Azure Storage
Documentation:
Info
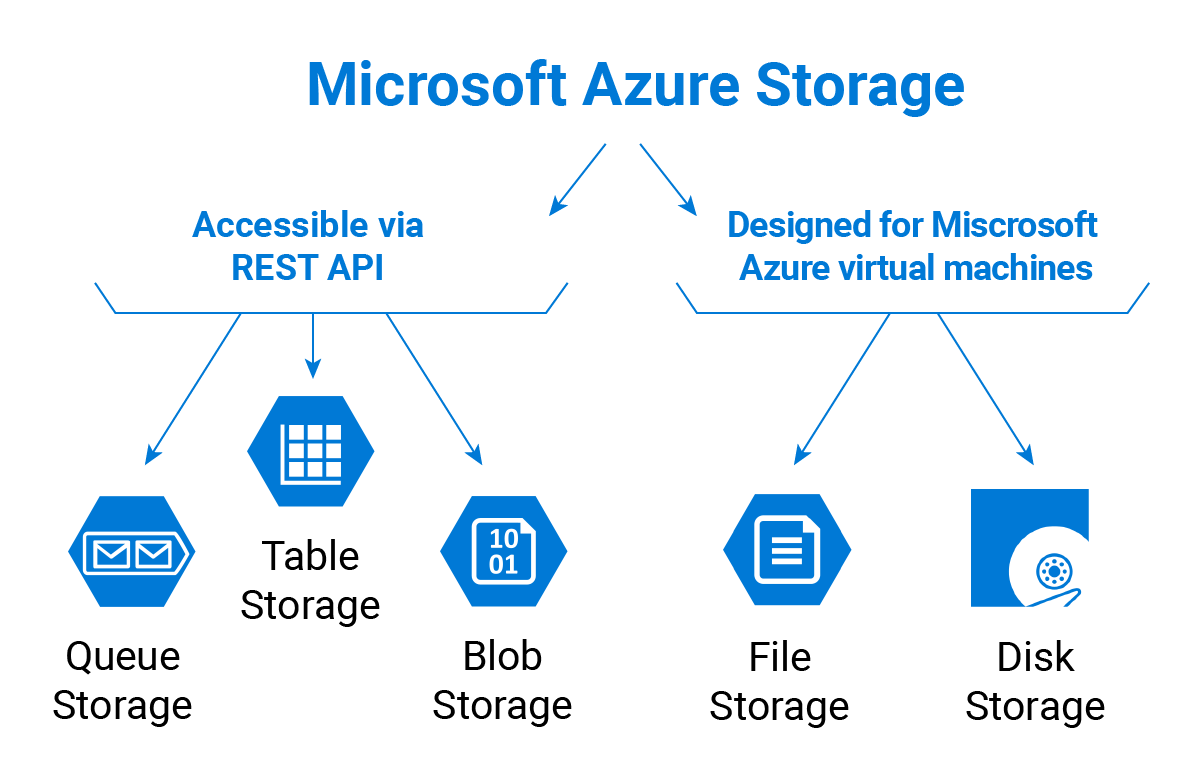
Azure Storage is Microsoft’s cloud storage solution for modern data storage scenarios. Azure Storage offers a massively scalable object store for data objects
Types of storage are used in your organization
- Virtual machine data : Includes
disksandfiles. Disks are persistent block storage for Azure IaaS virtual machines. Files are fully managed file shares in the cloud. - Unstructured data : Not have a clear relationship. The format of unstructured data is referred to as nonrelational. Includes
Azure Blob StorageandAzure Data Lake Storage, Blob Storage is a highly scalable, REST-based cloud object store, Data Lake is the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) as a service. - Structured data : Stored in a relational format that has a shared schema. Includes
Azure Table Storage, Azure Cosmos DB, and Azure SQL Database
Storage tiers
- Standard storage accounts are backed by magnetic hard disk drives (HDD). A standard storage account provides the lowest cost per GB.
