Squash commit
Info
Purpose: Combine N commit into one, and make it for new message
Reference resource
Method 1: rebase with -i flag
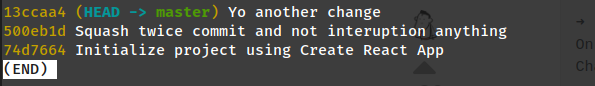
git rebase -i <hash-id-you-want-to-squash>Tip
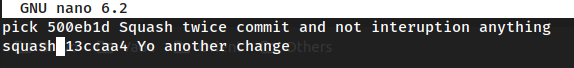
Change the secondary commit from
picktosquash, save and continue for set new message for commit
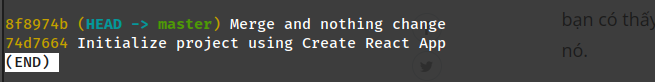
Method 2: reset with --soft flag
git reset --soft <hash-id-you-want-to-squash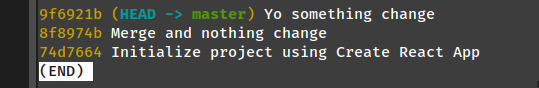
git commit -m "New message represent for twice or N commit"
Delete branch
Info
Follow the article to understand how we can remove the branch in local and remote, use
-dflag at: Git Delete Remote Branch – How to Remove a Remote Branch in Git
For locally
You can use -d with command git branch
# e.g: you want to delete release-v1 branch
git branch -D release-v1 # For delete branch
git branch -d release-v1 # For fully merged branchFor remote
You can use -d with command push
# e.g: you want to delete release-v1 branch, but not locally, but remotely
git push origin -d release-v1Change commit contents
Info
When you want make a change inside your commit,
gitgive us permission to handle it with--amendand option attaching
Change author of commit
You can change author for commit with flag --author with commit command
git commit --amend --author="Author Name <email@address.com>" --no-editChange message
And you can take it with new message with flag --message or -m with commit amend
git commit --amend --message "Hello_world"Tagging commit
Info
gitcommand support us release commit inside some repository platform, such asgithub,gitlabthrough using tagging with commit.
If you want explore more about this topic, here are some articles for you
Tagging one commit with annotate
When you want tagging in current commit, you can run tag with -a for annotate and -m for message
# NOTE: Use can asign tag with format v0.0.x or ver0.0.x. But notice about platform for compatible tagging
git tag -a <tag> -m "message if tag"If you want to specific commit, add commit SHA in last command above
git tag -a 0.0.1 -m "message" 6706483Rename tagging for old tags
You can read the question - How do you rename a Git tag? to understand how can we handle this case
git tag new old # Create a new local tag named `new` from tag `old`.
git tag -d old # Delete local tag `old`.
git push origin new :old # Push `new` to your remote named "origin", and delete tag `old` on origin (by pushing an empty tag name to it).
Force edit tagging
If you want to keep same context of tag, but change it to new commit or new message, you can handle it with -f option with below command
# Change new commit
git tag -a -f 0.0.1 <new-commit>
# Change new message
git tag <tag name> <tag name>^{} -f -m "<new message>"Share tagging (release)
Info
You can handle share tagging with
pushcommand through two way
Push with both branch, and tagging
git push -u origin brach-commig --tags 0.0.1Or you can push only tag to remote
git push -u origin 0.0.1Note
Reason why we can, because your
tagandbranchwill separate, and push same or not, it’s does matter
View Tagging
You can review your tag, content inside or what commit it attaching with through various commands
# Review your git tag
git tag
# View your git tag with specific expression
git tag -l *-rc*
# View your git tag with colume display
git tag --column <always/column/row/dense/...>
# View detail change in tag
git show tag-nameSet profile for multiple workspace
Note
Time to time when you stay in the project with configuration to enforce you to commit your code with same of prefix of organization, that why we need to learn set multiple
gitprofile for each project
You can double-check couple of documentations before starting
- Git Doc - git-config
- FreeCodeCamp - How to Use Multiple Git Configs on One Computer (Easiest)
- StackOverFlow - Is it possible to have different Git configuration for different projects?
If you are set git profile to global with both of these command
git config --global user.name "YOUR_NAME"
git config --global user.gmail "YOUR_GMAIL"you can find your global git profile at HOME directory at ~/.gitconfig. So you should be edit this file by replacing with these configurations
# This will define git should be used personal profile at Personal PATH
[includeIf "gitdir:~/Personal/**"]
path = ~/.gitconfig-personal
# In another case, git should be used work profile at Work PATH
[includeIf "gitdir:~/Work/**"]
path = ~/.gitconfig-workIf you clarify what need to set for both of profile, you should create two profile in home directory one for personal and one for work
[user]
name = Xeus Nguyen
email = personal_email@gmail.comname = Xeus Nguyen
email = work_email@gmail.comNow with each of directory, it will use git profile corresponding, you can double check it with command
git config --list