Quote
Hi @all, do you have a great week, huh ? This weekend will become more interested in learning with
eBPF, practice withciliumandhubble, one of most huge platforms to control and managing whole progress inside network ofKubernetesclusters. Are you ready, mate, let’s digest !!
Before start this week, I want to give appreciation and shout out for many communities, for powerful technologies who came up from
- eBPF - A revolutionary technology with origins in the Linux kernel
- CNCF - the open source, vendor-neutral hub of cloud native computing
- Isovalent - Community stand behind the
ciliumand sub-projects ofcilium - Cilium - an open source, cloud native solution for providing, securing, and observing network connectivity between workloads, fueled by the revolutionary Kernel technology eBPF
- Hubble, Tetragon - Ambassador and integration sub-projects of
cilium - eCHO - eBPF & Cilium Office Hours - Youtube series where we can find and learn more about
eBPFandciliumvia live stream every week
And don’t forget to checkout the super cool previous sessions of kubewekend down below
What is eBPF ?

Like I promising on the article about Profiling applications with Pyroscope, today we will learn and do research about eBPF - the technologies stand behind pyroscope
Question
Anyone in here are knowing about
eBPForBPF? This will be pleasant about question to the most powerful technology inside nowadaykubernetes
We have used BPF but you don’t ever known about that, probably I really surprise and suspicious about this one on first time hearing them 😄. No joke dude, listening in eCHO episode 1: Introduction to Cilium
You can use BPF via tools, such as tcpdump, bpftool, perf, wireshark - actually not much information but classic BPF build up libpcap and more network libraries. Read more about BPF at: Berkeley Packet Filter. If you have enough time and patience, read the source code from of them to see how the BPF work, no cap bruh 😅
Note
Since version 3.18, the Linux kernel includes an extended
BPFvirtual machine with ten 64-bit registers, noweBPFis coming up with the evolution ofBPFand bring for us many advantage characteristics from them
Introduce
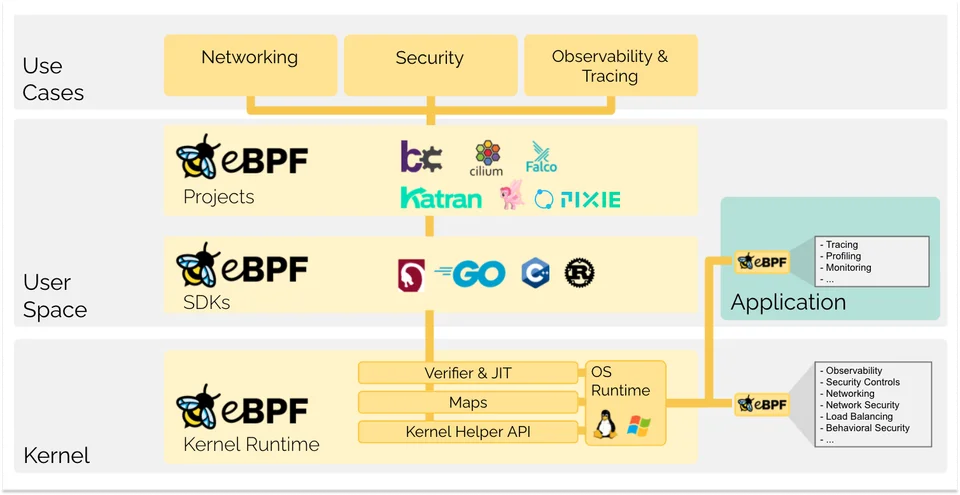
Info
eBPF
eBPF is a revolutionary technology with origins in the Linux kernel that can run sandboxed programs in a privileged context such as the operating system kernel. It is used to safely and efficiently extend the capabilities of the kernel without requiring to change kernel source code or load kernel modules.
eBPF brings useful and change formula fundamentally to running the programs within the operating system, I means it can be used for operating system then guarantees safety and execution efficiency as if natively compiled with the aid of a Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler and verification engine. This has led to a wave of eBPF-based projects covering a wide array of use cases, including next-generation networking, observability, and security functionality.
eBPF is used extensively to drive a wide variety of use cases
- Providing high-performance networking and load-balancing in modern data centers and cloud native environments
- Extracting fine-grained security observability data at low overhead
- Helping application developers trace applications
- Providing insights for performance troubleshooting
- Preventive application and container runtime security enforcement
- And moreover
Quote
The possibilities are endless, and the innovation that eBPF is unlocking has only just begun.
From What is eBPF? - ebpf.io
Info
BPF originally stood for Berkeley Packet Filter, but now that eBPF (extended BPF) can do so much more than packet filtering, the acronym no longer makes sense. eBPF is now considered a standalone term that doesn’t stand for anything. In the Linux source code, the term BPF persists, and in tooling and in documentation, the terms BPF and eBPF are generally used interchangeably. The original BPF is sometimes referred to as cBPF (classic BPF) to distinguish it from eBPF.
From What is eBPF? - ebpf.io
Features
In this part, we move to detailing about eBPF, which come up idea and more concept to understand about useful and how can we leverage a solution on eBPF
Explore more with the high quality contents from
- eBPF Documentation
- eBPF & XDP Reference Guide.
- eBPF Explained: Use Cases, Concepts, and Architecture
From my perspective, I do not have much experience with eBPF after use cilium and hubble, therefore hard to me to explain the detailing how eBPF actually work, you can read more information above reference, and I just brief some information from them
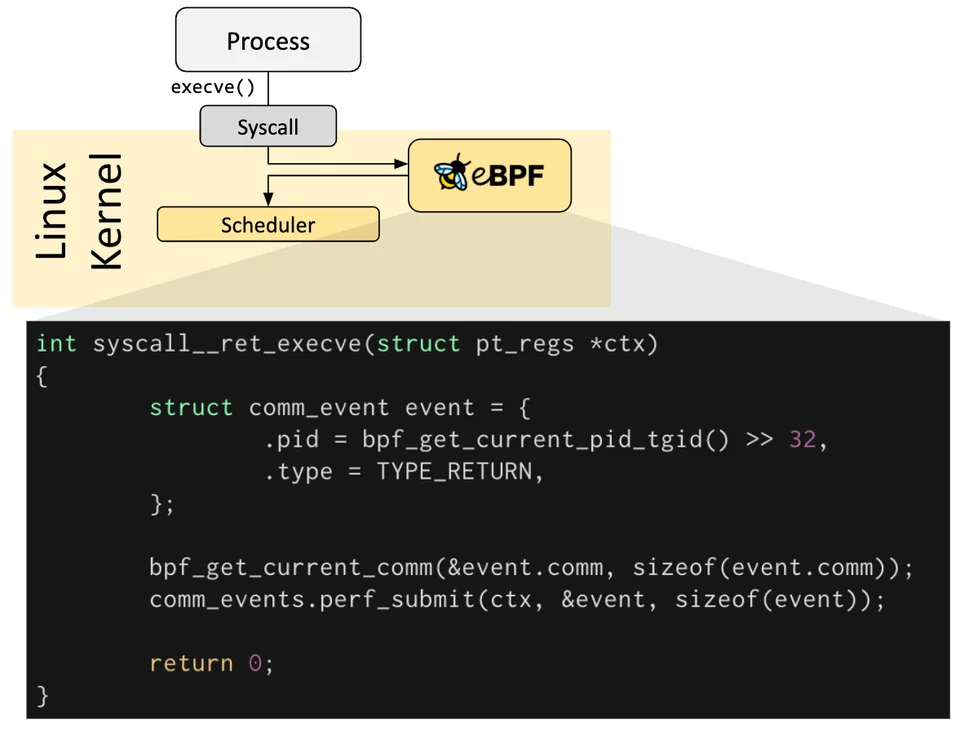
eBPF programs are event-driven and are run when the kernel or an application passes a certain hook point - include system calls, function entry/exit, kernel tracepoints, network events, and several others.
Pre-hook is possible to create a kernel probe (kprobe) or user probe (uprobe) to attach eBPF programs when not exist any defined on particular need
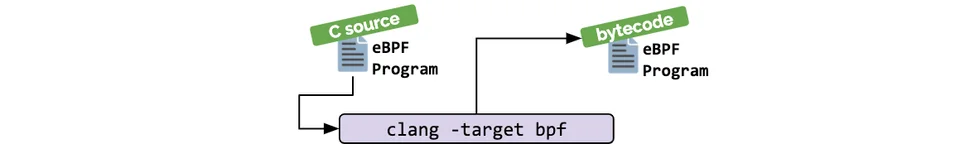
We can use abstraction on top of eBPF, such as cilium, bcc or bpftrace and do not require writing, that why I said about cilium is take cover all about eBPF 😄
But you can compile that if not really exist higher abstraction for compatibility via a compiler suite like LLVM to compile pseudo-C code into eBPF bytecode.