- Premium storage accounts are backed by solid-state drives (SSD) and offer consistent low-latency performance.
Note
You can change between Standard and Premium or vice versa. Must be create and move data to new one
Storage Service
Documentation: Explore Azure Storage services
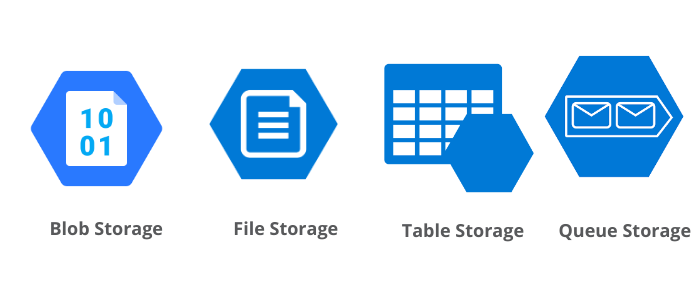
Azure Storage offers four data services by using an Azure storage account:
- Azure Blob Storage (containers): A massively scalable object store for text and binary data.
- Azure Files: Managed file shares for cloud or on-premises deployments.
- Azure Queue Storage: A messaging store for reliable messaging between application components.
- Azure Table Storage: A service that stores nonrelational structured data (also known as structured NoSQL data).
Blob Container
Info
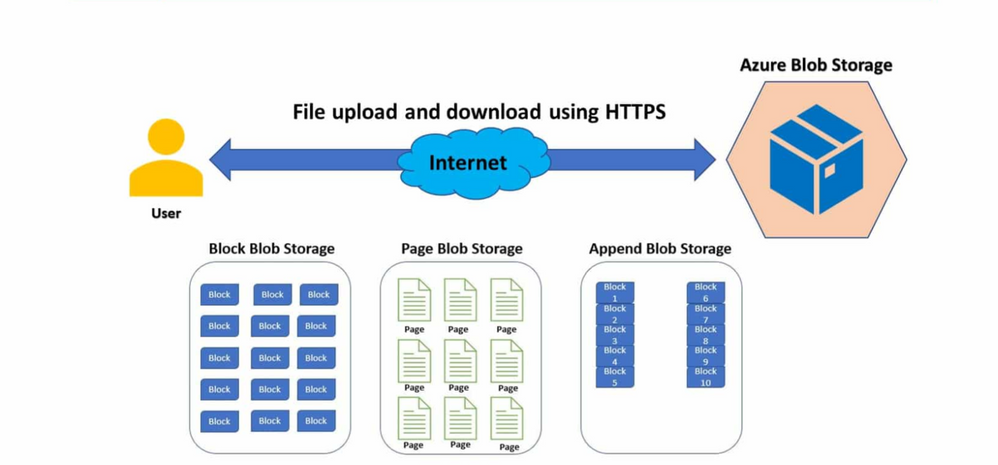
Blob Storage is Microsoft’s object storage solution for the cloud. Blob Storage is optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured or nonrelational data, such as text or binary data.
Usage:
- Serving images or documents directly to a browser.
- Storing files for distributed access.
- Streaming video and audio.
- Storing data for backup and restore, disaster recovery, and archiving.
- Storing data for analysis by an on-premises or Azure-hosted service.
Can be access via HTTP/HTTPS with support multiple language, REST API, Portal, Az-CLI, … Others, you can access blob via NFS protocol
Configuration characteristics of containers and blobs.
- All blobs must be in a container.
- A container can store an unlimited number of blobs.
- An Azure storage account can contain an unlimited number of containers.
- You can create the container in the Azure portal.
- You upload blobs into a container.
