Quote
Thank You and Happy Holidays! 👋
Hello everyone! It’s wonderful to be here. I feel truly grateful for your support throughout the entire year; your viewership is the motivation that allows me to create high-quality content. Thank you all so much for your support this year!
I’m looking forward to the new year, which will bring more efficiency and interesting projects.
I also want to announce that this will be the last session of Dueweekly Tech for the year. I’ll be back soon next year! I hope you enjoy the current session. Stay safe, and I’ll see you soon!
AIOps / MLOps / LLMOps
1. runpod - Top 12 Cloud GPU Providers for AI and Machine Learning in 2025
- List several GPU reservation providers for the machine learning world. This checklist will provide information on the strengths and weaknesses of each provider, helping you determine why you should choose a particular one for your specific use cases.
- Following this, a summary table will offer a detailed overview of all providers. Moving from the general to the specific in this way is an effective method for presenting information.
2. Alibaba - GPU Sharing Scheduler Extender Now Supports Fine-Grained Kubernetes Clusters
- The article introduces Alibaba Cloud’s approach to optimizing NVIDIA GPU utilization for users who select ACK (Alibaba Cloud Kubernetes). By leveraging a custom Scheduler Extender and Device Plugin, Alibaba Cloud has successfully implemented a sophisticated GPU scheduler. Based on experience, this solution is highly practical for anyone looking to easily adopt GPU scheduling.
- During the session, you will learn about their implementation via clear explanations and illustrations that help the reader visualize the technical components. The article also showcases the open-source tools they developed and integrated into their cloud platform:
gpushare-scheduler-extender(https://github.com/AliyunContainerService/gpushare-scheduler-extender.git) andgpushare-device-plugin(https://github.com/AliyunContainerService/gpushare-device-plugin.git). - Finally, you will be provided with an example showing how to adopt the Alibaba GPU Scheduler methodology by using the Kubernetes annotation
aliyun.com/gpu-mem.
Architecture
1. GeeksforGeek - Active Active vs. Active Passive Architecture
-
The article introduces two highly effective architectures for setting up High Availability (HA) in a system: Active-Active and Active-Passive. It provides a brief definition of each and a comparison across multiple aspects, offering insights into the benefits of both approaches.
-
To dive deeper into these architectures and the related concept of Disaster Recovery (DR), we recommend reviewing the four-part series on DR in AWS. This series helps you learn and visualize the necessary actions required to ensure HA for Disaster Recovery purposes.
- Disaster Recovery (DR) Architecture on AWS, Part I: Strategies for Recovery in the Cloud
- Disaster Recovery (DR) Architecture on AWS, Part II: Backup and Restore with Rapid Recovery
- Disaster Recovery (DR) Architecture on AWS, Part III: Pilot Light and Warm Standby
- Disaster Recovery (DR) Architecture on AWS, Part IV: Multi-site Active/Active
2. Azure - Load balancing options 🌟 (Recommended)
- The detailed article provides multiple perspectives on implementing load balancing in the Cloud. Azure includes a decision tree (illustration) to help readers visualize and determine the most compatible Load Balancer service for their expected needs.
- By delving into this article, you will gain an understanding of the Azure load balancing services offered, complete with brief descriptions, categories, and resource listings. This structured approach—considering which scenarios you want to follow—is excellent for anyone looking to design their system architecture from scratch.