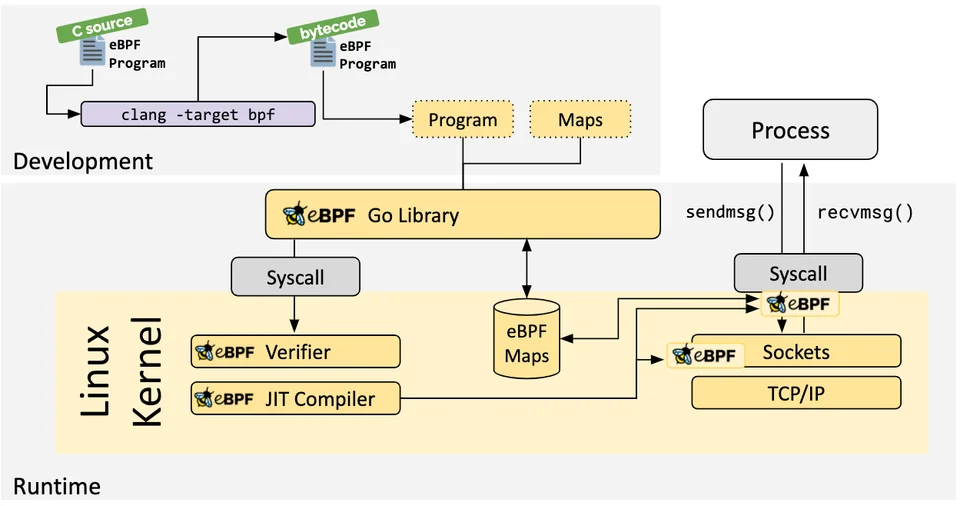
eBPF program can load to kernel via system call, and you need to pass through two steps before being attached to request hook verification and Jit compilation
-
On the
verificationprogress, It will ensure theeBPFprogram can be safe to run, and several conditions need to meet like holds the required capabilities (privileges), not crash or otherwise harm the system, *runs to completion (not loop forever or holding up processing) -
How about
JIT(Just-in-time), the compilation step translates the generic bytecode of the program into the machine specific instruction set to optimize execution speed of the program
To store and retrieve data, eBPF use technics called maps, help reduce the complexity when work with wide set of data structures, this one can be accessed from eBPF programs vis system call. Maps can be used for both a shared and a per-CPU variation with some supported type (e.g Hash tables, LRU, Ring Buffer, …)
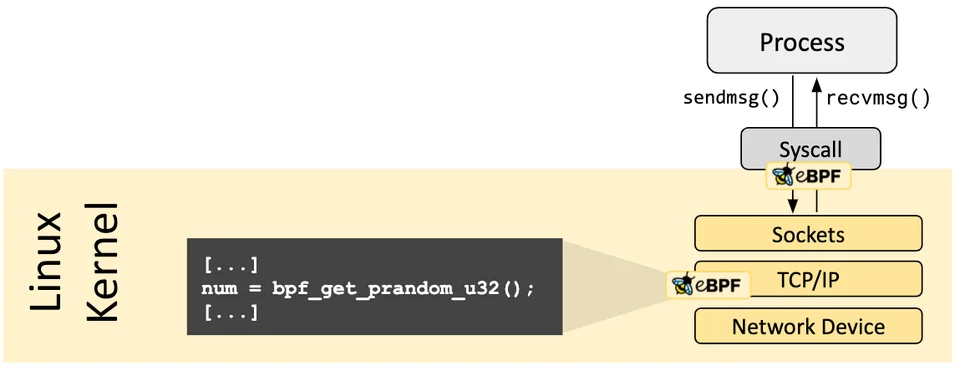
To flexible in finding compatible version of kernel and programs, ebpf can make function call into helper function to find stable API offered, such as helper function in used Generate random numbers, eBPF map access, Manipulate network packets and forwarding logic, Get process/cgroup context, Get current time & date, …
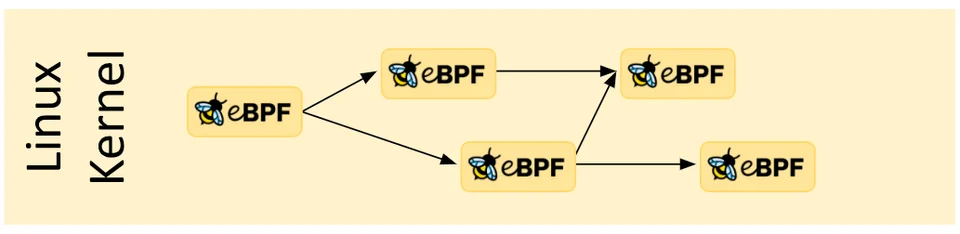
eBPF is work with concept called tail and function call - It means function can be definition and calling functions of eBPF program and tail can call and execute another eBPF program and replace the execution context

Quote
”With great power there must also come great responsibility” 🙌
IYKYN and From What is eBPF? - ebpf.io
eBPF is becoming the most powerful technology, because easily to see this one work with kernel - central component of an operating system that manages operations of computer and hardware. Therefore, eBPF need to ensure anything in securable and safety, and can be listed in some layers
-
Must be Required Privileges, all
eBPFneed ensure to running in privileges mode (root) or require the capability CAP_BPF, unless Unprivileges eBPF is enabled -
eBPFprograms need to pass Verifier to ensure safety of the program itself, we have talked this one above -
eBPFprograms runs through a Hardening process - It means wheneBPFrun need to be ensure these steps- Program execution protection : Kernel memory holding an eBPF program is protected and made read-only
- Mitigation against Spectre: Under speculation CPUs may mispredict branches and leave observable side effects that could be extracted through a side channel.
- Constant blinding: All constants in the code are blinded to prevent JIT spraying attacks.
-
Use Abstracted Runtime Context, not let
eBPFprogram access arbitrary kernel memory directly, but through eBPF helpers and put Data and data structures that lie outside of the context of the program
Quote
This is quite hard to understand right now, because of belong to deepest of operate system, your
kernellevel where work with network and hardware, really tough. But when you learn something new, I think go from concept but brief can be help you slowly to inspect to your tool and figure out how that work 😃
BTW, we reach out to reason why eBPF become actually ascendancy in Infrastructure in currently
Why eBPF ?
The honest answer come from the evolution, from technology, from the mindset, from the attacking as cybercriminal, and many things is really grow faster than ever
Let image about when you actually work your application inside the container, and it actually the OS in light weight, you really do anything else right now inside one of operation system, that will actually have kernel. And to be secure on dangerous world of technology, you need to be ensure about connection and workflow inside them, such as network, hardware and functional, performance that reason why eBPF is comeback and become more potential in currently, honestly
Quote
"eBPF's is actually impact on the Linux Kernel"
From eBPF’s impact on the Linux Kernel - eBPF Documentation - ebpf.io
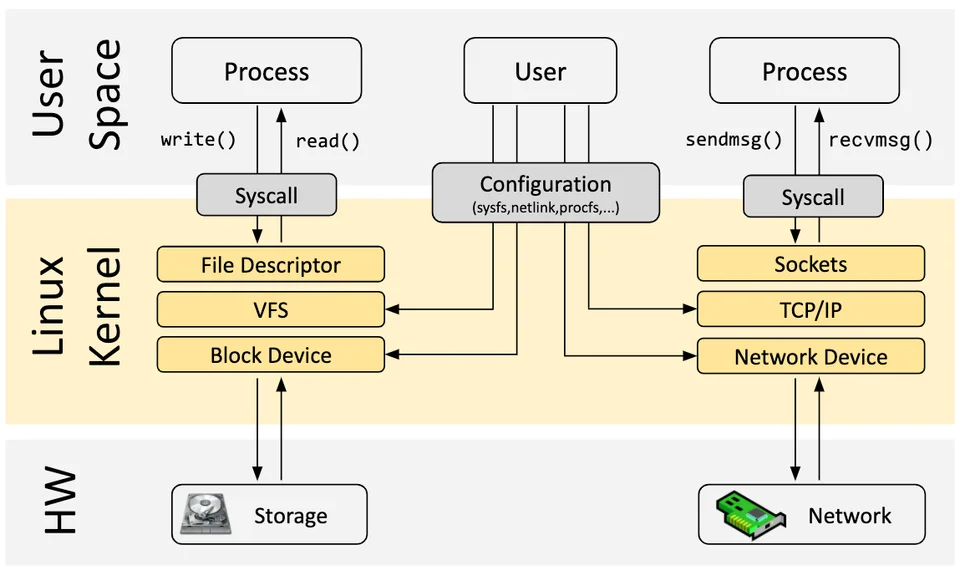
Info
Main purpose of the Linux kernel is to abstract the hardware or virtual hardware and provide a consistent API (system calls) allowing for applications to run and share the resources

Info
With eBPF, a new option is available that allows for reprogramming the behavior of the Linux kernel without requiring changes to kernel source code or loading a kernel module
That reason why eBPF is actually act like rewriting the definition when you programing and doing inspect on the progress to improvised your application through observability, tracing and profiling application, really become trending on next time in the future, probably 100%
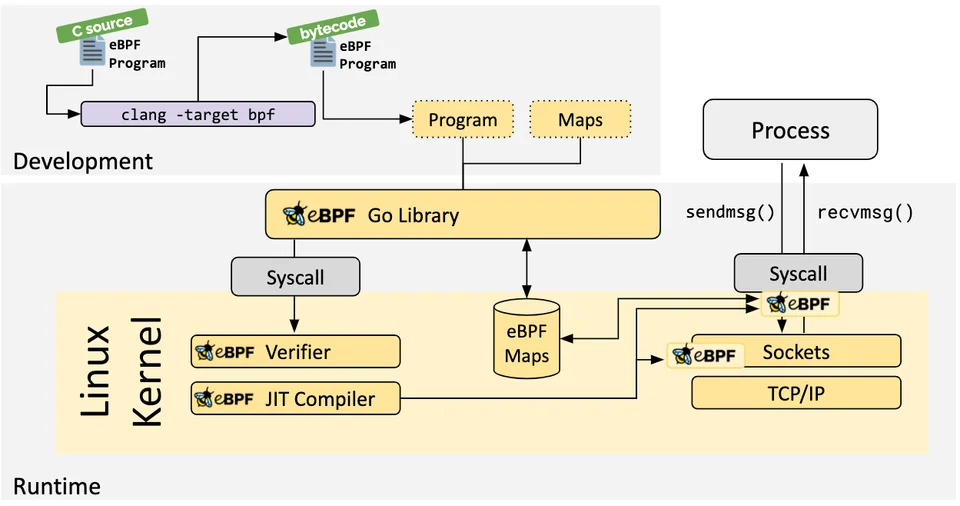
In currently, you can work on eBPF through some toolchains act like abstractions and libraries which you can interact with
- bcc - A framework that enables users to write python programs with eBPF programs embedded inside them
- bpftrace - High-level tracing language for Linux eBPF
- ebpf-go - Pure-Go library to read, modify and load eBPF programs and attach them to various hooks in the Linux kernel.