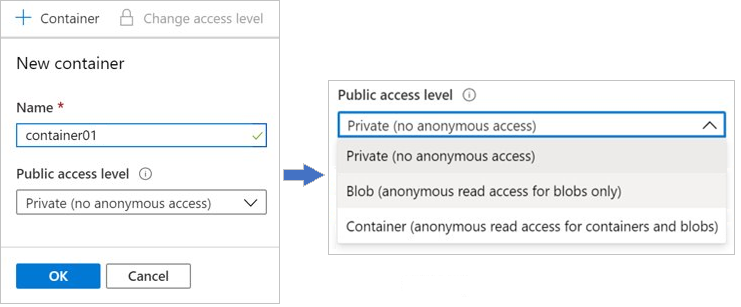
-
Name: Enter a name for your container. The name must be unique within the Azure storage account.
- The name can contain only lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens.
- The name must begin with a letter or a number.
- The minimum length for the name is three characters.
- The maximum length for the name is 63 characters.
-
Public access level: The access level specifies whether the container and its blobs can be accessed publicly. By default, container data is private and visible only to the account owner. There are three access level choices:
- Private: (Default) Prohibit anonymous access to the container and blobs.
- Blob: Allow anonymous public read access for the blobs only.
- Container: Allow anonymous public read and list access to the entire container, including the blobs.
Note
Create a blob container with PowerShell by using the
New-AzStorageContainercommand.
More about Blob Container
- blob access tiers with 4 type
Hot Cool Cold Archive - Add blob lifecycle management rules
- Determine blob object replication
- Upload blobs
- Determine Blob Storage pricing
Azure Files
Info
Azure files is highly available network file shares. You can access this storage via SMB (Server Message Block) Protocol or NFS Protocol. Others way, you can read the files with REST API or SDK
Usage:
- Many on-premises applications use file shares. This feature makes it easier to migrate those applications that share data to Azure.
- Configuration files can be stored on a file share and accessed from multiple virtual machines
- Diagnostic logs, metrics, and crash dumps can be written and processed or analyzed later
More about Azure File
- Manage Azure file shares
- Create file share snapshots
- Implement soft delete for Azure Files
- Use Azure Storage Explorer
- Deploy Azure File Sync
Azure Queue Storage
Info
Azure Queue Storage is used to store and retrieve messages. Queue messages can be up to 64 KB in size, and a queue can contain millions of messages. Queues are used to store lists of messages to be processed asynchronously.
Azure Table Storage
Info
Azure Table storage is a service that stores non-relational structured data (also known as structured NoSQL data) in the cloud, providing a key/attribute store with a schemaless design.
Storage Account
Has 4 tiers for choose and apply
- Standard general-purpose v2 : Support with 4 data services, Standard storage account for most scenarios
- Premium block blobs : Only for Blob Storage, Offer solution for high transaction rates, low storage latency, smaller objects and scalable with application
- Premium file shares : Only for File Storage, Use for enterprise or high-performance applications, requires both SMB and NFS
- Premium page blobs : Only Page blobs, Page blobs are ideal for storing index-based and sparse data structures, such as operating systems, data disks for virtual machines, and databases.