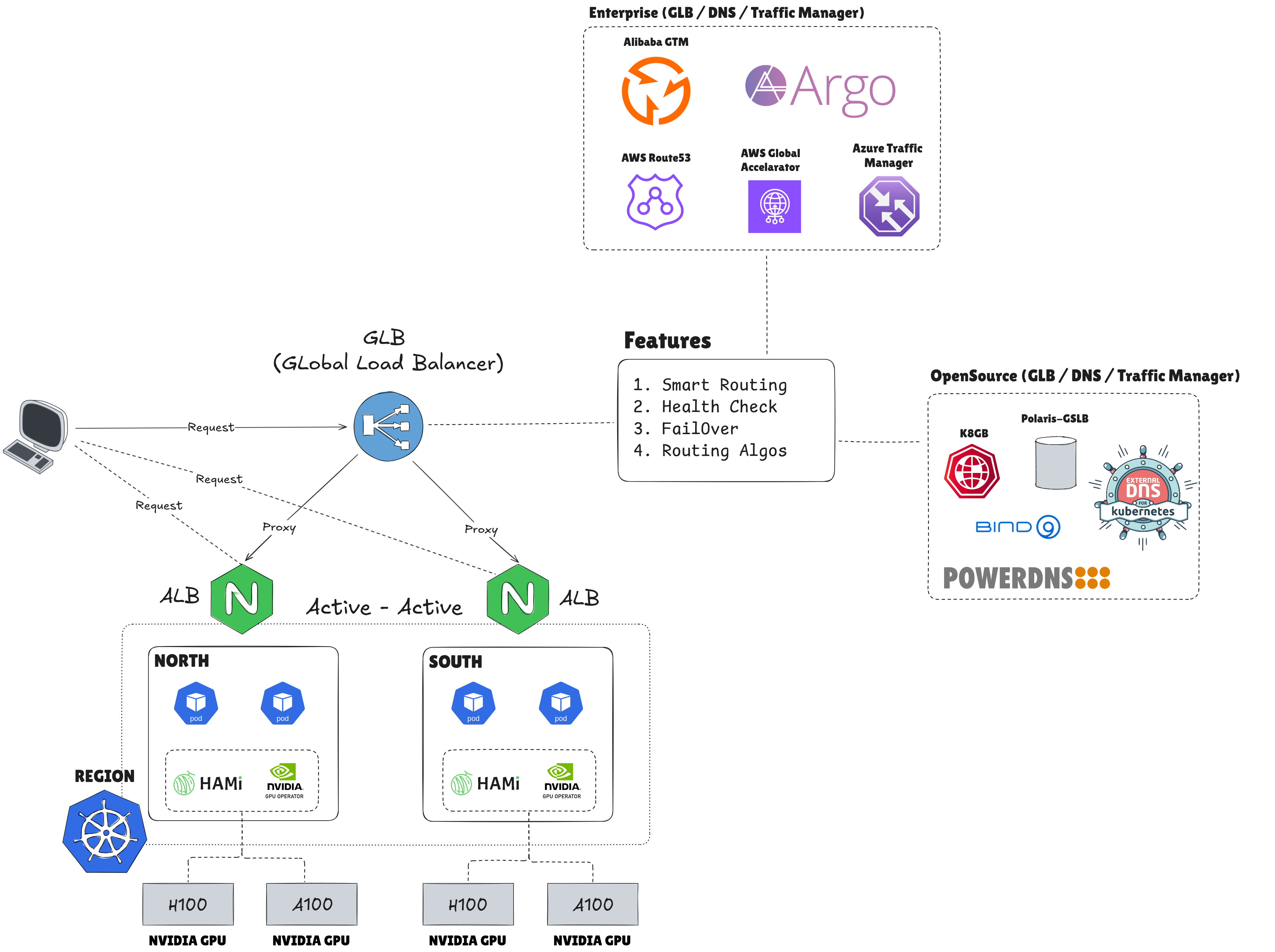
- This article presents an interesting topic related to Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) and the surrounding technologies. It offers excellent explanations, a comparison with local load balancing, details on the benefits of adopting GSLB, and other relevant information.
- If you are looking for a solution for global failover and smart routing when your services experience an outage, this article provides the definitive answer. Notably, this service is provided by multiple cloud vendors under different names, such as Azure Traffic Manager, Alibaba Global Traffic Manager (GTM), or AWS Global Accelerator.
4. Blog - Understanding Database Consistency Levels And Applying Them To A Single Web Service
- The article provides an overview of database consistency levels, explaining the special characteristics of each type. These levels are critical for defining your expectations when addressing problems related to distributed systems and ensuring your data is always up-to-date.
- We will walk through several standard consistency levels (e.g., Strong and Eventual) and other intermediate levels, such as Causal, Read Your Writes, and Monotonic Reads. The article also offers solutions to tackle consistency challenges, including techniques like vector clocks, restrictions (or constraints), or using queues for read and write requests.
