Quote
Hello @all, long time no see, it’s me again. Sorry, I don’t have time for doing personal blogging, but my job is crazy disaster, anything need to ready and I feel not well with my health to control over two things. Now, I take a break and don’t touch anything, therefore I write a blog again. Today, I learn a lot to setup first EKS cluster, especially Milvus Cluster as VectorDB. Let’s digest
Talk a bit about EKS
If you first time to come up with Kubernetes, you can enjoy and learn more about this techniques inside couple of my blog, that huge and truly insane
- Kubewekend Session 3: Basically about Kubernetes architecture
- Azure Kubernetes Service
- DevOps Training Session 13: Cloud - K8s Overview
Back again with EKS, It’s Kubernetes Services of AWS Cloud, try to explore more about that at Amazon EKS - Kubernetes concepts
Info
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) is an AWS managed service based on the open source Kubernetes project. While there are things you need to know about how the Amazon EKS service integrates with AWS Cloud (particularly when you first create an Amazon EKS cluster)
As you can see in description, EKS is built and used as usual Kubernetes but leverage in AWS Resources, It’s mean you will bring Kubernetes to approach with S3, ALB (Application Load Balancer), EBS (GP2, GP3), VPC, and …
To create and get for yourself one EKS Cluster, you need to approach at least with one of things eksctl - The official CLI for Amazon EKS. But, you can use Terraform or Pulumi to handle the job created with same effort, it’s totally up to you.
Note
Kubernetes is one of interesting technology nowadays, no one can refuse that and you will have multiple way to approach, and you can handle your cluster in multiple way. But with EKS, leverage in AWS Resources bring back you more challenge and powerful, you can get more value from them
You can try to calculate your cluster setup cost around how much and I think you will fair enough to give EKS a chance to work in your organizations, follow the link to get more information. (NOTE: EKS will charge much money, you will pay for EC2, EBS and Control Plane. But you need to concern use newest version to prevent charge extended support EKS with high price)
BTW, EKS is well place where you want to both used AWS Resources and operating microservice used them, that tuff with price but high quality back. I think it’s fair enough but if you choose you can concern with AKS, DOKS, …
Set up Milvus in EKS
Info
Turn back the story, I need to focus setup Milvus VectorDB inside EKS and It’s about journey to handle that but really pitfall you need to catch and I try to warn about that with you to get good setup
Install and Setup Prerequisites
You can read about setup through article Deploy a Milvus Cluster on EKS. Following the documentation, you need to prepare some tools inside your machine, such as
- AWS CLI - AWS Command Line
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip awscliv2.zip
sudo ./aws/install
rm -rf aws awscliv2.zip- Kubectl - Kubernetes Command Line
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
sudo chmod +x kubectl
sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin- helm - Kubernetes Package Managers
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3 | bash- eksctl - The official CLI for Amazon EKS. (NOTE: Install version
0.194.0, reason why you will know in down below)
# for ARM systems, set ARCH to: `arm64`, `armv6` or `armv7`
ARCH=amd64
PLATFORM=$(uname -s)_$ARCH
curl -sLO "https://github.com/eksctl-io/eksctl/releases/latest/download/eksctl_$PLATFORM.tar.gz"
# (Optional) Verify checksum
curl -sL "https://github.com/eksctl-io/eksctl/releases/latest/download/eksctl_checksums.txt" | grep $PLATFORM | sha256sum --check
tar -xzf eksctl_$PLATFORM.tar.gz -C /tmp && rm eksctl_$PLATFORM.tar.gz
sudo mv /tmp/eksctl /usr/local/binNext you need to prepare IAM to access into AWS Organization. For me, I usually handle AWS with highest permission AdministratorAccess, It’s totally not recommend.