- libbpf - Automated upstream mirror for libbpf stand-alone build.
And one more thing, super recommend you about communities, articles, series and books to explore more information about eBPF and another dependencies
- eBPF & Cilium Community, Youtube channel where you start to learn about
eBPF - Learning eBPF, Liz Rice, O’Reilly, 2023
- What is eBPF?, Liz Rice, O’Reilly, 2022
- BPF Performance Tools, Brendan Gregg, Addison-Wesley Professional Computing Series, Dec 2019
- Isovalent Lab about eBPF
- ebpf-beginners, The beginner’s guide to eBPF by Liz Rice
- learning-ebpf, Lab practice with Learning eBPF book of Liz Rice and O’Reilly
But we can understand more about eBPF in this series kubewekend through operate cilium, hubble, tetragon and pyroscope, read the next part, more pleasant thing stand behind
Approach eBPF in real life
Quote
When take the deep dive into
eBPFis becoming quite long and more thing to understand, witheBPFin raw you will hard to be imaged or structured for what this technology can do in currently. Wait, don’t worry buddy,eBPFis go far than we are imaging, there is tons of tools, platform for multiple purpose approacheBPF, and that make your game become more easy than ever.
Let’s take some example
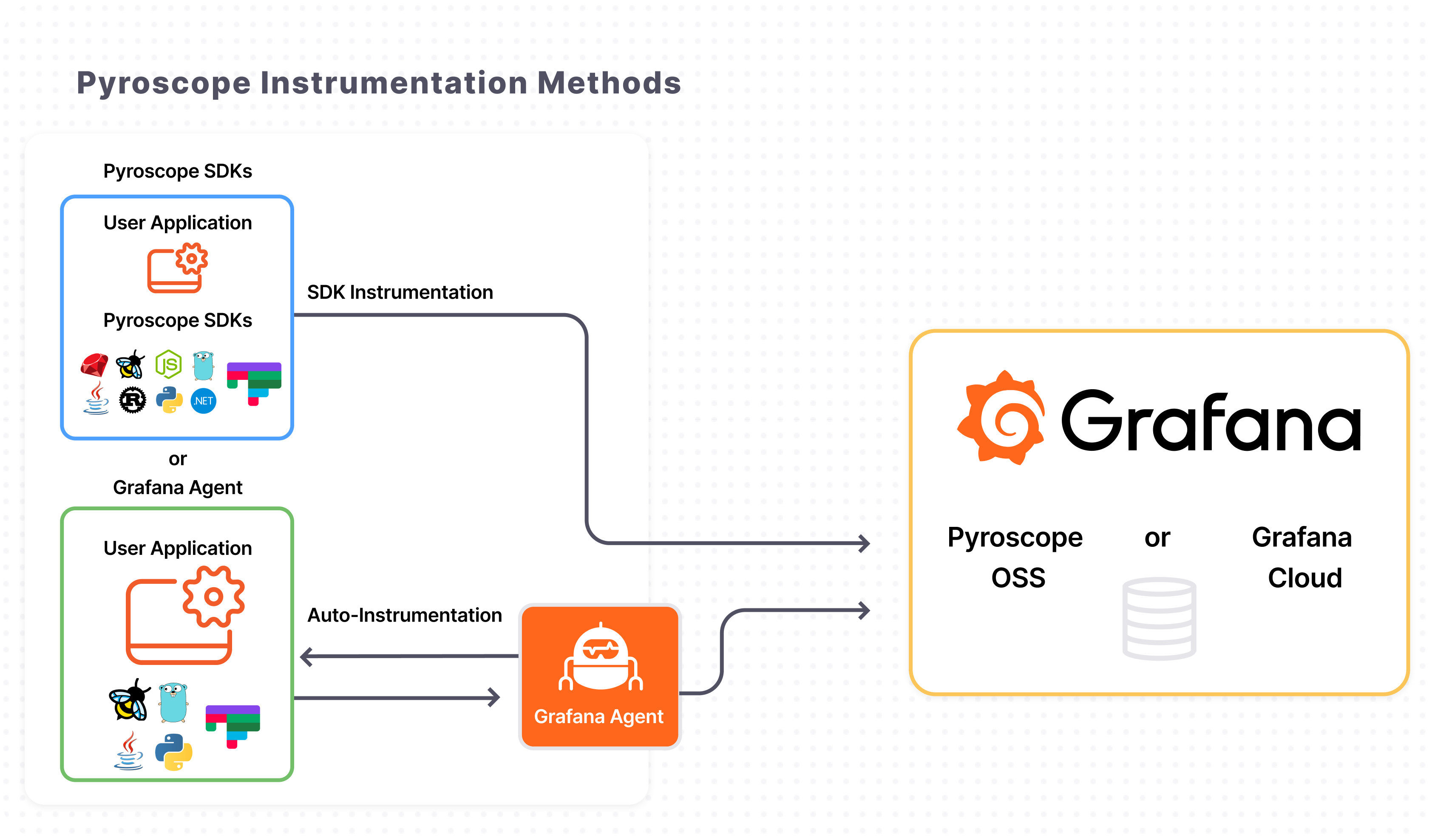
”When you have tough case inside your application, and dunno any reason why your application become slowly” - now you can use eBPF for observability tools like Pyroscope to check what is going on with your application, memory leaks, pressure CPU and moreover
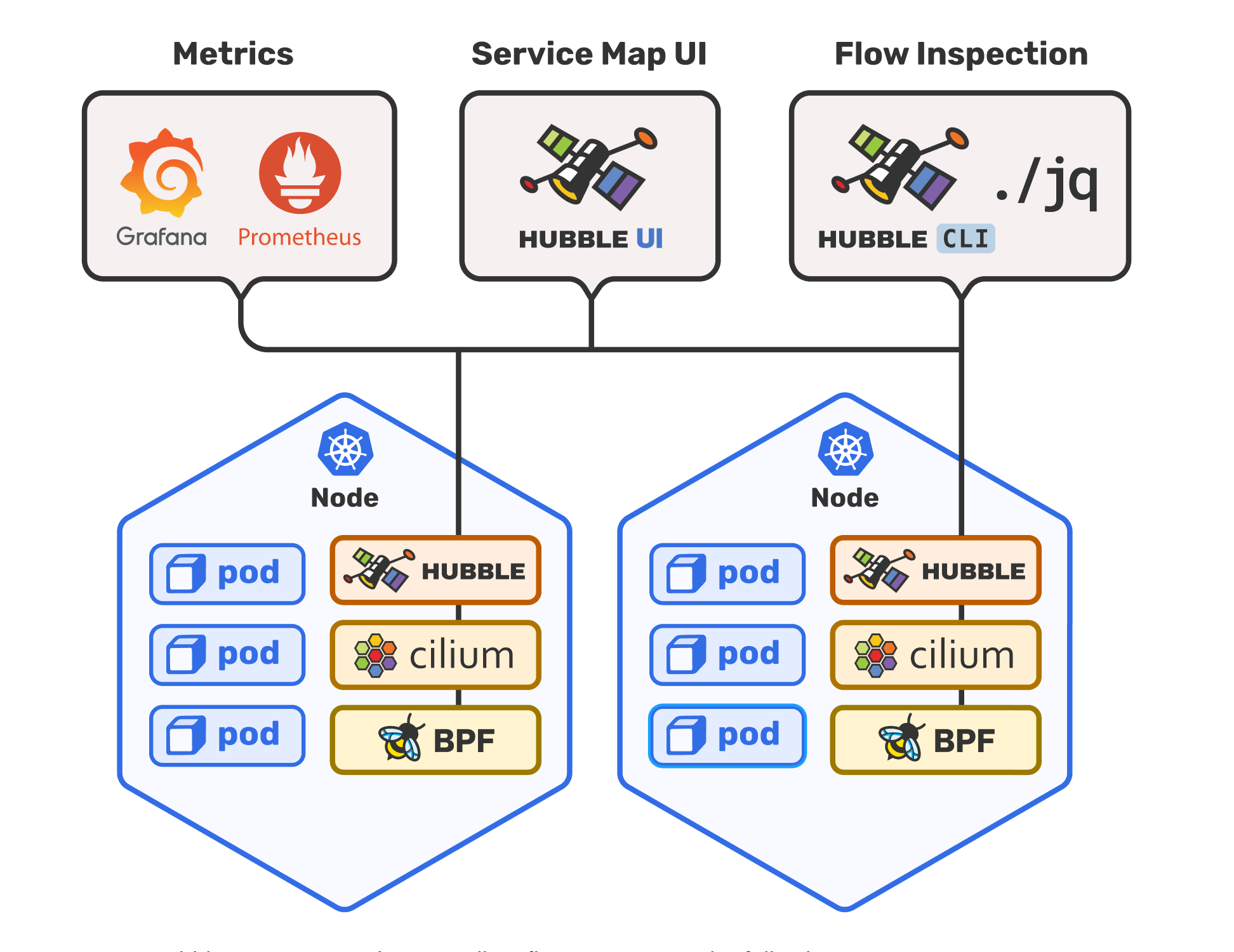
”When you want to control, understand traffic inside your native cloud platform such as Kubernetes” - now you can use eBPF for networking monitoring with Cilium and Hubble to understand Network, Service & Security inside Kubernetes Clusters
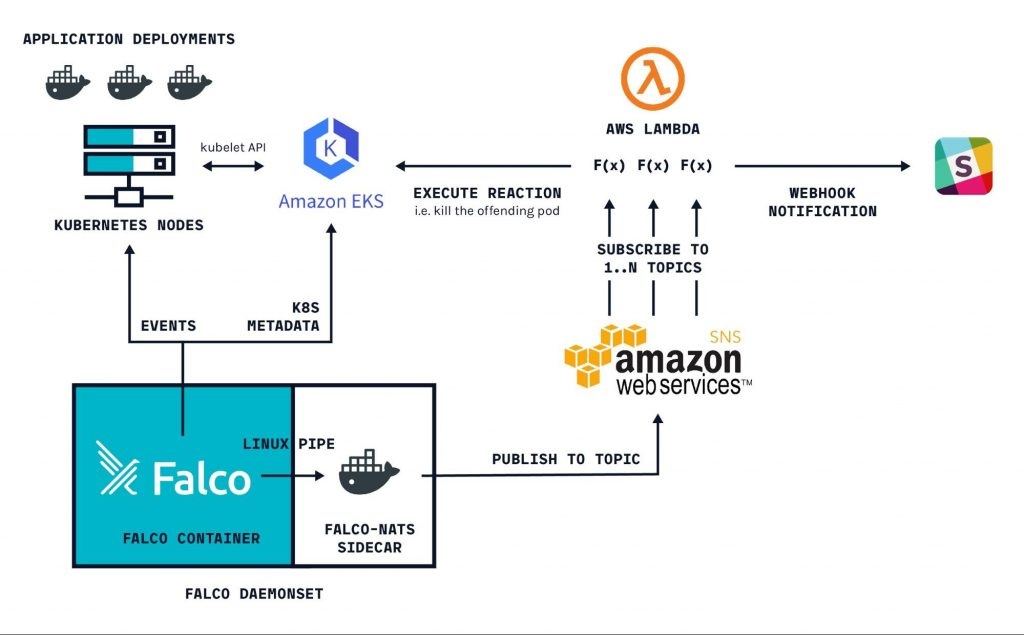
”When you want to enables powerful realtime, eBPF-based Security Observability and Runtime Enforcement, detects and is able to react to security-significant events” - now you can use Tetragon and Falco to handling that stuff
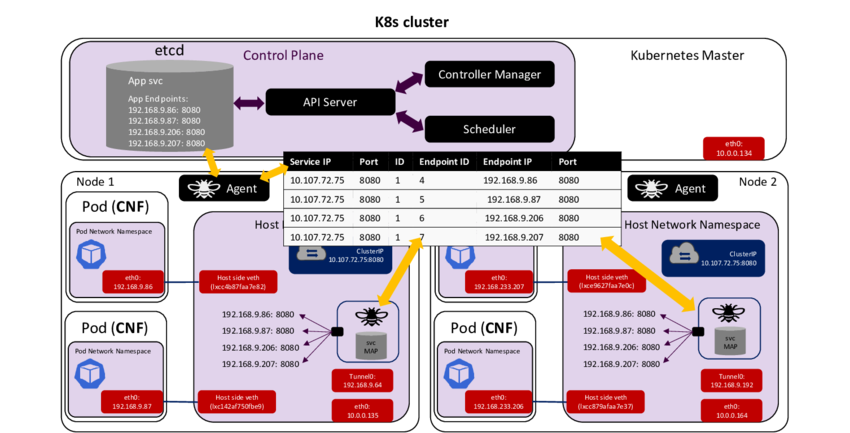
”You want to create and handle huge performance load balancer” - now you can use Cilium to control what happen behind the scene of Load Balancer
You can explore more about eBPF technically and compatible platform for your native cloud services of your
- KodeCloud - eBPF Essentials for DevOps Professionals
- eBPF Applications Landscape
- eBPF Infrastructure Landscape
- Linux Extended BPF (eBPF) Tracing Tools
- awesome-ebpf
- eBPF Docs
Quote
This is why I said
eBPFis growing up and go far way, that become the influence on next time. So why we don’t we learn abouteBPF- easily and shorten way to catch up what is going on in Cloud Native. Inkubewekend, we are figure out that and in this session 4, we will learn aboutciliumandhubble
Cilium

With me cilium is one of most impressed I ever seen, that contain multiple things from networking, service mesh, the methodology how can control and give policy for your connection of pods inside Native Cloud like Kubernetes. It’s a unique and maybe huge platform when you take a look on the technics 🤯. So what is cilium and why I get excited about it
Introduce
Info
Cilium
Cilium is used to provide and transparently secure network connectivity and load balancing between application workloads such as application containers, processes, or VMs. Cilium operates at Layer 3/4 to provide traditional networking and security services as well as Layer 7 to protect and secure use of modern application protocols such as HTTP, gRPC, and Kafka.
Cilium is a part of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation and is their most advanced and widely used CNI for Kubernetes - that is reason why you see me related this one on previous session - Another components
Cilium will become a part of Kubewekend cluster and we will do more practically with this technology inside progress of Kubewekend, so excited 🙌
Info