5. Dev.to - Beyond A Records: How Advanced DNS Routing Powers Modern Applications 🌟 (Recommended)
- Modern applications increasingly rely on DNS (Domain Name System) for core functionality. DNS is ubiquitous, evolving from simple A Record setups to sophisticated systems that prioritize global reach, high availability, performance-critical routing, and overall efficiency.
- During this session, you will learn about the underlying algorithms and how to manage routing traffic from a single domain to multiple targets. Furthermore, you will delve into more complex use cases, such as combining DNS with deployment strategies like Canary Releases for A/B testing. You will also learn how to integrate these concepts to ensure application resilience, optimize routing rules, and achieve the latency reduction that is crucial for any modern application.
6. Google - How Google Does It: Building the largest known Kubernetes cluster, with 130,000 nodes
- This article chronicles Google’s scaling story for their Kubernetes system, where they aimed to serve large customers by unlocking the previous limitation of 20,000 to 65,000 nodes and stabilizing the cluster size around an astonishing 100,000 nodes. During this massive experiment, they introduced and adopted several new techniques, including a potential new scheduling strategy for Kubernetes defined in KEP-4671: Gang Scheduling (https://github.com/kubernetes/enhancements/tree/master/keps/sig-scheduling/4671-gang-scheduling).
- Google provides detailed information on the activities and results of each experimental phase. The most impressive result they achieved was scheduling an enormous number of 130,000 Pods in 3 minutes and 40 seconds.
Cloud
1. Medium - Smarter Traffic, Better Performance: A Hands-On Journey with AWS Route 53 Routing Policies 🌟 (Recommended)
- The article highlights the key features of AWS Route 53 that provide granular control over traffic flow. Adopting Route 53 leads to solutions for Smart Routing and Failover, ensuring high availability and low latency for your services. Health Checks, in particular, are a core feature for building Route 53’s powerful resilience and tackling multi-region challenges.
- You will delve deeper into the configuration of Route 53 with detailed, illustrated setup instructions covering multiple approaches, such as Failover Routing, Latency-Based Routing, Weighted Routing, and Geolocation Routing. Although the demonstration uses the AWS Console (instead of Infrastructure as Code tools like Terraform), it serves as an effective Proof of Concept (POC) to validate the real-world capabilities of Route 53 in resolving critical operational issues.
2. AWS - Implementing multi-Region failover for Amazon API Gateway 🌟 (Recommended)
- This post continues the discussion on AWS, focusing on combining services like Route 53 and API Gateway to enhance system availability using a multi-region architecture. The article explains the architectural changes needed when transitioning from a single-region deployment to a multiple-region setup for failover, particularly how to deploy entire gateways and configure Route 53 to direct traffic to the correct backend services.
- Furthermore, the documentation allows you to follow a Proof of Concept (POC) to validate that this concept works as expected. You will also see how to perform a manual failover using Amazon Route 53 Application Recovery Controller (ARC), which acts as a real control plane for disaster recovery operations.
3. Medium - Azure Traffic Manager Overview & Step By Step Guide
- Regarding Azure, it follows a concept similar to AWS but utilizes different service names. Azure Traffic Manager (ATM) (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/traffic-manager/traffic-manager-overview) functions as a DNS-based traffic load balancer. It supports various routing methods, including Priority, Weighted, Performance, Geographic, Multivalue, and Subnet, ensuring features like high availability, downtime prevention, and intelligent traffic distribution are all addressed.
- Consistent with the AWS example, the article includes a detailed walkthrough via the Azure Portal to familiarize you with setting up Azure Traffic Manager for multiple virtual machines deployed across different regions.
4. Alibaba - Optimize Global Application Performance with Intelligent DNS and GTM Integration
- The next focus for traffic management is Alibaba Cloud. This article adopts the same perspective as the three preceding ones but is specific to Alibaba Cloud services like Cloud DNS (https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/dns/product-introduction-dns2-0), Global Traffic Manager (GTM) (https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/dns/gtm2-product-introduction), and Server Load Balancer (SLB) (https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/slb/). The introduction outlines the core features of GTM and explains how to map it to SLB to route traffic from multiple regions to multiple IP addresses within a specific region.