Replication strategies
Documentation:
We explore four replication strategies:
- Locally redundant storage (LRS)
- Zone redundant storage (ZRS)
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
- Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS)
| Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Locally redundant storage |  Lowest-cost replication option and offers the least durability compared to other strategies. If data-centers is not working, all data will not working, lost or unrecoverable. Usase: - Easily reconstructed if data loss occurs - Constantly changing like in a live feed, and storing the data isn’t essential. - Restricted to replicating data only within a country/region due to data governance requirements. |
| Zone redundant storage |  Synchronously replicates your data across three storage clusters in a single region. Each storage cluster is physically separated from the others and resides in its own availability zone. ZRS ensures you can access and manage your data if a zone becomes unavailable. ZRS provides excellent performance and low latency. |
| Geo-redundant storage | 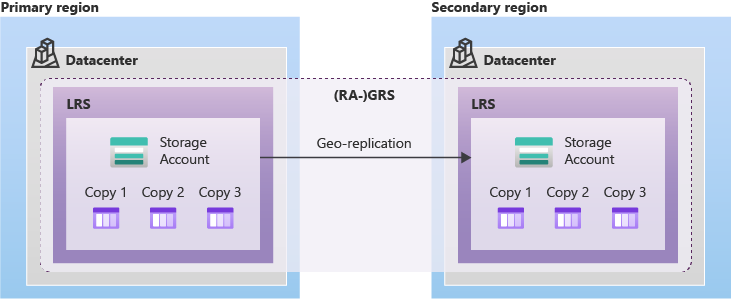 Replicates your data to a secondary region. There are two options for choosing - GRS replicates your data to another data center in a secondary region. The data is available to be read only if Microsoft initiates a failover from the primary to secondary region. - Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS), replicates your data to another data center in a secondary region, and also provides you with the option to read from the secondary region Both Data in First and Second will replicate with LRS and update data from first to second by asynchronously |
| Geo-zone redundant storage | 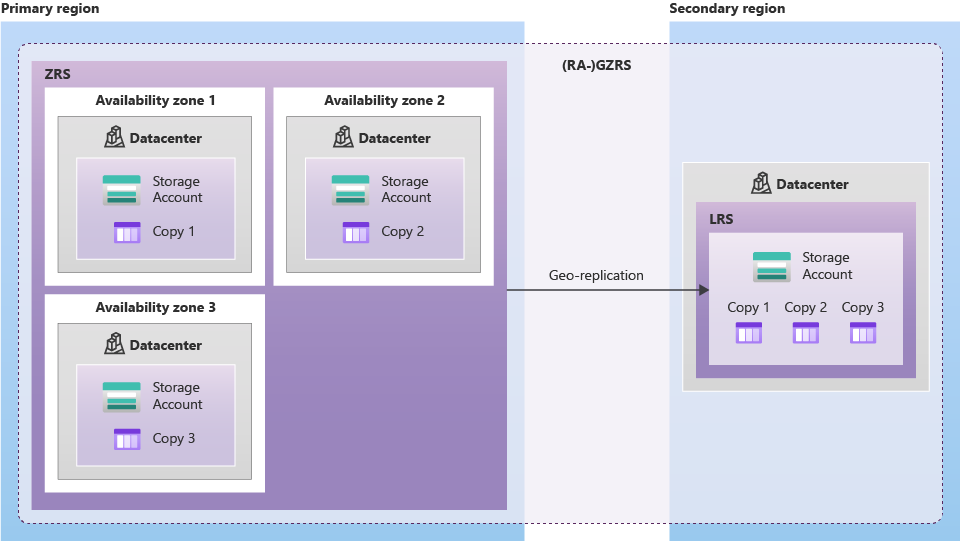 Combines the high availability of zone-redundant storage with protection from regional outages as provided by geo-redundant storage, you can continue to read and write data if an availability zone becomes unavailable or is unrecoverable |
When choosing replication strategies
| Node in data center unavailable | Entire data center unavailable | Region-wide outage | Read access during region-wide outage |
|---|---|---|---|
| - LRS - ZRS - GRS - RA-GRS - GZRS - RA-GZRS | - ZRS - GRS - RA-GRS - GZRS - RA-GZRS | - GRS - RA-GRS - GZRS - RA-GZRS | - RA-GRS - RA-GZRS |
Access storage
Documentation:
Info
Every object you store in Azure Storage has a unique URL address. Your storage account name forms the subdomain portion of the URL address. The combination of the subdomain and the domain name, which is specific to each service, forms an endpoint for your storage account.
| Service | Default endpoint |
|---|---|
| Container service | //mystorageaccount.blob.core.windows.net |
| Table service | //mystorageaccount.table.core.windows.net |
| Queue service | //mystorageaccount.queue.core.windows.net |
| File service | //mystorageaccount.file.core.windows.net |
| You can configure for customize your storage account domain, with two way |
- Direct mapping lets you enable a custom domain for a subdomain to an Azure storage account. For this approach, you create a
CNAMErecord that points from the subdomain to the Azure storage account. - Intermediary domain mapping is applied to a domain that’s already in use within Azure. This approach might result in minor downtime while the domain is being mapped.