-
But as usual, when you want to quick setup and not want to corrupt anything in provisioning progress, choosing highest permission is better way. BTW, you can try to define one of these as EKS Policies, if you want to keep anything secure
-
With Milvus Cluster require S3 Access, you need to define add-on permission for this resource. You can do specific for what bucket created for Milvus or you can use highest permission of S3 like
AmazonS3FullAccess
Setup Bucket for Milvus
In my circumstance, I prefer to use terraform for provisioning s3 bucket
### S3 bucket for milvus object storage ###
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "milvus_object" {
bucket = "milvus-object-bucket"
}After setup code block to create aws_s3_bucket, you need to run terraform workflow
# Setup PATH, Install dependencies, ...
terraform init
# Get the Plan to see what resource create or destroy
terraform plan
# Apply when use pleasure with plan
terraform applySetup EKS Cluster
As you can see, EKS have multiple ways to setup, and we can choose to use eksctl for new way to provision cluster for us, why not.
eksctl will create EKS cluster by using AWS Cloudformation. With default, when you try to run easy command with eksctl, you will get one managed nodegroup containing two m5.large nodes.
eksctl create clusterBut in this case, I will try to make more customize because eksctl permits us to do stuff like define what VPC, EC2 Size, Plugin, … You will have file like this
# API of ekctl to make conversation
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
# Config information for Cluster
metadata:
# Name Cluster
name: "milvus-cluster"
# Region
region: "ap-southeast-1"
# Version EKS Cluster
version: "1.29" # Support at least March 2025
# Config IAM for Cluster
iam:
# Enable withOIDC to automatically create an IRSA for the amazon CNI plugin and limit permissions granted to nodes in your cluster
# Documentation: https://eksctl.io/usage/security/#withoidc
withOIDC: true
# Give permission depend on RBAC for each sa
serviceAccounts:
- metadata:
name: aws-load-balancer-controller
namespace: kube-system
wellKnownPolicies:
awsLoadBalancerController: true
- metadata:
name: milvus-s3-access-sa
# if no namespace is set, "default" will be used;
# the namespace will be created if it doesn't exist already
namespace: milvus
labels: {aws-usage: "milvus"}
# Attach directly the aws policies for serviceAccount
# Documentation: https://eksctl.io/usage/iamserviceaccounts/?h=service#usage-with-config-files
attachPolicyARNs:
- "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonS3FullAccess"
# Use existed VPC to create EKS.
# If you don't config vpc subnets, eksctl will automatically create a brand new VPC
# Documentation: https://eksctl.io/usage/vpc-configuration/?h=vpc#use-existing-vpc-other-custom-configuration
vpc:
subnets:
private:
ap-southeast-1a: { id: subnet-123abc }
ap-southeast-1b: { id: subnet-456xyz }
ap-southeast-1c: { id: subnet-789def }
# Definition NodeGroups as EC2 Instance for EKS Cluster
# Documentation: https://eksctl.io/usage/nodegroup-managed/
managedNodeGroups:
- name: ng-milvus
labels: { role: milvus }
instanceType: m6i.large
desiredCapacity: 1
privateNetworking: true
# A new feature that lets you enable and manage Kubernetes operational software for your AWS EKS clusters
# Documentation: https://eksctl.io/usage/addons/
addons:
# Networking: Using VPC
- name: vpc-cni # no version is specified so it deploys the default version
attachPolicyARNs:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy
# Networking: Using to service discovery
- name: coredns
version: latest # auto discovers the latest available
# Networking: Using to service routing
- name: kube-proxy
version: latest
# Storage: Using AWS EBS
- name: aws-ebs-csi-driver
wellKnownPolicies: # add IAM and service account
ebsCSIController: trueAfter you define, you can use eksctl command to setup your cluster
eksctl create cluster -f cluster.yamlWait around 10 - 15 mins, and you can get kubeconfig from aws eks command
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region "ap-southeast-1" --name "milvus-cluster"And now, you can use kubectl to retrieve new cluster.