- As expected, the author provides several scenarios and solutions for addressing different use cases, leveraging GTM to ensure failover and improve accessibility.
5. AWS - AWS Global Accelerator Custom Routing with Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service
- I was interested in how AWS manages traffic shifting across multiple regions, particularly with its Kubernetes system, EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service), which led me to the service AWS Global Accelerator (AGA) (https://aws.amazon.com/global-accelerator/). AGA allows for deterministic routing to specific Amazon EC2 destinations using your application logic, and the author is now sharing a similar approach inspired by this for EKS workloads.
- This session provides a complete tutorial that clearly demonstrates how to configure AGA to distribute traffic to VPC Private Subnets, using a practical real-world use case focused on serving a game server for multiple gamers.
- For more in-depth knowledge about AGA, you should refer to the suggested posts.
6. Medium - Implementing granular failover in multi-Region Amazon EKS 🌟 (Recommended)
- Failover is a critical and interesting topic when operating a system across multiple regions. This article provides an excellent tutorial if you are looking for information on the best approaches, technology stacks, and organizational strategies to manage failover with Kubernetes Clusters. Specifically on AWS, the solution leverages Route 53, one of the most powerful services for this cloud provider.
- During this session, you will follow a comprehensive tutorial. The technical stack used (AWS Load Balancer and Route 53) is highly relevant for those operating EKS environments. By the end, you will acquire the strategies needed to implement routing policies that handle failover gracefully, ensuring the resilience of your applications.
7. Alibaba - ALB Ingress Handles Cloud-Native Application Traffic Management Easily
- This article introduces an excellent option for Kubernetes in Alibaba Cloud (ACK): the ALB Ingress Controller. While built on a concept similar to the standard Nginx Ingress, the ALB Ingress is more sophisticated. It supports complex routing rules, certificate discovery, and built-in traffic monitoring. Furthermore, it supports a wide range of Layer 7 protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and QUIC.
- As you follow this session, you will find that the ALB Ingress Controller is a great choice, as it significantly reduces the effort required to implement Ingress in ACK by leveraging Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs). Your primary task is simplified to defining your application endpoints and configuring your Ingress resource to point traffic to the ALB.
Kubernetes
1. Medium - Enterprise Kubernetes Networking: CNI, Service Mesh, Multi-Cluster & Gateway API 🌟 (Recommended)
- This is one of the most comprehensive articles of the year, providing extensive coverage of the challenges, issues, and key features of Kubernetes networking. It offers an excellent opportunity to deep dive and gain in-depth knowledge of the subject. A big shout-out goes to Salwan Mohamed (https://medium.com/@salwan.mohamed) for contributing such a valuable resource to the community.
- The content covers many topics with real-world case studies, including addressing the networking stability requirements of a Banking Application within a Kubernetes environment. While the style suggests it may be the product of AI generation, the quality and depth of the resource are impressive, making it a highly valuable read.
2. Cloud Native Deep Dive - Managing Traffic In Kubernetes For Gateways & Service Mesh
- This tutorial article guides us on how to use Istio (https://istio.io/) to manage traffic within Kubernetes using the concepts of Gateways and the Service Mesh. The author rightly emphasizes the critical importance of networking in infrastructure; issues here can halt the entire system. While networking can be a challenging domain, it is essential for anyone in DevOps or Network Engineering to master.
- In this session, you will learn several core Istio concepts, such as Circuit Breaking, Timeouts, Load Balancing, and Weighted Routing. Building on this foundational knowledge, you can delve deeper into the Kubernetes networking landscape and unlock the complexities of this topic, specifically how Istio controls the traffic flow in both North-South (Ingress/Egress) and East-West (Service-to-Service) directions.
- This article, titled “Gateway API with Service Mesh” powered by Istio, will guide you through setting up a single Gateway to manage North-South (Ingress) traffic while simultaneously utilizing a Service Mesh to manage East-West (Service-to-Service) traffic.
- You can set up and run the entire project locally on your machine using Kind (Kubernetes in Docker). All necessary setup information and resources are documented in the associated GitHub repository: GitHub - k8s-gateway-api-service-mesh-demo.