For secure, you can apply some method for protect your storage account like Firewall, virtual network or disable. And you need to know before configuration that
- The Firewalls and virtual networks settings restrict access to your storage account from specific subnets on virtual networks or public IPs.
- You can configure the service to allow access to one or more public IP ranges.
- Subnets and virtual networks must exist in the same Azure region or region pair as your storage account.
Security strategies
Documentation:
Let’s look at some characteristics of Azure Storage security.
- Encryption. All data written to Azure Storage is automatically encrypted by using Azure Storage encryption.
- Authentication. Microsoft Entra ID and role-based access control (RBAC) are supported for Azure Storage for both resource management operations and data operations.
- Assign RBAC roles scoped to an Azure storage account to security principals, and use Microsoft Entra ID to authorize resource management operations like key management.
- Microsoft Entra integration is supported for data operations on Azure Blob Storage and Azure Queue Storage.
- Data in transit. Data can be secured in transit between an application and Azure by using Client-Side Encryption, HTTPS, or SMB 3.0.
- Disk encryption. Operating system disks and data disks used by Azure Virtual Machines can be encrypted by using Azure Disk Encryption.
- Shared access signatures. Delegated access to the data objects in Azure Storage can be granted by using a shared access signature (SAS).
- Authorization. Every request made against a secured resource in Blob Storage, Azure Files, Queue Storage, or Azure Cosmos DB (Azure Table Storage) must be authorized. Authorization ensures that resources in your storage account are accessible only when you want them to be, and to only those users or applications whom you grant access.
| Authorization strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Entra ID | Microsoft Entra ID is Microsoft’s cloud-based identity and access management service. With Microsoft Entra ID, you can assign fine-grained access to users, groups, or applications by using role-based access control. |
| Shared Key | Shared Key authorization relies on your Azure storage account access keys and other parameters to produce an encrypted signature string. The string is passed on the request in the Authorization header. |
| Shared access signatures | A SAS delegates access to a particular resource in your Azure storage account with specified permissions and for a specified time interval. |
| Anonymous access to containers and blobs | You can optionally make blob resources public at the container or blob level. A public container or blob is accessible to any user for anonymous read access. Read requests to public containers and blobs don’t require authorization. |
SAS Token

Info
A shared access signature (SAS) is a uniform resource identifier (URI) that grants restricted access rights to Azure Storage resources. SAS is a secure way to share your storage resources without compromising your account keys.
Characteristics of a SAS.
-
A SAS gives you granular control over the type of access you grant to clients who have the SAS.
-
An account-level SAS can delegate access to multiple Azure Storage services, such as blobs, files, queues, and tables.
-
You can specify the time interval for which a SAS is valid, including the start time and the expiration time.
-
You specify the permissions granted by the SAS. A SAS for a blob might grant read and write permissions to that blob, but not delete permissions.
-
SAS provides account-level and service-level control.
- Account-level SAS delegates access to resources in one or more Azure Storage services.
- Service-level SAS delegates access to a resource in only one Azure Storage service.
-
There are optional SAS configuration settings:
-
IP addresses. You can identify an IP address or range of IP addresses from which Azure Storage accepts the SAS. Configure this option to specify a range of IP addresses that belong to your organization.
-
Protocols. You can specify the protocol over which Azure Storage accepts the SAS. Configure this option to restrict access to clients by using HTTPS.
-
NOTE: WHEN CREATE SAS NEED TO PROVIDE

More about security for Azure Storage
- Determine Azure Storage encryption
- Create customer-managed keys
- Apply Azure Storage security best practices
Note
The lifecycle management feature is available in all Azure regions for general purpose v2 (GPv2) accounts, blob storage accounts, premium block blobs storage accounts, and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 accounts.