But hold on, before we go to next one, I will help you prevent some mistake inside eksctl in V0.193.0 to relate with issue https://github.com/eksctl-io/eksctl/issues/7987
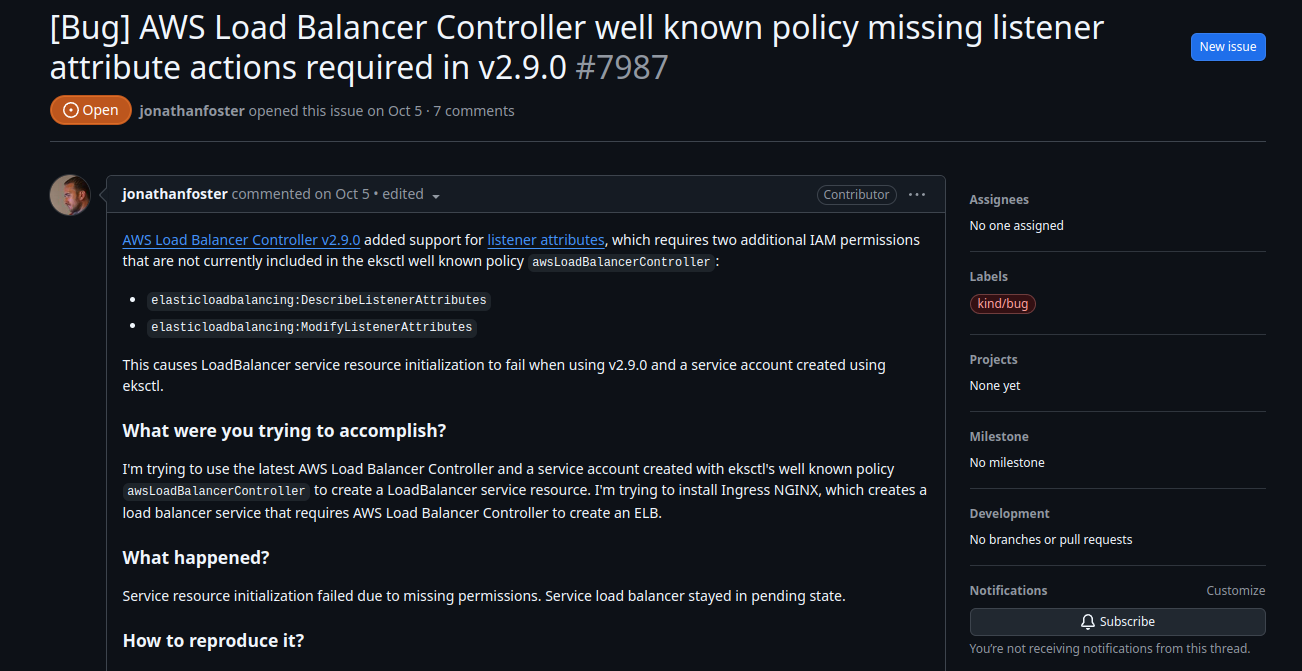
This bug will create error when you try to create load balancer with serviceAccount permission, you will assign for aws-load-balancer-controller in next part. This service account will miss two configuration and cause you a noise when create load balancing
elasticloadbalancing:DescribeListenerAttributeselasticloadbalancing:ModifyListenerAttributes
So why I give you advice to install eksctl in V0.194.0 because the commit is attached with this version. You can read about fix at https://github.com/eksctl-io/eksctl/blob/v0.194.0/pkg/cfn/builder/iam_test.go#L503
But if you unlucky to see this warning, don’t afraid you can fix it up if you can find exactly role attach with your service account inside AWS IAM, modify context with add elasticloadbalancing:DescribeListenerAttributes and save to apply
Next, you will do second work relate about your exist VPC and Subnet because you use VPC CNI to setup network inside Cluster. Therefore, It means to your pod will try discover and make conversation via that network, load balancer work and spawn inside subnet, you need to add following tag if aws doesn’t add it for you. Read more about this one at View Amazon EKS networking requirements for VPC and subnets
Warning
If you want to deploy load balancers to a subnet, the subnet must have the following tag:
- Private Subnet:
kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb:1- Public Subnet:
kubernetes.io/role/elb:1- Public and Private Subnet:
kubernetes.io/cluster/<name-cluster>:shared
Some advices and best practices when you try combine EKS with VPC to load balancer
- VPC and Subnet Considerations
- How do I automatically discover the subnets that my Application Load Balancer uses in Amazon EKS?
Setup StorageClass
Note
Milvus uses
etcdas meta storage and needs to rely on thegp3StorageClass to create and manage PVC.