4. Tigera - Secure and Scalable Kubernetes for Multi-Cluster Management
- This article addresses a central topic of the Dueweekly series: Multi-Cluster Architecture spanning public clouds, private data centers, or hybrid environments. Tigera introduces their solution, Calico Cluster Mesh (https://www.tigera.io/tigera-products/cluster-mesh/), designed to tackle this challenge and provide a superior, less complex experience compared to traditional service meshes.
- The author discusses the inherent challenges encountered in multi-cluster architectures, which resonate with common industry experience. By utilizing Calico Cluster Mesh, you can reduce the complexity of this problem and significantly enhance the efficiency, security, and scalability of your clusters through benefits such as: Enhanced Security Across the Board, Intelligent Traffic Management, and Unified Observability: Seeing is Securing.
5. Medium - Controlling Kubernetes Network Traffic Part 1
- The first part of this series will cover fundamental Kubernetes Networking terminology, including North-South and East-West traffic flow, Ingress, and the Gateway API. In this article, the author provides extensive information about both Ingress and Gateway implementations in Kubernetes, highlighting solutions from major cloud providers (AWS, Azure, and Google) and open-source projects. This detailed explanation will give you more options to choose from when designing your cluster’s traffic management.
- Finally, the article includes a comparison between the two primary Kubernetes networking approaches (Ingress and Gateway API), outlining the specific use cases that each is best suited to address.
6. Medium - Controlling Kubernetes Network Traffic Part 2
- The second part of this series will focus on the depth of networking in Kubernetes, covering advanced topics such as CNI (Container Network Interface), Network Policies, Service Mesh, and eBPF. Consistent with the first part, this article provides great insights and helps you visualize the necessary components, offering both enterprise and open-source options for setup within your Kubernetes cluster.
7. Blog - k8gb: The Best Open Source GSLB Solution for Cloud Native
- The blog summarizes research into implementing Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) in Kubernetes using k8gb (https://www.k8gb.io/) to control traffic across multiple clusters, ensuring both load balancing and fault tolerance. GSLB can establish geographic affinity rules to route traffic closer to users, thereby enhancing overall performance. Conversely, it can automatically redirect traffic to a functioning cluster upon failure, minimizing user impact.
- The author outlines the journey of finding a solution for the GSLB problem in Kubernetes, starting with initial approaches like Commercial Load Balancers (F5 GSLB) and Public Cloud Global Load Balancers (e.g., AWS AGA, GCP External Application LB). The article highlights the drawbacks of each initial option before transitioning to and selecting an open-source solution like k8gb or the Karmada Ingress Controller (https://karmada.io/docs/userguide/service/multi-cluster-ingress/).
8. AWS - Exposing Kubernetes Applications, Part 1: Service and Ingress Resources
9. AWS - Exposing Kubernetes Applications, Part 2: AWS Load Balancer Controller
10. AWS - Exposing Kubernetes Applications, Part 3: Ingress-Nginx Controller
- This is an excellent article series for anyone seeking more information about Kubernetes Ingress Controllers, targeting both the AWS Load Balancer Controller for the AWS Cloud and the Ingress-Nginx Controller for open-source environments. These articles provide comprehensive tutorials that guide you through implementing scenarios ranging from common to complex, utilizing clear illustrations to aid visualization and understanding.
- The article presents several strategies for addressing the challenge of scaling Kubernetes globally. These architectural patterns include Federation, Service Mesh, and Shared Services. It also covers the various challenges you must overcome to identify the optimal solution for successfully implementing a multi-cluster architecture.
12. Traefik - Understanding Multi-Cluster Kubernetes: Architecture, Benefits, and Challenges
- This article addresses the topic of multi-cluster Kubernetes architecture. In this session, you will become familiar with several key architectural terms that, while sometimes used differently, convey the same fundamental meaning, such as Control Plane, Data Plane, and Worker Plane.
- You will also gain further insight into the challenges associated with this problem domain, the benefits of adopting a multi-cluster approach over a single cluster, and other valuable information related to Kubernetes and solving multi-cluster problems.