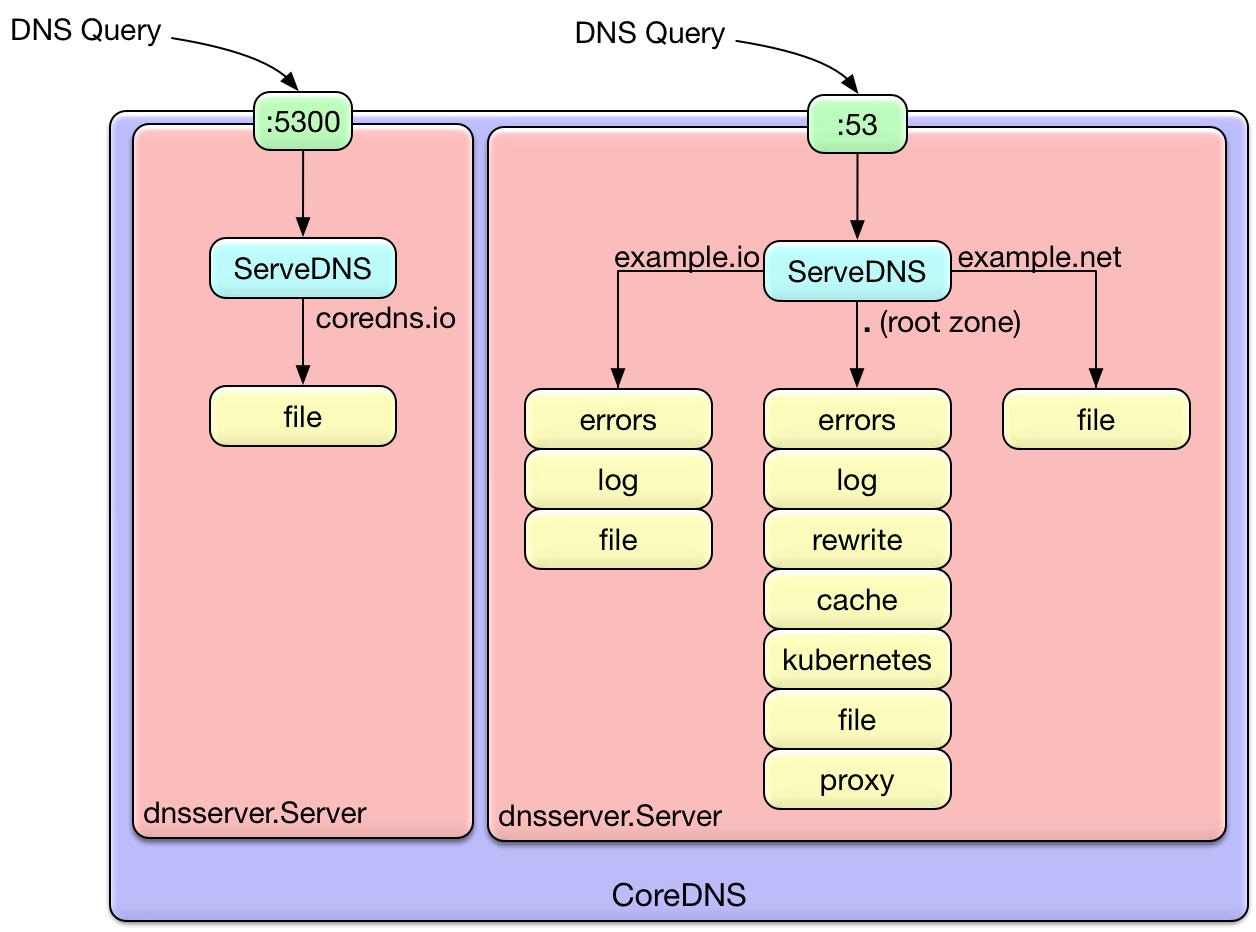
But as soon as, we will refer to cilium that can help you have more tool to apply dns inside kubernetes cluster
How are actually Kubernetes workflow
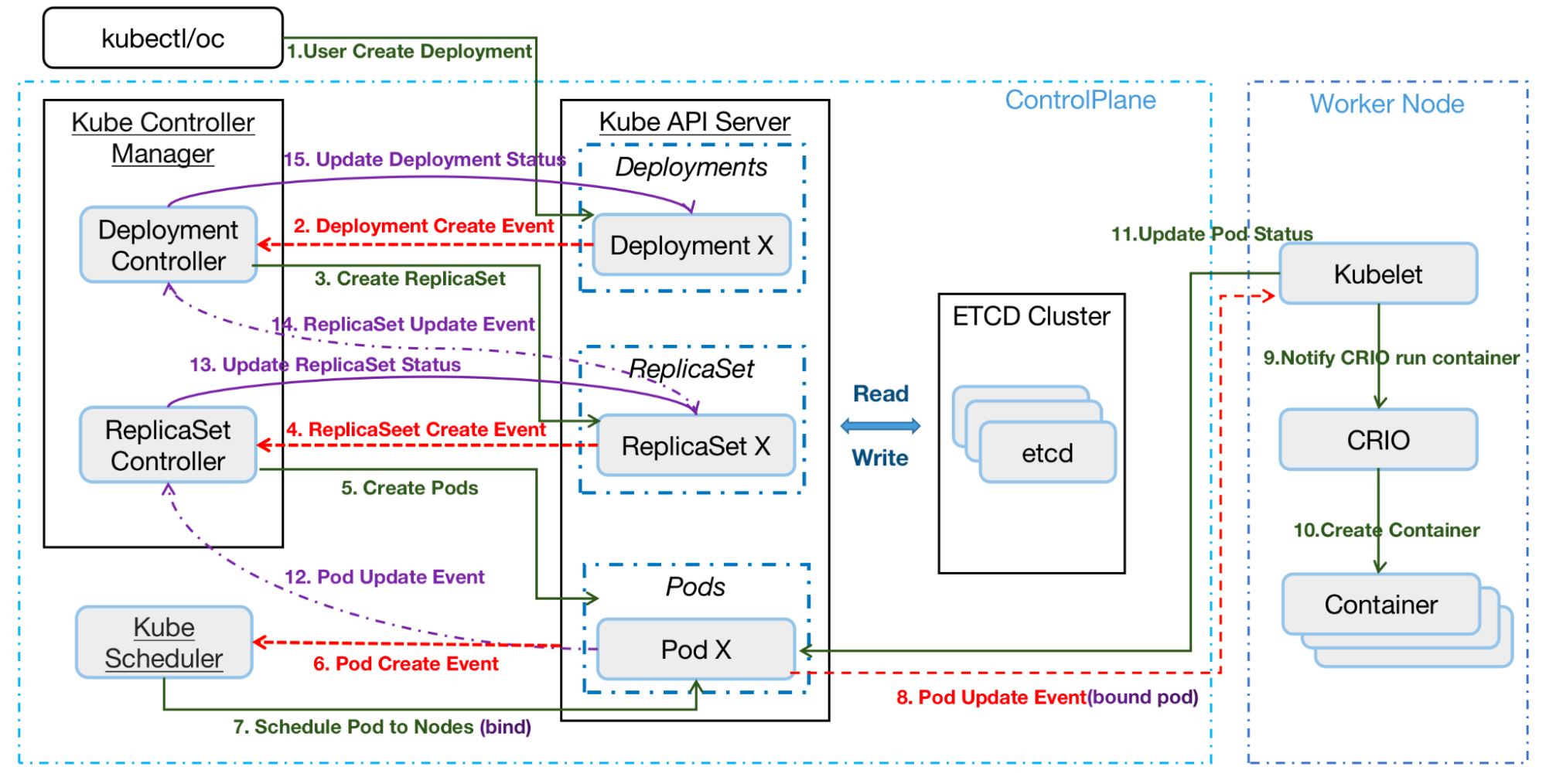
Base on Kubernetes API Performance Metrics: Examples and Best Practices, we can image the how kubernetes actually work
The general workflow:
- User creates a Deployment using a REST API or the command line.
- API Server (kube-apiserver) writes the Deployment spec into etcd.
- The
Deployment Controllerwatches for new Deployments to create an event and takes action to reconcile against the Deployment spec and create a ReplicaSet manifest, then posts them to API server and writes theReplicaSetspec intoetcd. - The
ReplicaSet controllerwatches for the ReplicaSet created event, and creates the new Pod manifests. It posts them to the API server and writes the Pod spec intoetcd. - The Scheduler watches pod creation events and detects an unbound Pod. It schedules and updates the Pod’s Node binding.
Kubelet, running on the node, detects a new Pod scheduling and executes it using the Container runtime (for example, cri-o).Kubeletretrieves the Pod status through the Container runtime and updates it to the API Server. General Deployment create events are available with thekubectl get event -n namespacecommand.
You can explore more about how the workflow inside kubernetes via some cool articles
Conclusion
Success
That all for this session, I know that is a lot but not enough, i probably for sure 100%. But I am completely the walkthrough about general
kubernetes, and know about how of each component submit a role and operate. To more understand, you need actually practice and play withkubernetesto gain experience and knowledge, that shorten way for learning aboutkubernetes
Quote
Well that is a lot of information in this article, for sure. Hope you find well information or take note some knowledge about
kubernetes, reason why we usekubernetesor what components do we have inside cluster.kubewekendwill provide you more aboutkubernetes, do more fun with concept and now stay safe, learn more and see you on next session ASAP, bye bye 😄 😄 😄