Quote
Hi @all, as you can see Kubernetes is becoming the potential technology in the world in couple recently year. The knowledge about Kubernetes honestly to say It’s really huge, so today we can learn a bit about once of tools to maintain and deploy the workload inside Kubernetes Cluster, Helm. Let’s digest
Installation

Official Homepage: 🔗Click to the link
Info
What is Helm ?
Helm helps you manage Kubernetes applications — Helm Charts help you define, install, and upgrade even the most complex Kubernetes application.Charts are easy to create, version, share, and publish — so start using Helm and stop the copy-and-paste.
Helm is a graduated project in the CNCF and is maintained by the Helm community.
Helm already installing and using on CI/CD, If you want to learn and work with helm, feel free to installing on Installing Guide
I prefer to use command to get latest version of helm
# Run whole process
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh
# Run with one command
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3 | bashHelm Template
All of application will base on template for releasing, you can understanding the concept with helm template
mychart
|-- Chart.yaml
|-- charts
|-- templates
| |-- NOTES.txt
| |-- _helpers.tpl
| |-- deployment.yaml
| |-- ingress.yaml
| `-- service.yaml
`-- values.yamlQuestion
Why we need the helm template ?
- Make everything become simple for managing and replacing
- Changing only one place and anything will come update for each environment (Consider when you want to change, make sure anything is working)
- Flexible variables base on environment with
values.yamlfile
Related articles:
Priority of Value in Helm
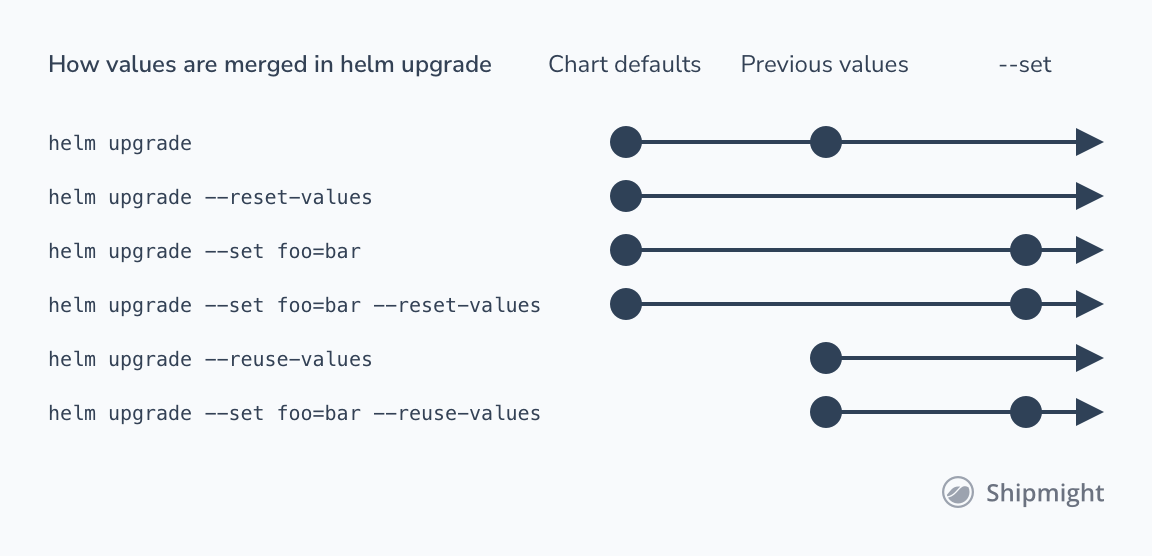
Tip
To override values in a chart
- use either the
--valuesflag and pass in a file or use the--setflag and pass configuration from the command line- To force string values, use
--set-string.- You can use
--set-fileto set individual values from a file when the value itself is too long for the command line or is dynamically generated.- You can also use
--set-jsonto set json values(scalars/objects/arrays)from the command line.You can specify the
--values'/'-fflag multiple times. The priority will be given to the last (right-most) file specified.You can specify the
--setflag multiple times. The priority will be given to the last (right-most) set specified.You can update the values for an existing release with this command as well via the
--reuse-valuesflag. TheRELEASEandCHARTarguments should be set to the original parameters, and existing values will be merged with any values set via--values'/'-for--setflags.
Related articles
Command usage
Helm will submit the role for both of CI and CD progress*
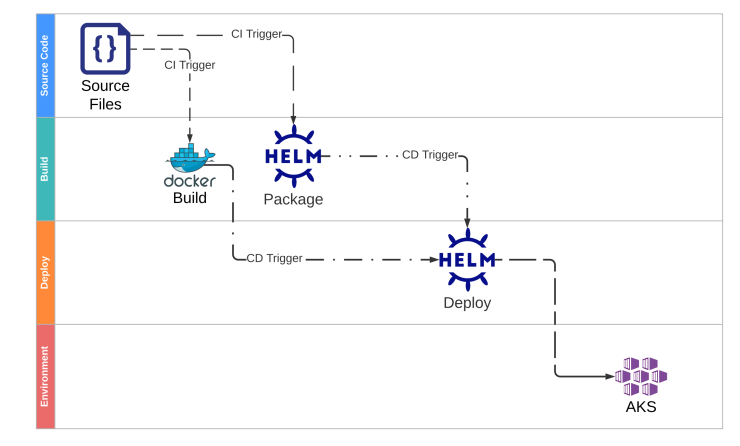
CI (Continuous Integration)
helm dependency
Documentation: doc
Purpose: manage a chart’s dependencies
Info
Manage the dependencies of a chart.
