What is content discovery?
- Content can be many things, a file, video, picture, backup, a website feature.
- When we talk about content discovery, we’re not talking about the obvious things we can see on a website; it’s the things that aren’t immediately presented to us and that weren’t always intended for public access.
- This content could be, for example, pages or portals intended for staff usage, older versions of the website, backup files, configuration files, administration panels, etc.
- There are three main ways of discovering content on a website which we’ll cover. Manually, Automated and OSINT (Open-Source Intelligence).
Manual Discovery - Robots.txt
- Robots.txt: The robots.txt file is a document that tells search engines which pages they are and aren’t allowed to show on their search engine results or ban specific search engines from crawling the website altogether.
- It can be common practice to restrict certain website areas so they aren’t displayed in search engine results. These pages may be areas such as administration portals or files meant for the website’s customers. This file gives us a great list of locations on the website that the owners don’t want us to discover as penetration testers.
QUIZ: Access the website via IP address and get disallow result: /staff-portal
Manual Discovery - Favicon
- Favicon: The favicon is a small icon displayed in the browser’s address bar or tab used for branding a website.
- Sometimes when frameworks are used to build a website, a favicon that is part of the installation gets leftover, and if the website developer doesn’t replace this with a custom one, this can give us a clue on what framework is in use.
- OWASP host a database of common framework icons icon_framework
Once we know the framework stack, we can use external resources to discover more about it
QUIZ: Do step by step like manual and get the flagvicon: f276b19aabcb4ae8cda4d22625c6735f ⇒ cgiirc
Manual Discovery - Sitemap.xml
- Sitemap.xml : Unlike the robots.txt file, which restricts what search engine crawlers can look at, the sitemap.xml file gives a list of every file the website owner wishes to be listed on a search engine.
- These can sometimes contain areas of the website that are a bit more difficult to navigate to or even list some old webpages that the current site no longer uses but are still working behind the scenes.
QUIZ: What is the path of the secret area that can be found in the sitemap.xml file? /s3cr3t-area
Manual Discovery - HTTP Headers
HTTP Headers: When we make requests to the web server, the server returns various HTTP headers. These headers can sometimes contain useful information such as the webserver software and possibly the programming/scripting language in use.
QUIZ: What is the flag value from the X-FLAG header? Do comment: curl http://MACHINE_IP -v ⇒ THM{HEADER_FLAG}
Manual Discovery - Framework Stack
Framework Stack: Once you’ve established the framework of a website, either from the above favicon example or by looking for clues in the page source such as comments, copyright notices or credits, you can then locate the framework’s website. From this we can discover something cool about the websites.
QUIZ: What is the flag from the framework’s administration portal? THM{CHANGE_DEFAULT_CREDENTIALS}
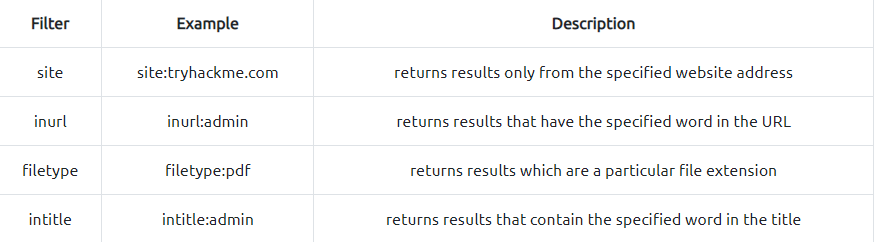
OSINT - Google Hacking / Dorking
Google Hacking / Dorking: utilizes Google’s advanced search engine features, which allow you to pick out custom content. You can, for instance, pick out results from a certain domain name using the site: filter
Have look common filter for dorking and you can access documentation for get more information about dorking
OSINT - Wappalyzer
Wappalyzer is an online tool and browser extension that helps identify what technologies a website uses, such as frameworks, Content Management Systems (CMS), payment processors and much more, and it can even find version numbers as well.
OSINT - Wayback Machine
Wayback Machine is a historical archive of websites that dates back to the late 90s. You can search a domain name, and it will show you all the times the service scraped the web page and saved the contents. This service can help uncover old pages that may still be active on the current website.
OSINT - GitHub
Nothing to say, the best way to search anything
OSINT - S3 Buckets
S3 Buckets are a storage service provided by Amazon AWS, allowing people to save files and even static website content in the cloud accessible over HTTP and HTTPS. The owner of the files can set access permissions to either make files public, private and even writable. Sometimes these access permissions are incorrectly set and inadvertently allow access to files that shouldn’t be available to the public.
The format of the S3 buckets is http(s)://{name}.s3.amazonaws.com
Automated Discovery
What is Automated Discovery?
Info
Automated discovery is the process of using tools to discover content rather than doing it manually. This process is automated as it usually contains hundreds, thousands or even millions of requests to a web server. These requests check whether a file or directory exists on a website, giving us access to resources we didn’t previously know existed. This process is made possible by using a resource called wordlists.
What are wordlists?
Info
Wordlists are just text files that contain a long list of commonly used words; they can cover many different use cases. For example, a password wordlist would include the most frequently used passwords, whereas we’re looking for content in our case, so we’d require a list containing the most commonly used directory and file names. An excellent resource for wordlists that is preinstalled on the THM AttackBox is https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists which Daniel Miessler curates.*
Automation Tools
Info
There are several tools to automated discovery with wordlists and i recommend using the dirsearch the cool thing with wordlists cover something cool and it just file to solve or find something with directory and yeah it had a lot of features and u can read the manual in github repository and yeah you can do this command and find the result on quiz
dirsearch -u <url> (change url with the url u want to search and yeah)