At the foundation of Cilium is a new Linux kernel technology called eBPF, which enables the dynamic insertion of powerful security visibility and control logic within Linux itself. Because eBPF runs inside the Linux kernel, Cilium security policies can be applied and updated without any changes to the application code or container configuration.
By leveraging Linux eBPF, Cilium retains the ability to doing some interesting things, like
-
Protect and secure APIs transparently - For most of modern application protocols such as REST/HTTP, gRPC and Kafka.
Ciliumplays role like firewall in L3 and L4 of Networking modelling.Ciliumprovides the ability to filter on individual application protocol requests. -
Secure service to service communication based on identities - Assigns a security identity to groups of application containers, provide the methodology to validate the identity at the receiving node for them. (Use key-value store)
-
Secure access to and from external services - Allows to limit access to and from application containers to particular IP ranges.
-
Simple Networking - Easily to IP allocation without any coordination between hosts, supported for Overlay - Encapsulation-based virtual network spanning all hosts or Native Routing: Use of the regular routing table of the Linux host.
-
Load Balancing - Implements distributed load balancing for traffic between application containers and to external services and is able to fully replace components such as kube-proxy. The load balancing is implemented in eBPF using efficient hashtables allowing for almost unlimited scale.
-
Bandwidth Management - Implements bandwidth management through efficient EDT-based (Earliest Departure Time) rate-limiting with eBPF for container traffic that is egressing a node
-
Monitoring and Troubleshooting - Gain visibility and to troubleshoot issues is fundamental to the operation of any distributed system, such as Event monitoring with metadata - Retrieve what packet drop with full metadata, Metrics export via Prometheus - export metrics for Prometheus can be visualization, and use Hubble to deep inspect what is going in Kubernetes via Cilium’s provided
How to Install ?

Quote
Back to previous session, on the session 2, we are successful build and operate our cluster, but if you concern about when you try
kubectlget nodes, the state ofkubewekendcluster is on not ready. It means we don’t enable any CNI (Container Network Interface) inside cluster, check that on Kind Configuration at Session 2. Therefore, we wait to in currently to operate and installciliumtokubewekendcluster
For start this lab, you can explore step at Github - Kubewekend
You can find more information about setup cilium at: Cilium Quick Installation
# Download cilium
wget https://github.com/cilium/cilium-cli/releases/download/v0.16.11/cilium-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# Extract
tar -xzf cilium-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# Install cilium
sudo mv cilium /usr/local/bin/And now you have cilium-cli on your host
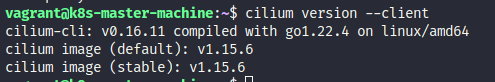
You can install cilium to your cluster via this CLI
# Install cilium to your cluster
cilium install --version 1.15.6
# Validate of cilium after installation
cilium status --wait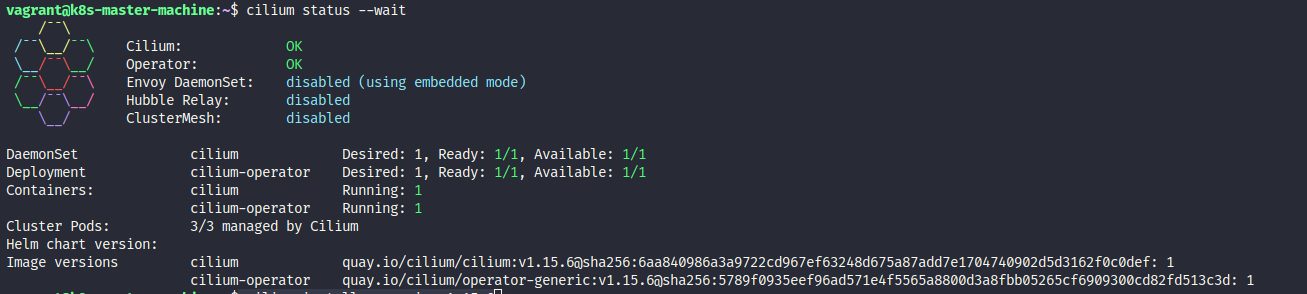
And re-check again your state of node, all pods and node are ready for in-use, before to doing that check make sure you install kubectl if you don’t have buddy
# Install kubectl from official page
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
# Change permission for your kubectl tool
chmod +x kubectl
# Install kubectl to your host
sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin
You can check and validate your state of cluster and pod via get command
kubectl get pods -A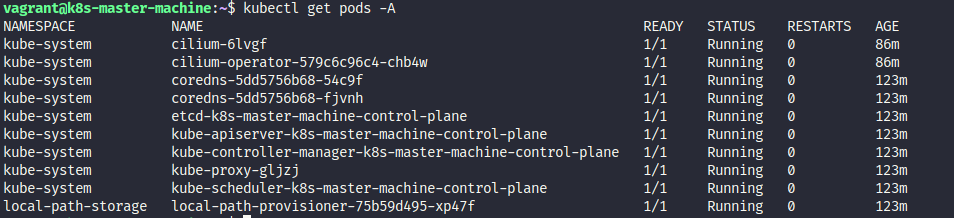
kubectl get nodes
Success
Alright, everything is going same route, BTW we are full completely provision, and you can bring that cluster for your work LOL 😅. Sorry for my joke, but It really its because you have full components inside
kubewekendand so the other session we will try to install extend things inside this cluster and have fun but now we keep moving withciliumand practical with this one.