You can check addons in cluster.yaml, you will see aws-ebs-csi-driver that one is driver CSI to help your cluster connect and create EBS from your Kubernetes. To do that stuff, Kubernetes have StorageClass to define information about communicate mechanism
# Milvus uses etcd as meta storage and needs to rely on the gp3 StorageClass to create and manage PVC.
# Documentation: https://milvus.io/docs/eks.md#Create-a-StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: ebs-gp3-sc
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
provisioner: ebs.csi.aws.com
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
parameters:
type: gp3After you copy and put that in the file, you can try to apply this manifest into exist EKS with kubectl
kubectl apply -f storageclass.yamlWith current cluster, gp2 is default storageclass, you need use kubectl patch command to change gp2 into gp3 for default
kubectl patch storageclass gp2 -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"false"}}}'
Setup AWS LoadBalancer Controller
You have multiple way to help your service go live in Kubernetes, such as Ingress, API Gateway and LoadBalancer. With EKS, if you don’t want to become frustrated to setup something strange inside cluster, do best practice aws loadbalancer to reduce lot of complex. (NOTE: Sometime It’s truly exist funny error, but it’s up to you 😄)
Easily to setup aws-load-balancer-controller, we can use helm for easier applying definition to our cluster directly. You can read blog of mine about Awesome Helm
# Add EKS Chart to repo
helm repo add eks https://aws.github.io/eks-charts
# Update Repo
helm repo updateInstall the AWS Load Balancer Controller with aws-load-balancer-controller chart
helm install aws-load-balancer-controller eks/aws-load-balancer-controller \
-n kube-system \
--set clusterName='milvus-cluster' \
--set serviceAccount.create=false \
--set serviceAccount.name=aws-load-balancer-controller # Use sa defined - problem in eksctl V0.193.0Wait a bit and you can see result with kubectl command
kubectl get deployment -n kube-system aws-load-balancer-controllerYou need to learn about how to use aws-load-balancer-controller, I think you concern to refer with AWS Load Balancer Controller Documentation
Setup Milvus Cluster
Note
Now your cluster is ready to setup, you need to use
helmto import chart and start installation.
Because Milvus Cluster is not running as standalone, your configuration can become complicate a bit, so for convenient, you need to prepare milvus.yaml to help helm create expectation Milvus cluster. To know about how configuration, you can try to access to ArtifactHub - milvus and find what things you need to overwrite or not
cluster:
enabled: true
# Create service as Load Balancer for Milvus Database
service:
type: LoadBalancer
port: 19530
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: external
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-name: milvus-service
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-scheme: internet-facing
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-nlb-target-type: ip
# Disable minio to use S3 instead
minio:
enabled: false
externalS3:
enabled: true
host: "s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com"
port: "443"
useSSL: true
bucketName: "<bucket-name>"
useIAM: true
cloudProvider: "aws"
region: "ap-southeast-1"
# Disable Pulsal and use Kafka instead
pulsar:
enabled: false
kafka:
enabled: true
# Enable Authentication to Milvus DB
extraConfigFiles:
user.yaml: |+
common:
security:
authorizationEnabled: true
# Enable Attu
attu:
enabled: true
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: "alb"
annotations:
# Read More at: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-load-balancer-controller/v2.10/guide/ingress/annotations/#ingress-annotations
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing # Public intenet
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip # Pod IP
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTPS":443}]' # 443
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: xxxxxx # Arn ACM HTTPS
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-policy: ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS13-1-2-2021-06Now you can reach to helm and create cluster what you want
helm repo add milvus https://zilliztech.github.io/milvus-helm/
helm repo update
helm install milvus-db milvus/milvus -n milvus -f milvus.yamlNow you need to wait to all of components work with no error, you will meet some problem because reason
- App restart one to two time for wait
etcdandkafkaalready ready - You can’t modify replica number
etcd,kafkaandzookeeperwith cluster mode because you will meet the error related with replicate factor
Your patience will get fair result if you wait enough long 😄. Just kidding, you can try to get cluster with kubectl
kubectl get pods -n milvusTo get svc and attu, you can try another kubectl command
# Get svc for milvus db
kubectl get svc -n milvus
# Get ingress for attu
kubectl get ingress -n milvus Adjust domain for Milvus
Before you can approach this UI, you need to handle to map your expectation domain with TLS to ready connect from browser
You can use Terraform to create Route53 record, if your domain will serve and managed with supportive from ACM (AWS Certificate Managed), your new domain will help you serve TLS, HTTPS quickly
### S3 bucket for milvus object storage ###
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "milvus_object" {
bucket = "milvus-object-bucket"
}
# Get exist ALB was created by Milvus Cluster
data "aws_lb" "milvus_lb" {
arn = "xxxxxxxxxxx"
}
data "aws_lb" "milvus_attu" {
arn = "yyyyyyyyyyy"
}
# Create domain with ACM from AWS
resource "aws_route53_record" "milvus_attu" {
zone_id = "zone_id_xyz"
name = "milvus-attu.example.com"
type = "CNAME"
ttl = "300"
records = [data.aws_lb.milvus_attu.dns_name]
}
resource "aws_route53_record" "milvus_endpoint" {
zone_id = "zone_id_xyz"
name = "milvus.example.com"
type = "CNAME"
ttl = "300"
records = [data.aws_lb.milvus_lb.dns_name]
}Run terraform workflow and you will try to connect into Milvus Cluster from browser.