Helm charts store their dependencies in ‘charts/‘. For chart developers, it is often easier to manage dependencies in ‘Chart.yaml’ which declares all dependencies.
The dependency commands operate on that file, making it easy to synchronize between the desired dependencies and the actual dependencies stored in the ‘charts/’ directory.
Just use update optional for update charts/ based on the contents of Chart.yaml
Example:
Documentation: The Chart.yaml File
apiVersion: v2
name: xxxx
description: A Helm chart for Kubernetes
# A chart can be either an 'application' or a 'library' chart.
#
# Application charts are a collection of templates that can be packaged into versioned archives
# to be deployed.
#
# Library charts provide useful utilities or functions for the chart developer. They're included as
# a dependency of application charts to inject those utilities and functions into the rendering
# pipeline. Library charts do not define any templates and therefore cannot be deployed.
type: application
# This is the chart version. This version number should be incremented each time you make changes
# to the chart and its templates, including the app version.
# Versions are expected to follow Semantic Versioning (https://semver.org/)
version: 0.1.0
# This is the version number of the application being deployed. This version number should be
# incremented each time you make changes to the application. Versions are not expected to
# follow Semantic Versioning. They should reflect the version the application is using.
appVersion: 1.16.0
dependencies:
- name: common
version: 0.1.0
repository: "file://../../library/common/"If you can see with Chart.yaml, you could understand what meaning of Chart with important value like
apiVersion: The chart API version (required) - Default to usehelm3with apiv2to applied deploymentname: The name of the chart (required) - This one will be effect to your kubernetes service, if namexxxx, for example your deployment name will bexxxxdependencies: A list of the chart requirements (optional) - Take thecommonwithpre-definefor mapping changedeployments and YAML manifestsfor application.
Note
NOTICE: Application will use file with relative path, make sure
../../library/common/exist
On CI progress, pipeline will trigger the action
helm dependency update ../xxxxx/charts/xxxx/Success
With this action, your new chart application will create and publish artifact with
- New value file if you change environment value
- New variable of
secretconfigmap, if you update them- Add new configuration like applying
HPAto your application, for example
CD (Continuous Delivery)
helm upgrade
Documentation: doc
Purpose: upgrade a release
Info
This command upgrades a release to a new version of a chart.
The upgrade arguments must be a release and chart. The chart argument can be either: a chart reference(‘example/mariadb’), a path to a chart directory, a packaged chart, or a fully qualified URL. For chart references, the latest version will be specified unless the
--versionflag is set.
Apply --install for purpose running both update and install if not exist Chart on Cluster
Question
You need to understand concept of
value-filework withhelm updateto make sure not mistake occur when defining. NOTICE: The value will be set base on priority. Read Priority of Value in Helm to explain more
- All environment with sensitive need to be masking like connection strings, password database, secret key, … by force to using
--setflag to set this part on the pipeline. - Base on environment, you need to upgrading the specify value for each them like
production-values.yaml uat-values.yaml systemtest-values.yaml - If you do not set any value, default
values.yamlis specify for general value
On CD progress, pipeline will trigger the action
helm upgrade --install xxxx -f ../xxxxx/environments/systemtest-values.yaml --set mongodb.password=$(MONGODB_PWD) ../xxxxx/charts/xxxx Success
With this action, If not wrong anything, your new application will release to K8s Cluster
Another command
helm search
To search the version of chart from your repo which one you add into cluster, or from hub e.g ArtifactHub or selfhosted
# Search all repo available from helm chart add into cluster
helm search repo
# (Detail) Search on repo you add into cluster
helm search repo chart-path --version <version>
helm search repo chart-path --versions # Get list
# Search from artifacthub or self instance
helm search hubhelm install
To install helm chart from self-define or community from ArtifactHub
helm install <name-release> <chart-url>If you wanna specific version, you can add additional option flag --version
helm install <name-release> --version <version> <chart-url>helm list
To list releases on namespacehelm list -n <namespace>helm repo
To add, list, remove, update, and index chart repositories# Add a chart repository
helm repo add [NAME] [URL] [flags]
# Update information of available charts locally from chart repositories
helm repo update [REPO1 [REPO2 ...]] [flags]helm uninstall
To uninstall a release
helm uninstall RELEASE_NAME [...] [flags]Debug Template
Documentation: Doc
Info
Debugging templates can be tricky because the rendered templates are sent to the Kubernetes API server, which may reject the YAML files for reasons other than formatting.
There are a few commands that can help you debug.
helm lintis your go-to tool for verifying that your chart follows best practiceshelm template --debugwill test rendering chart templates locally.helm install --dry-run --debugwill also render your chart locally without installing it, but will also check if conflicting resources are already running on the cluster. Setting —dry-run=server will additionally execute any lookup in your chart towards the server.helm get manifest: This is a good way to see what templates are installed on the server.
Conclusion
Success
On this topic, you will learn and understand about helm for
- Install
Helmfor your environment, for debug or release- Understand priority value of helm chart
- How to use command with helm ?
- Tools for helping you debug the template before apply for real environment