What can Cilium do?
So We are doing installation cilium to the kubewekend cluster, if you use status command, you can known about status of cilium inside kubewekend cluster, including
cilium-operatorin deploymentsciliumin daemonset
Info
Give you some information about
Operatorin Kubernetes, Operators are software extensions to Kubernetes that make use of custom resources to manage applications and their components. Operators follow Kubernetes principles, notably the control loop.From Operator pattern - kubernetes.io
Info
About
daemonset, this is called type of workload inside Kubernetes Cluster, DaemonSet ensures that all (or some) Nodes run a copy of a Pod. As nodes are added to the cluster, Pods are added to them. As nodes are removed from the cluster, those Pods are garbage collected. Deleting a DaemonSet will clean up the Pods it created.Some typical uses of a DaemonSet are:
- running a cluster storage daemon on every node
- running a logs collection daemon on every node
- running a node monitoring daemon on every node
If you have those one in kubernetes, you can practice around the command cilium to understand what cilium can do for
External cilium pods
You can use --help flag with cilium-cli to see more information
vagrant@k8s-master-machine:~$ cilium --help
CLI to install, manage, & troubleshooting Cilium clusters running Kubernetes.
Cilium is a CNI for Kubernetes to provide secure network connectivity and
load-balancing with excellent visibility using eBPF
Examples:
# Install Cilium in current Kubernetes context
cilium install
# Check status of Cilium
cilium status
# Enable the Hubble observability layer
cilium hubble enable
# Perform a connectivity test
cilium connectivity test
Usage:
cilium [flags]
cilium [command]
Available Commands:
bgp Access to BGP control plane
clustermesh Multi Cluster Management
completion Generate the autocompletion script for the specified shell
config Manage Configuration
connectivity Connectivity troubleshooting
context Display the configuration context
encryption Cilium encryption
help Help about any command
hubble Hubble observability
install Install Cilium in a Kubernetes cluster using Helm
status Display status
sysdump Collects information required to troubleshoot issues with Cilium and Hubble
uninstall Uninstall Cilium using Helm
upgrade Upgrade a Cilium installation a Kubernetes cluster using Helm
version Display detailed version information
Flags:
--context string Kubernetes configuration context
--helm-release-name string Helm release name (default "cilium")
-h, --help help for cilium
-n, --namespace string Namespace Cilium is running in (default "kube-system")
Use "cilium [command] --help" for more information about a command.To setup completion with cilium in your shell, use completion and command into your shell profile, such as zsh or bash
# Use if your profile is bash
echo "source <(cilium completion bash) >> .bashrc"
# Use if your profile is zsh
echo "source <(cilium completion zsh) >> .zshrc"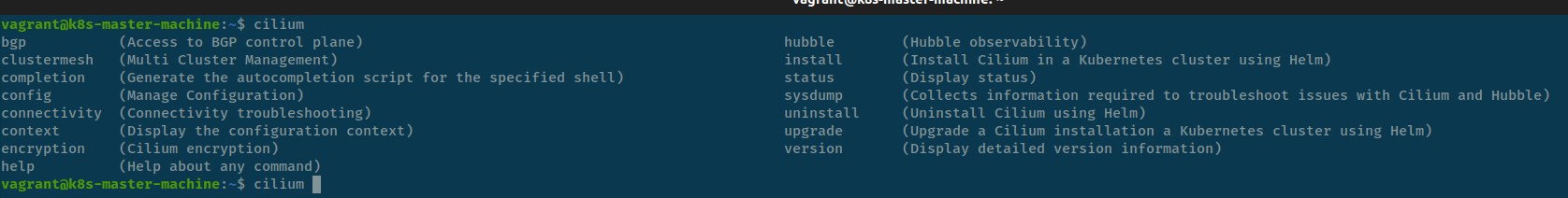
You can check about cilium connectivity access in kubewekend cluster with providing scenarios from cilium via connectivity test
# If you validate connectivity
## Read manual of connectivity test command
cilium connectivity test --help
## Run tests inside cluster
cilium connectivity test
# If you want ti check network performance
## Read manual of connectivity perf command
cilium connectivity perf --help
## Run tests for check network performance
cilium connectivity perf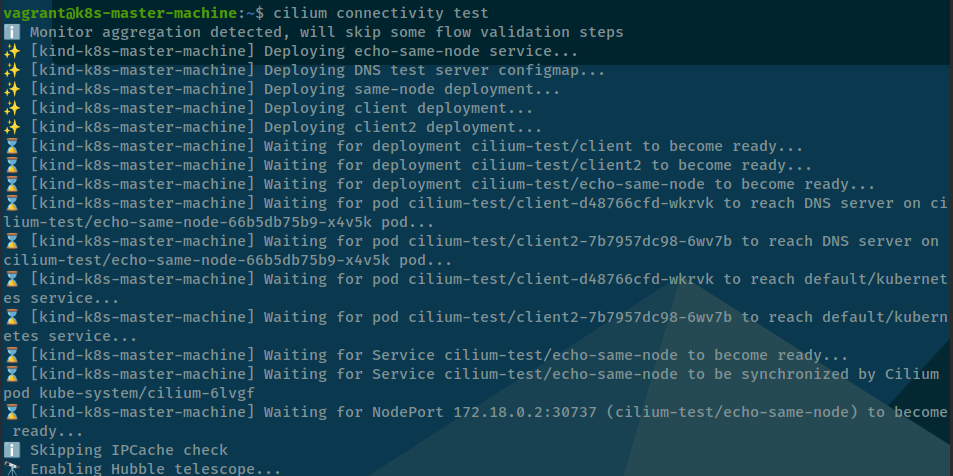
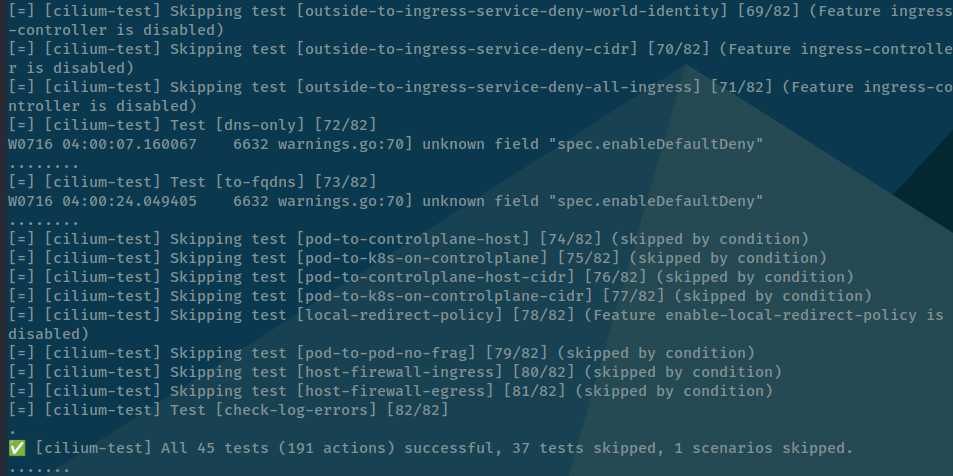
You will have 82 tests scenarios in kubewekend cluster, afterward you will get the result, if not any failure, your cilium work great with cluster
Fun things if you want to check about echo-same-node deployment, you can play with port-forward command inside kubectl and use reverse ssh to check the web-service before we setup cilium to expose service via domain