Note
Your start user and password with Milvus Cluster is
root:MilvusWARNING: NEED TO CHANGE AFTER FIRST LOGIN
Apply Cluster Autoscaler (CA) for Milvus
Overview
Note
You can ensure the availability for Milvus cluster through applying Cluster Autoscaling, that is one of method to help your EKS cluster can adapt HA (High Availability) strategy
There is exist many way to autoscale on node level with EKS, such as
In my perspective, we should start from standard method Cluster Autoscaler (CA), popular Cluster Autoscaling solution maintained by SIG Autoscaling.
Info
Cluster Autoscaler (CA) is responsible for ensuring that your cluster has enough nodes to schedule your pods without wasting resources. It watches for pods that fail to schedule and for nodes that are underutilized. It then simulates the addition or removal of nodes before applying the change to your cluster.
This one is legit method to apply for EKS MilvusDB, cuz that ensure a lot of requirements and leverage how the AWS operate the EKS, like
- Scalability
- Performance
- Cost
- Node Groups
- EC2 Auto Scaling Groups
- EC2 Managed Node Groups
There is no doubt to consider to use CA, you can double check more article and source code like README.md to see the mechanism that method used
To start, you need to create IAM Policies to help this mechanism actual work, cuz you need the workload represent for this implement can have permission to tackle this scaling
You can use Terraform or AWS CLI, it’s up to you, just remember the policy context need to create
{
"Version" : "2012-10-17",
"Statement" : [
{
"Effect" : "Allow",
"Action" : [
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups",
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingInstances",
"autoscaling:DescribeLaunchConfigurations",
"autoscaling:DescribeScalingActivities",
"autoscaling:SetDesiredCapacity",
"autoscaling:TerminateInstanceInAutoScalingGroup",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplateVersions",
"eks:DescribeNodegroup"
],
"Resource" : "*"
}
]
}If you want to double check the advance option, you can read at 🔗Link
After created the IAM Policy, you can reach to update the autoscaling group, cuz CA will use this definition to scale your node in cluster up or down depend on DesiredReplicas
Apply new spec ASG
First of all, double check what configure your cluster applying
aws autoscaling \
describe-auto-scaling-groups \
--query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='milvus-cluster']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" \
--output table \
--region ap-southeast-1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | 2 | 2 | 2 |
+------------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+Three number are represented for min, max, desire
Now, you need to increase number node with MaxSize with at least 1 more. But you need to get autoscaling group name
export ASG_NAME=$(aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='milvus-cluster']].AutoScalingGroupName" --output text --region ap-southeast-1)Now you need to modify with new spec for Milvus ASG
aws autoscaling \
update-auto-scaling-group \
--auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} \
--min-size 2 \
--desired-capacity 2 \
--max-size 3 \
--region ap-southeast-1After that, query the configuration again
aws autoscaling \
describe-auto-scaling-groups \
--query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='milvus-cluster']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" \
--output table \
--region ap-southeast-1-----------------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | 2 | 3 | 2 |
+------------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+Create EKS Service Account
To using the IAM Policy from AWS, your EKS need to ensure about Service Account, it’s mechanism to handle and create token to authenticate from your workload with IAM.