# Expose your service via localhost
kubectl port-forward -n cilium-test service/echo-same-node 8080:8080
# Because we do not hand-on any network inside `vmbox`, so we will use another way expose this service to your via `ssh-tunneling`
# Documentation: https://www.ssh.com/academy/ssh/tunneling-example
ssh -N -L 8080:127.0.0.1:8080 -i .vagrant/machines/k8s-master-machine/virtualbox/private_key vagrant@127.0.0.1 -p 6996Access your host at http://localhost:8080
Internal cilium pods
Quote
Quite fun a little bit, move on to inside
ciliumand inspect what is going on inside, view all the commands to use inside agent at https://docs.cilium.io/en/latest/cheatsheet/
# Find out the cilium pod
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
# Exec to the cilium pod to inspect more extensions
kubectl exec --tty --stdin -n kube-system cilium-xxxxx -- /bin/bashFirst of all, you run status command to deep inspect about the agent
# Check basic status
cilium status
# Check more about information on all controllers, health and redirects
cilium status --all-controllers --all-health --all-redirects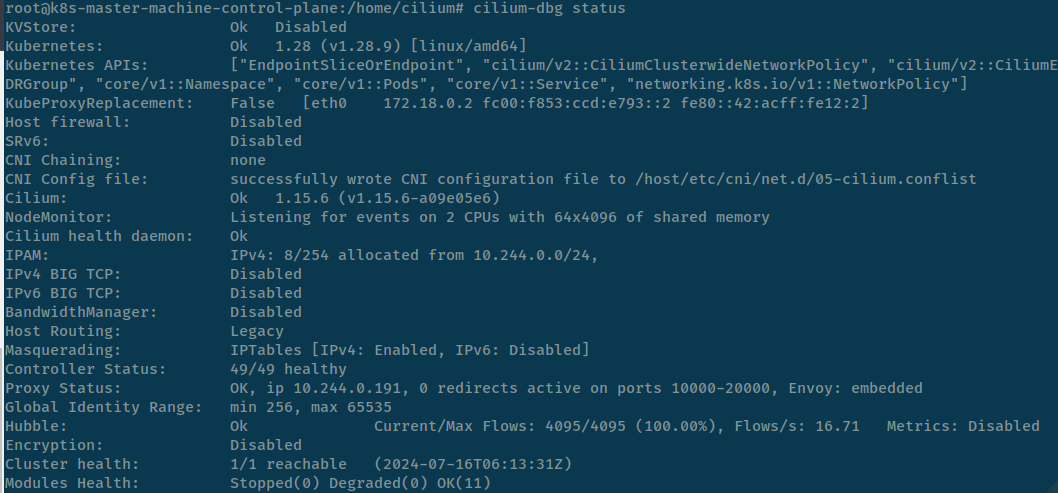
Get current agent configuration
# Check configuration in basic
cilium config
# View all configuration of agent
cilium config --all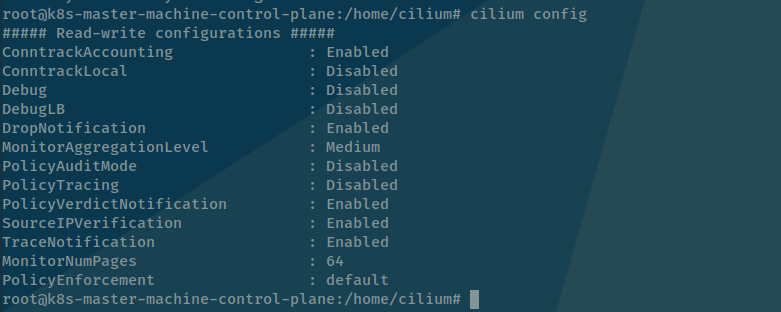
Run a monitoring to capture all traffic like tcpdump inside cluster, with monitor command
# All Traffic monitoring
cilium monitor
# Monitoring with verbose version
cilium monitor -v
# Monitoring with only L7
cilium monitor -t l7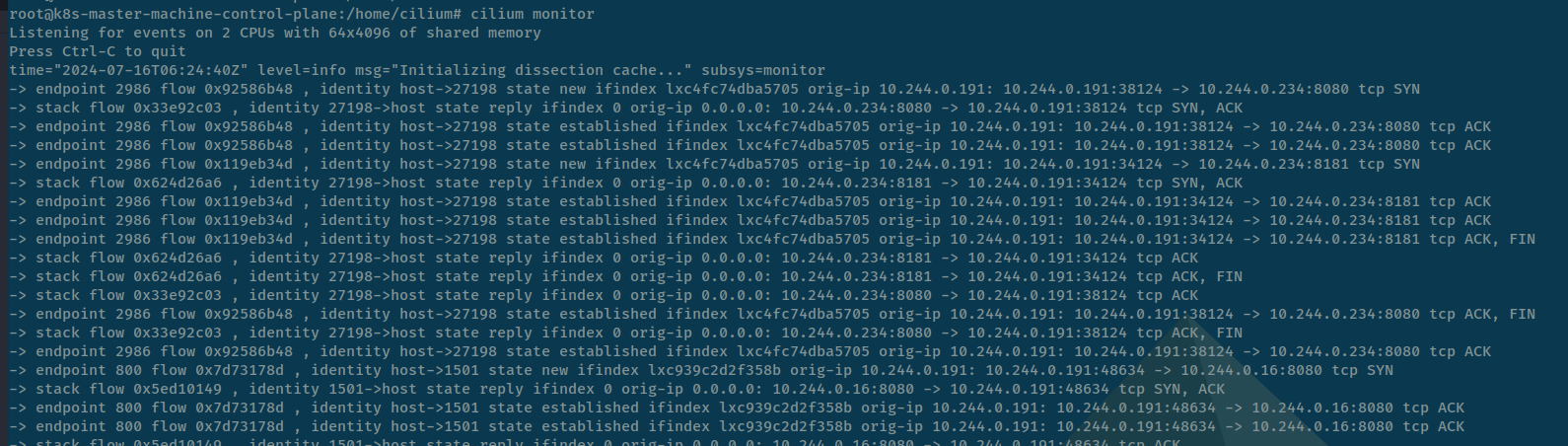
Move on to check about service to view all loadbalancer services inside cluster
# View all services routing
cilium service list
# View specific services routing
cilium service get <id> -o json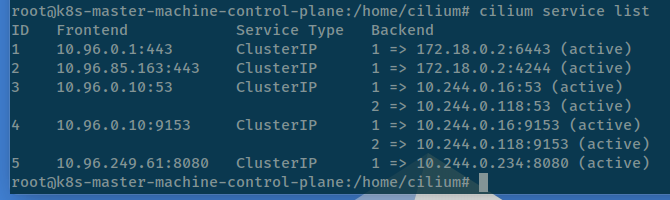
Info
If you can see in service list, you can understand what is going on about networking map of all services inside Kubernetes cluster, metadata from IP, Type of service and if you do more inspect with specific you can see more information about
servicesin network landscape
More over you can see about bpf level of load balancer
cilium bpf lb listBut we don see anything because we do not operate any load balancer configuration, this stuff we will be considered on session when operate the application, don’t worry 😄
In the last one, we will try to see the endpoint inside cluster is useful optional in cilium
# Get list of all local endpoints
cilium endpoint list
# Get detailed view of endpoint properties and state
cilium endpoint get <id>
# Show recent endpoint specific log entries
cilium endpoint log <id>
# Turn on or off debug in monitor of target endpoint
cilium endpoint config <id> Debug=true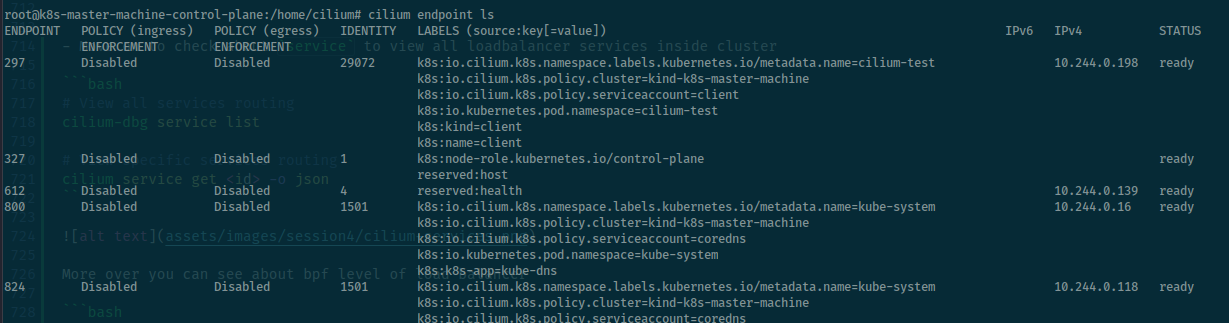
Quote
ciliumis more powerful, but if i list all, we will make this session become boring. So if you want to explore more features, check out at: https://docs.cilium.io/en/latest/cmdref/
Success
We practice with
CLIto much, and I know some persons are not familiar with this and can be annoyed. Therefore, we stopciliumand explore more in others session becausekubewekendis still long LOL. Moving on the another sub-project ofciliumishubbleandhubbleUIto see how the networking inside Kubewekend operate
Hubble
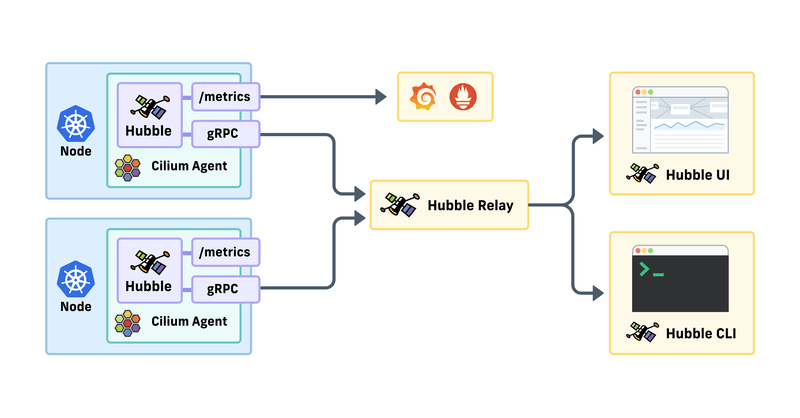
Moving to introduce part to understand what is hubble and figure out what hubble can do inside Kubewekend, before start you can double check at Documentation
Introduce
Info
Hubble
A fully distributed networking and security observability platform. It is built on top of Cilium and eBPF to enable deep visibility into the communication and behavior of services as well as the networking infrastructure in a completely transparent manner.
By building on top of Cilium, Hubble can leverage eBPF for visibility, such as
-
Service dependencies & communication map - Monitoring about communication between services, frequently, service dependency graph look like, HTTP call look like and with Kafka you can understand topics comsume from or produce to
-
Network monitoring & alerting - Monitoring about any network communication failing, Why is communication failing and help us figure out problems, deep inspect about DNS, TCP and packet request inside TCP handshake like ACK SYN or what ever
-
Application monitoring - Provide the rate of 5xx or 4xx HTTP response codes for a particular service or across all clusters, the 95th and 99th percentile latency between HTTP requests and responses in my cluster, which services are performing worst ? What is the latency between two services ?
-
Security observability - Monitoring about any connections blocked by network policies, any services access from outside cluster and understand services have resolved a particular DNS name
Info
Like the introduce from official homepage of
cilium, I recommend you to watch eCHO episode 2: Introduction to Hubble to explore about Hubble and understand about this one
Now we will move to practice with Hubble and see what do service can do, alright !!
How to install
Back to Kubewekend cluster, you need return shell of vagrant host to continue enable hubble via cilium-cli
cilium hubble enableAnd now use status to see if hubble run or not
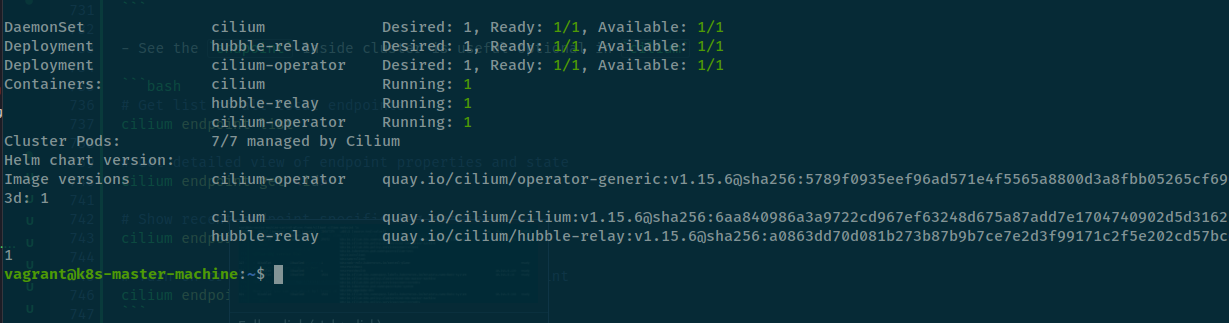
With hubble enable, kubewekend cluster will add a new thing run as deployment hubble-relay. But your version is deploy will not have any accesable, you need install add-on like hubble-client and hubble-ui to more visualize about hubble.
Info
In the general architecture, Hubble exposes gRPC services from the Cilium process that allows clients to receive flows and other type of data.
When we try to enable hubble with cilium, we will have hubble-relay, what is this service meaning? Explore at: Hubble internals
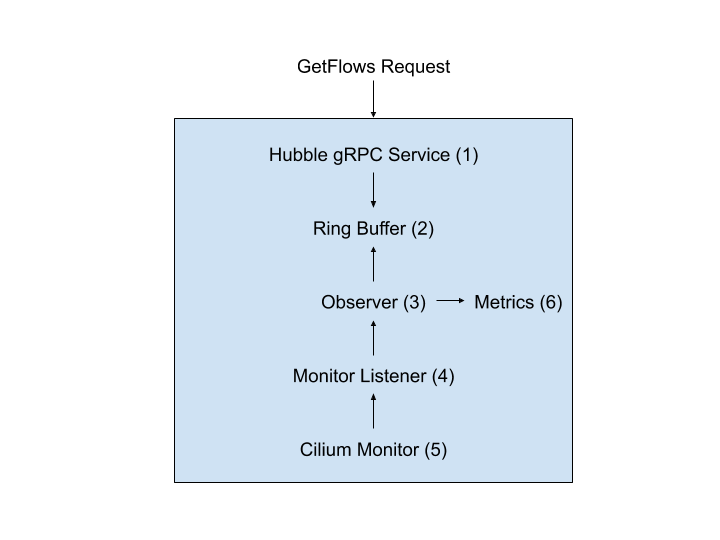
In Hubble will exist two components, following Hubble internals - cilium.io
- Hubble Server: The server will implement two gRPC services. The Observer service which may optionally be exposed via a TCP socket in addition to a local Unix domain socket and the Peer service, which is served on both as well as being exposed as a Kubernetes Service when enabled via TCP.
- Hubble Relay: The Hubble component that brings multi-node support. It leverages the Peer service to obtain information about Hubble instances and consume their gRPC API in order to provide a more rich API that covers events from across the entire cluster
Now when hubble-relay we need install hubble-server by hubble-client, and to installing that one you need use few command to download and setup that for your vagrant host
HUBBLE_VERSION=$(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/hubble/master/stable.txt)
HUBBLE_ARCH=amd64
if [ "$(uname -m)" = "aarch64" ]; then HUBBLE_ARCH=arm64; fi
curl -L --fail --remote-name-all https://github.com/cilium/hubble/releases/download/$HUBBLE_VERSION/hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}
sha256sum --check hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256sum
sudo tar xzvfC hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz /usr/local/bin
rm hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}Now validate the hubble API Access
What can Hubble do?
Note
In order to access the Hubble API, create a port forward to the Hubble service from your local machine. This will allow you to connect the Hubble client to the local port 4245 and access the Hubble Relay service in your Kubernetes cluster.
# Use via cilium
cilium hubble port-forward
# use via kubectl
kubectl port-forward -n kube-system service/hubble-relay 4245:80And lastly, you can view status and observe via hubble
# View status
hubble status
# Observe API
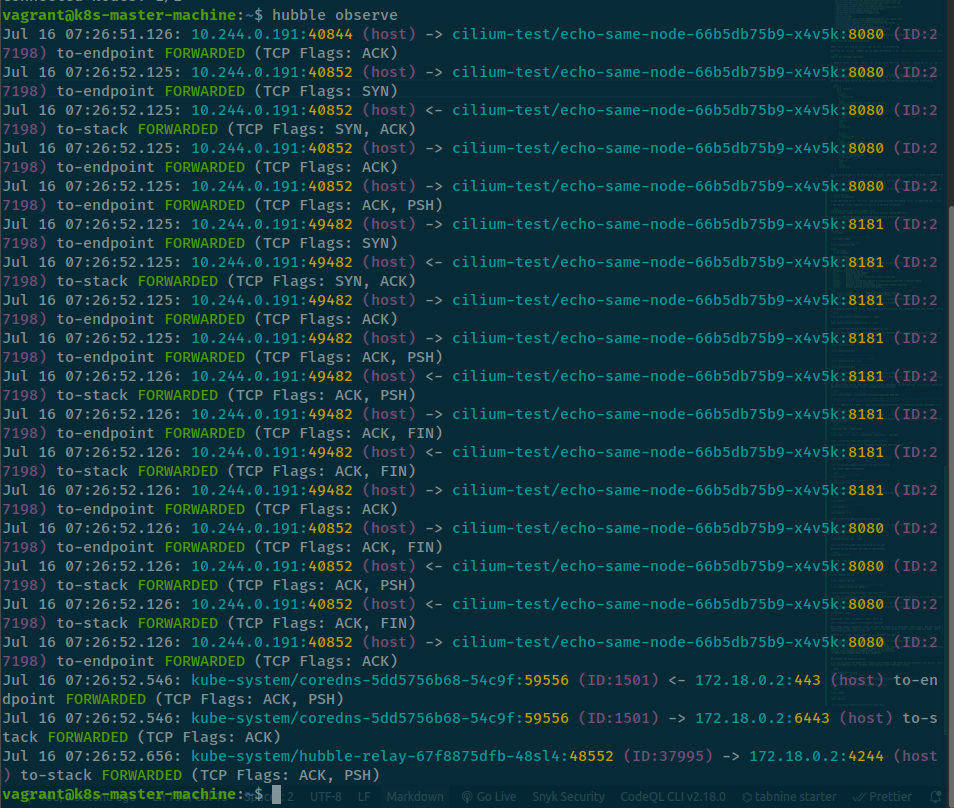
hubble observeHubble Status
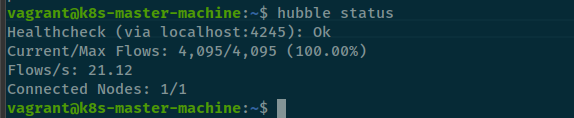
Hubble observe
Info
Like you run
tcpdumpinside thekubernetesand collect all of thing inside, but one question put in here, does that insecure or secure for monitoring?