On the Overview, we are already create IAM Policy for autoscaling, and now we create SA to reuse that
# For example: IAM Policy is EKSClusterAutoScaler
eksctl create iamserviceaccount \
--name cluster-autoscaler \
--namespace kube-system \
--cluster suppor-milvus-cluster-v2 \
--attach-policy-arn "arn:aws:iam::xxxxxxx:policy/EKSClusterAutoScaler" \
--approve \
--override-existing-serviceaccounts \
--region ap-southeast-1After you apply this command, your EKS Milvus will create serviceaccounts with name cluster-autoscaler in namespace kube-system. Check it out with command
kubectl get serviceaccounts -n kube-system cluster-autoscaler -o yamlDeploy cluster-autoscaler deployment
In the last step, To deploy cluster-autoscaler, you need run apply command to approve and deloyments manifest of cluster-autoscaler into your host with auto-discovery mode. Manifest is write and use from cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events", "endpoints"]
verbs: ["create", "patch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/eviction"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/status"]
verbs: ["update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
resourceNames: ["cluster-autoscaler"]
verbs: ["get", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["watch", "list", "get", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- "namespaces"
- "pods"
- "services"
- "replicationcontrollers"
- "persistentvolumeclaims"
- "persistentvolumes"
verbs: ["watch", "list", "get"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["replicasets", "daemonsets"]
verbs: ["watch", "list", "get"]
- apiGroups: ["policy"]
resources: ["poddisruptionbudgets"]
verbs: ["watch", "list"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["statefulsets", "replicasets", "daemonsets"]
verbs: ["watch", "list", "get"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses", "csinodes", "csidrivers", "csistoragecapacities"]
verbs: ["watch", "list", "get"]
- apiGroups: ["batch", "extensions"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["coordination.k8s.io"]
resources: ["leases"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: ["coordination.k8s.io"]
resourceNames: ["cluster-autoscaler"]
resources: ["leases"]
verbs: ["get", "update"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["create", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["cluster-autoscaler-status", "cluster-autoscaler-priority-expander"]
verbs: ["delete", "get", "update", "watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-autoscaler
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: cluster-autoscaler
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
labels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: 'true'
prometheus.io/port: '8085'
spec:
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65534
fsGroup: 65534
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
serviceAccountName: cluster-autoscaler
containers:
- image: registry.k8s.io/autoscaling/cluster-autoscaler:v1.26.2
name: cluster-autoscaler
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 600Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 600Mi
command:
- ./cluster-autoscaler
- --v=4
- --stderrthreshold=info
- --cloud-provider=aws
- --skip-nodes-with-local-storage=false
# `least-waste` will expand the ASG that will waste the least amount of CPU/MEM resources
# Doc: https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/tree/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/aws#common-notes-and-gotchas
- --expander=least-waste
# Note: Change <YOUR CLUSTER NAME> by your cluster name
- --node-group-auto-discovery=asg:tag=k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled,k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/<YOUR CLUSTER NAME>
volumeMounts:
- name: ssl-certs
mountPath: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt # /etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt for Amazon Linux Worker Nodes
readOnly: true
imagePullPolicy: "Always"
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
volumes:
- name: ssl-certs
hostPath:
path: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt"If you replace the cluster name by your cluster name, you can apply this manifest with command
kubectl apply -f cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yamlWaiting few second and check your deployment inside kube-system namespace with command
kubectl get deployments -n kube-system cluster-autoscalerYou can set more annotation and option into cluster-autoscaler, explore and read more at Cluster Autoscaler on AWS
Conclusion

Success
That’s all thing, I want to share with you when I create first EKS for myself, and it’s good experience to have opportunity to do, capture the journey and share to whole of you. I thinks EKS is not hard to setup, quite easily but when you try to leverage AWS Services, you need to make sure you control over of that because if you mess up, your cost will reach to huge number.
Quote
Couple tough week with me, not have any mood to handover anything else, mess up with work and do some stuff didn’t make me comfortable. This week is kind of that, but I put it back and try to reach to good feeling, back again with useful article and hope so you feel well with this one. Thanks again buddy, stay safe, learn a new thing and we will meet in next weekend. Bye 👋