Following, we try to use hubble to inspect and figure out what inside kubernetes, so if you follow the eCHO episode 2: Introduction to Hubble
- You can see the all request from L7 like HTTP, DNS and moreover like Kafka and header or request actually still there, so that why Hubble is running inside
clusterinstead like service. - Therefore, you need have
kubernetesconfiguration to connect and installhubbleinside yourkubernetescluster. - Honestly, secure or insecure base on your decision, in my perspective,
hubbledo great and right target purpose, so consider when try to enable Hubble and use Hubble to doing same thing, for prevent GDPA I not sure about that
Quote
But we are practitioner, and we try and failure that why we stand there learn about new technologies. If you find more about GDPA, maybe I don’t make sure anything be secure on
kubewekendcluster that why we will find and figure out in this series
Now we are reaching to web-ui part, which one can make hubble become special for some cases. Try this command to enable ui
cilium hubble enable --uiWait for a minute, and use status command with cilium to view your ui is enabling
Use port-forward to expose web-ui to your localhost
# Use via cilium
cilium hubble ui
# Use port-foward of kubectl instead
kubectl port-forward -n kube-system service/hubble-ui 12000:80You will hard to connect to vagrant host if you not attacked to vmbox, so instead of I use ssh-tunnel to connect hubble-ui
ssh -N -L 12000:127.0.0.1:12000 -i .vagrant/machines/k8s-master-machine/virtualbox/private_key vagrant@127.0.0.1 -p 6996Now you can access http://localhost:12000 to view web-ui of hubble
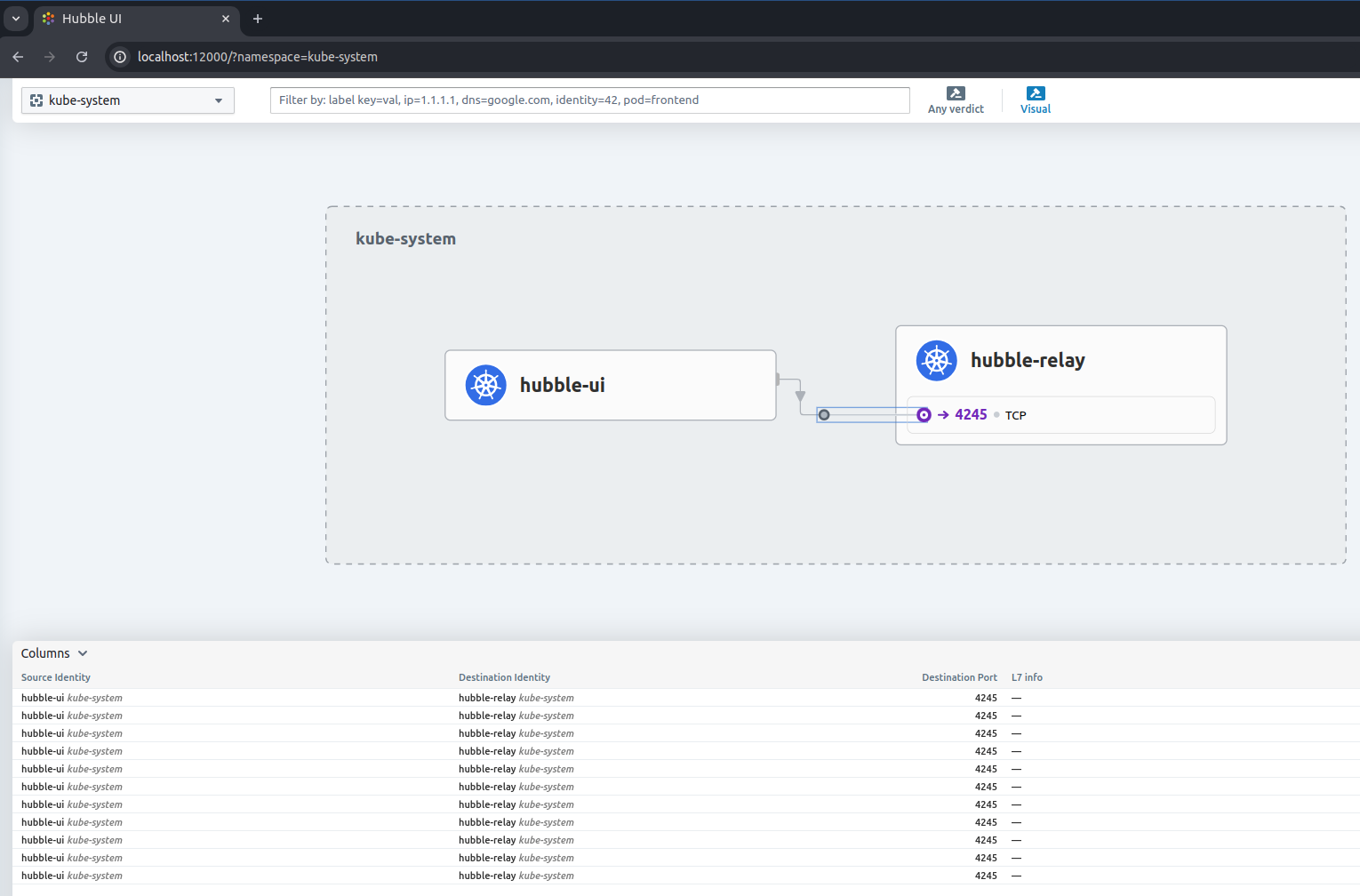
Inspect real time with example when use connectivity scenarios
while true; do cilium connectivity test; done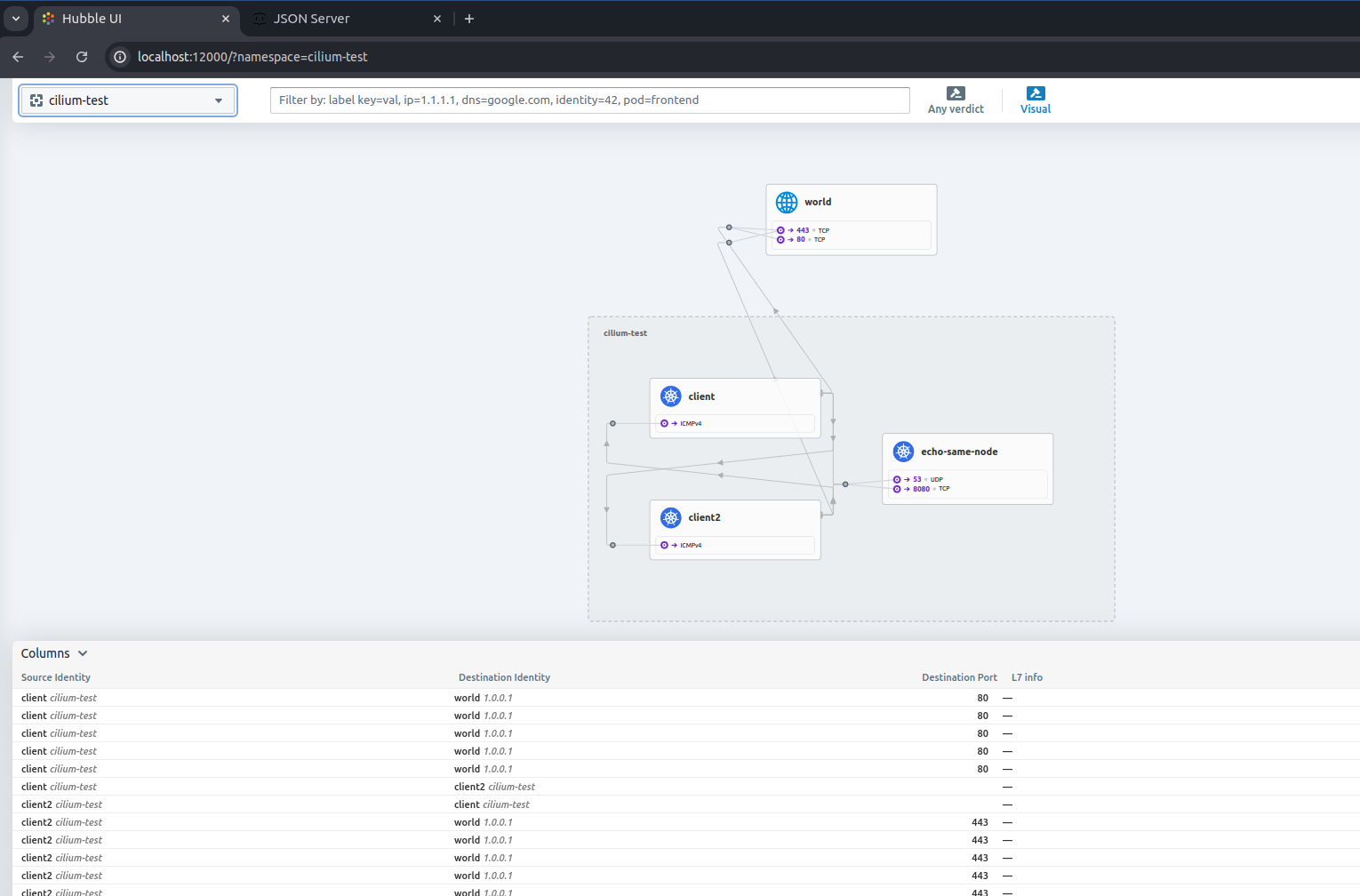
Success
If you can see, all of traffic what route path and communication between of them is exposing, that visualization can make you more understand of your cluster and what is going on inside, and lastly It’s totally free.
Quote
And when you want to find the alternative but cost a little, go check about kubeshark - API Traffic Analyzer, not equally
hubblebut contain some feature can be used and really supper cool 🥶 BTW. But trust me,hubbledo incredible things and quite fun a lots, awesome technics
Conclusion
Success
This is @all for this weekend, hope you find well with my contents and drop me idea on my email if you want figure out some thing. Happier to share with you about
eBPFwhat technology is cherished and researched for a long time to be able to share, and do more especially withciliumandhubble, those things will become the new wind on native-cloud and create a place in the community, honestly I believe
Quote
So give thankful and appreciate for
eBPF,BPF,Isovalent,CiliumandHubbleto bring pleasant technology, huge community and do lot of funs thing inside the Kubernetes. And give warmful for my viewers who to catch my contents. And one again, stay safe and learn more things, I will see you as soon as next the weekend. Bye Bye @all 🙌🙌